A Framework For Building Resilience And Achieving Sustainable Development In Least Developed Countries
Table of Contents
Strengthening Institutional Capacity and Governance
Strong, accountable, and transparent governance forms the bedrock of sustainable development. Without it, other initiatives falter. This section details crucial aspects of institutional strengthening.
Good Governance and Anti-Corruption Measures
Effective governance requires a multifaceted approach:
- Promoting good governance principles at all levels: This necessitates establishing clear rules, regulations, and procedures, ensuring consistent application across all sectors and levels of government. Independent oversight bodies are crucial for monitoring adherence.
- Implementing robust anti-corruption mechanisms: Corruption diverts resources, undermines public trust, and stifles economic growth. Strong anti-corruption laws, coupled with independent investigative bodies and transparent judicial processes, are essential to combat this pervasive issue. Promoting ethical conduct within the public sector is also key.
- Ensuring inclusive participation in decision-making processes: Sustainable development requires the active engagement of all stakeholders, including marginalized communities, women, and youth. Mechanisms for participatory decision-making, such as community consultations and public forums, are vital for ensuring that policies truly reflect the needs and priorities of the population.
- Enhancing transparency and accountability in public resource management: Open access to information on government budgets, expenditures, and procurement processes is crucial for promoting accountability. Independent audits and public financial reporting mechanisms are vital for ensuring responsible use of public funds.
Capacity Building and Human Capital Development
Investing in human capital is an investment in the future. This includes:
- Improving education systems, focusing on STEM and vocational training: Education is the cornerstone of development. Curricula should prioritize Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) subjects to equip individuals with the skills needed for a modern economy. Vocational training programs provide crucial skills for employment in various sectors.
- Providing access to healthcare and improving public health infrastructure: Health is a fundamental human right and a prerequisite for sustainable development. Investment in healthcare infrastructure, disease prevention programs, and access to essential medicines is critical for a healthy and productive population.
- Empowering women and promoting gender equality: Gender equality is not merely a social justice issue; it's an economic imperative. Empowering women through education, economic opportunities, and political participation drives economic growth and improves development outcomes.
- Strengthening civil society organizations and local governance structures: Active civil society organizations play a vital role in holding governments accountable, advocating for citizen needs, and contributing to sustainable development initiatives. Strengthening local governance structures ensures that development efforts are responsive to local contexts and needs.
Investing in Sustainable Infrastructure and Economic Diversification
Sustainable economic growth in LDCs hinges on strategic investments and diversification.
Infrastructure Development
Prioritizing sustainable infrastructure investments is crucial for economic growth and resilience:
- Investing in renewable energy sources to mitigate climate change impacts: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro reduces reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating climate change impacts while improving energy security and affordability.
- Developing resilient infrastructure to withstand natural disasters: Climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Investing in resilient infrastructure, such as flood defenses, earthquake-resistant buildings, and drought-resistant water systems, is critical for minimizing losses.
- Improving transportation networks to facilitate trade and commerce: Efficient transportation networks are essential for connecting rural areas to markets and facilitating regional and international trade. Investments in roads, railways, and ports are vital for economic integration.
- Expanding access to clean water and sanitation: Access to clean water and sanitation is fundamental to human health and well-being. Investments in water infrastructure and sanitation systems are essential for improving public health and reducing the burden of waterborne diseases.
Economic Diversification and Value Chain Development
Over-reliance on a few commodities renders LDCs vulnerable to price fluctuations. Diversification is key.
- Promoting diversification into high-value-added sectors: Shifting from low-value commodity exports to high-value-added sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and tourism can significantly boost economic growth and create higher-skilled jobs.
- Developing local industries and supporting entrepreneurship: Supporting local industries and fostering entrepreneurship creates jobs, generates innovation, and promotes economic growth. Access to finance, training, and mentorship programs are crucial for entrepreneurs.
- Strengthening regional and international trade linkages: Integrating into regional and international trade networks enhances market access, promotes competition, and fosters economic growth. Trade facilitation measures and participation in regional trade agreements are essential.
- Creating sustainable and inclusive job opportunities: Sustainable development requires creating jobs that are not only economically viable but also environmentally and socially responsible. Promoting green jobs and inclusive employment practices are crucial.
