AI Therapy: Privacy Concerns And Potential For Surveillance
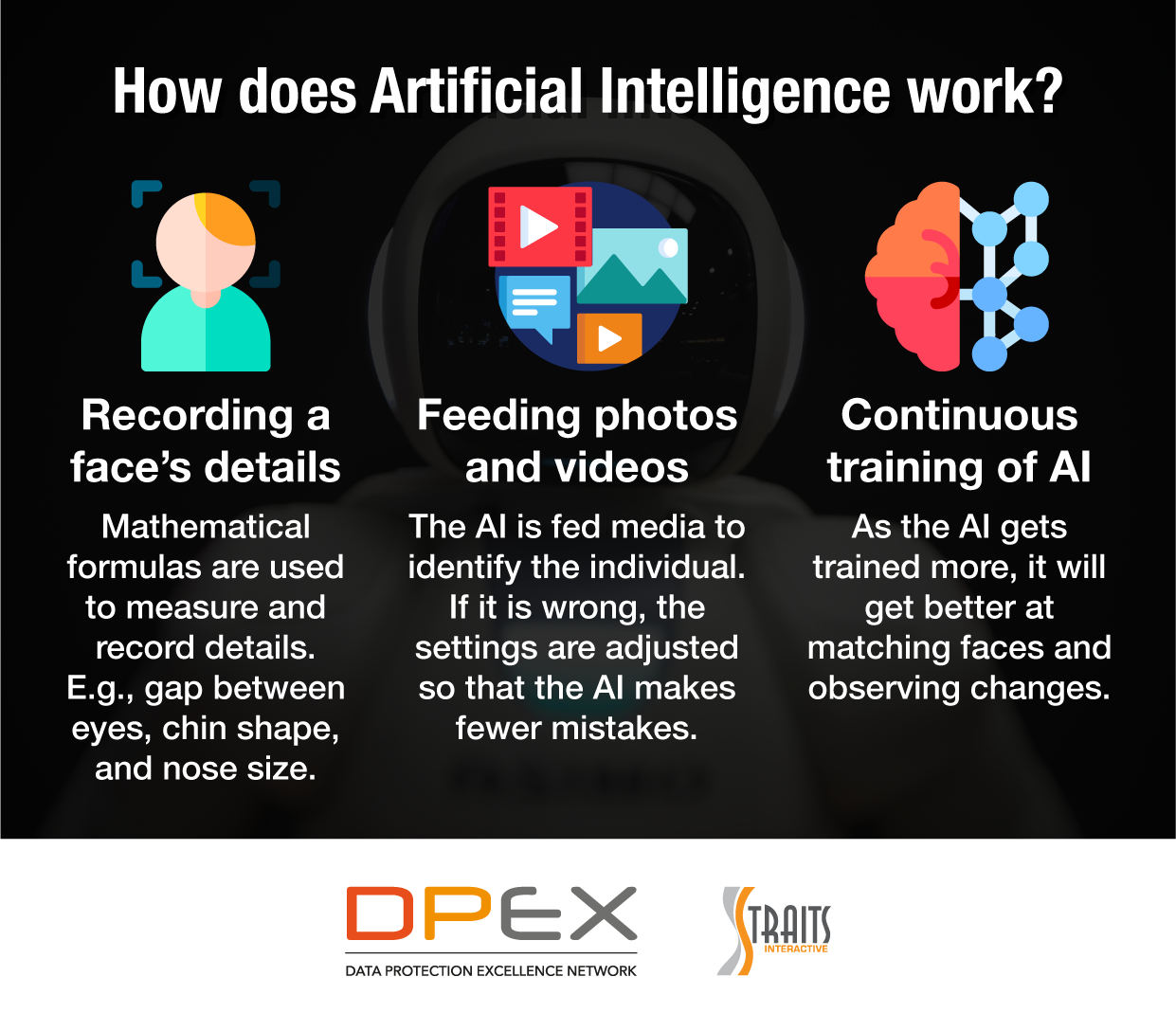
Table of Contents
Data Security and Confidentiality in AI Therapy
The sensitive nature of mental health data necessitates robust security measures. AI therapy platforms collect vast amounts of personal information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Failure to adequately protect this data can have devastating consequences.
Data Breaches and Their Consequences
Digital storage of sensitive patient data inherently increases vulnerability to breaches. A successful breach can expose highly personal information, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and personal details revealed during therapy sessions. The consequences of such breaches are far-reaching:
- Reputational damage: Patients may suffer social stigma and discrimination.
- Emotional distress: The violation of trust can exacerbate pre-existing mental health conditions.
- Identity theft: Stolen personal information can be used for fraudulent activities.
Examples from other healthcare sectors demonstrate the devastating impact of data breaches. The legal ramifications can be severe, involving hefty fines and lawsuits. The potential for identity theft and financial loss adds another layer of complexity to the risks.
Encryption and Anonymization Techniques
Strong encryption protocols are paramount for protecting patient data. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, safeguarding it from unauthorized access. Data anonymization techniques aim to remove identifying information, making it difficult to link data back to individuals. However, complete anonymity remains a challenge.
- Different types of encryption: Symmetric-key encryption, asymmetric-key encryption, and end-to-end encryption offer varying levels of security.
- Challenges in achieving complete anonymity: Sophisticated techniques can sometimes re-identify anonymized data.
- Regulatory compliance: Adherence to regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is crucial for maintaining patient confidentiality.
Data Storage and Ownership
A crucial ethical consideration is the ownership of data generated during AI therapy sessions. Is it the patient, the therapist, or the AI company that owns and controls this information? This question raises significant ethical implications regarding data use, sharing, and control.
- Different data ownership models: Various models exist, each with its own implications for patient rights and privacy.
- Transparent data policies: Clear and accessible data policies are essential for informing patients about how their data will be used and protected.
- Patient rights: Patients should have the right to access, modify, and delete their data.
The Potential for Surveillance and Algorithmic Bias in AI Therapy
AI therapy platforms inherently collect vast amounts of data, creating the potential for both unintended surveillance and biased outcomes.
Monitoring and Tracking Patient Behavior
AI algorithms can track various aspects of user behavior, including session frequency, response times, and emotional keywords expressed during interactions. While this data might be used to personalize treatment, it also raises concerns about constant monitoring and potential misuse.
- Examples of data collected: Detailed logs of interactions provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's mental state.
- Potential for misinterpretation: Algorithmic interpretations may not accurately reflect the complexities of human emotion and experience.
- Risk of over-diagnosis: Overreliance on automated analysis may lead to inaccurate or premature diagnoses.
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI algorithms are trained