Enhancing Climate Change Resilience and Disaster Risk Reduction
LDCs are disproportionately vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
Addressing climate change requires both adaptation and mitigation strategies:
- Implementing climate-smart agriculture practices: Climate-smart agriculture involves adopting practices that increase productivity, enhance resilience to climate change impacts, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Investing in early warning systems for natural disasters: Early warning systems are critical for enabling timely evacuations and minimizing losses from natural disasters.
- Promoting climate-resilient infrastructure development: Designing and building infrastructure that can withstand the impacts of climate change is crucial for protecting assets and ensuring continued functionality.
- Enhancing community-based disaster risk reduction strategies: Community-based disaster risk reduction empowers local communities to participate in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
Environmental Sustainability and Resource Management
Protecting natural resources is vital for long-term sustainability:
- Promoting sustainable land and water management practices: Sustainable land and water management practices, such as soil conservation, water harvesting, and efficient irrigation techniques, are crucial for ensuring food security and protecting ecosystems.
- Conserving biodiversity and protecting ecosystems: Biodiversity is essential for ecosystem functioning and provides numerous benefits to human society. Protecting biodiversity through conservation efforts is crucial for long-term sustainability.
- Reducing deforestation and promoting reforestation: Deforestation contributes significantly to climate change. Reducing deforestation and promoting reforestation are crucial for carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation.
- Managing waste effectively and promoting circular economy principles: Effective waste management and the adoption of circular economy principles, such as reducing, reusing, and recycling, minimize environmental impacts and create economic opportunities.
Fostering Inclusive Growth and Reducing Inequality
Sustainable development requires inclusive growth that benefits all segments of society.
Poverty Reduction and Social Inclusion
Addressing inequality is fundamental to achieving sustainable development:
- Implementing targeted poverty reduction programs: Targeted poverty reduction programs, such as cash transfers, job creation initiatives, and access to essential services, are crucial for improving the living standards of the poor.
- Promoting access to essential services for marginalized communities: Ensuring access to essential services, such as healthcare, education, and sanitation, for marginalized communities is vital for reducing inequalities and promoting social inclusion.
- Addressing gender inequality and empowering women: Empowering women through education, economic opportunities, and political participation is crucial for reducing inequalities and promoting sustainable development.
- Promoting social inclusion and peaceful coexistence: Promoting social inclusion and peaceful coexistence requires addressing social divisions and building trust among diverse communities.
Sustainable Tourism and Cultural Preservation
Sustainable tourism can be a powerful engine for economic growth and cultural preservation:
- Developing responsible tourism strategies: Responsible tourism strategies focus on minimizing environmental impacts, maximizing local benefits, and promoting cultural preservation.
- Preserving cultural heritage and promoting cultural diversity: Protecting cultural heritage and promoting cultural diversity are essential for creating unique tourism experiences and fostering cultural pride.
- Creating local employment opportunities through tourism: Tourism can create significant employment opportunities for local communities, provided that employment practices are inclusive and sustainable.
- Ensuring the benefits of tourism are shared equitably: Ensuring equitable distribution of the benefits of tourism is crucial for preventing social divisions and ensuring that local communities benefit from tourism development.
Conclusion
Building resilience and achieving sustainable development in Least Developed Countries demands a holistic, multifaceted strategy. This framework highlights the crucial interconnections between good governance, sustainable infrastructure, climate resilience, and inclusive growth. By strengthening institutional capacity, investing wisely in sustainable infrastructure, enhancing climate resilience, and fostering truly inclusive growth, LDCs can create a path toward a more prosperous and equitable future. This framework serves as a crucial starting point for collaborative efforts, demanding sustained commitment from governments, international organizations, and civil society. Let's work together to advance the cause of sustainable development in Least Developed Countries and build a more just and sustainable world for all.

Featured Posts
-
 How To Watch The Dallas Wings Vs Las Vegas Aces Wnba Preseason Game Live
May 07, 2025
How To Watch The Dallas Wings Vs Las Vegas Aces Wnba Preseason Game Live
May 07, 2025 -
 Lewis Capaldi Makes Surprise Comeback After Two Year Break
May 07, 2025
Lewis Capaldi Makes Surprise Comeback After Two Year Break
May 07, 2025 -
 Decouvrir Le Lioran Au Depart D Onet Le Chateau
May 07, 2025
Decouvrir Le Lioran Au Depart D Onet Le Chateau
May 07, 2025 -
 Julius Randles Impact A Shift In Timberwolves Fan Sentiment
May 07, 2025
Julius Randles Impact A Shift In Timberwolves Fan Sentiment
May 07, 2025 -
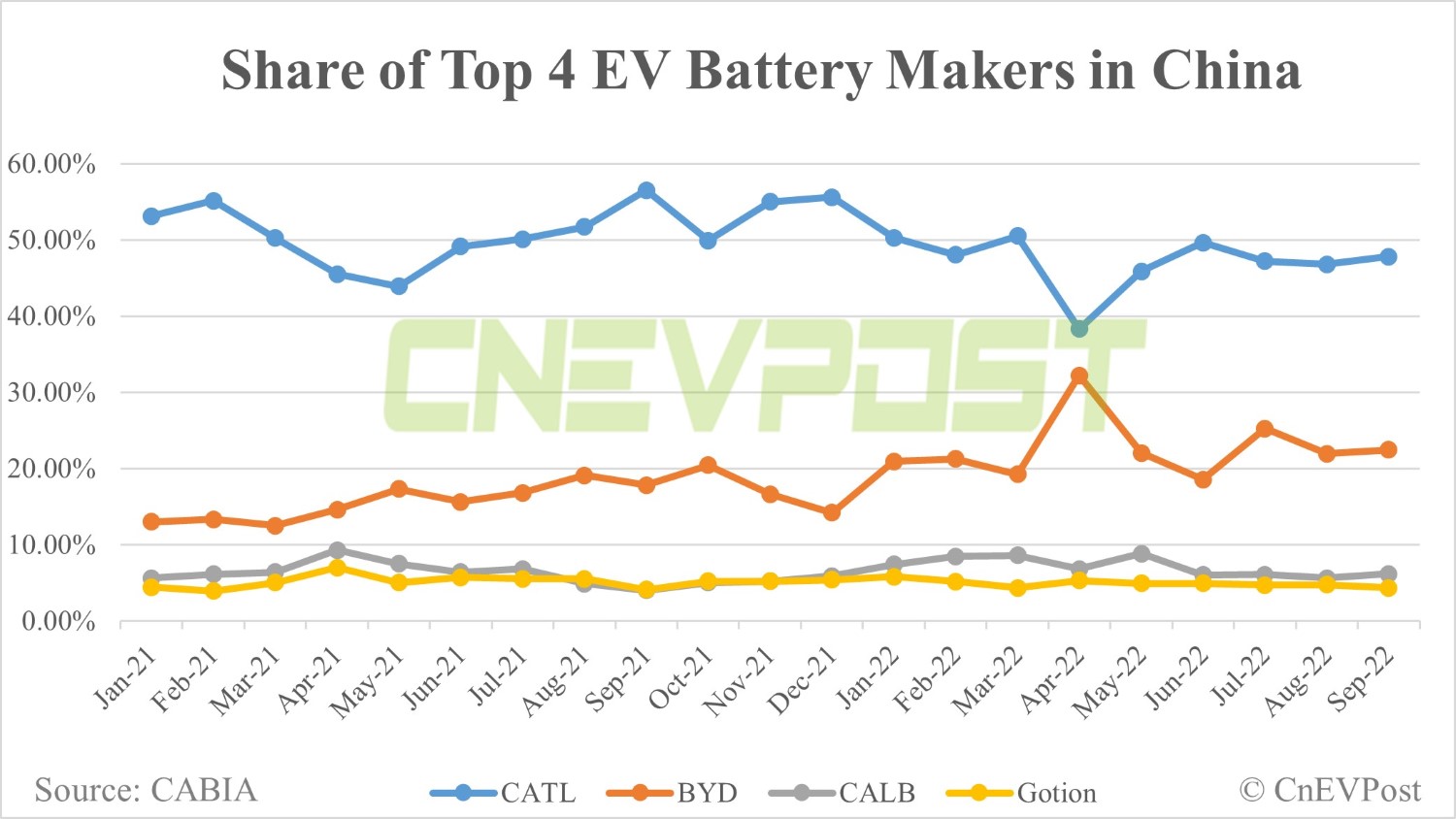 Chinas Catl Seeks 1 Billion Loan To Boost Indonesian Battery Production
May 07, 2025
Chinas Catl Seeks 1 Billion Loan To Boost Indonesian Battery Production
May 07, 2025
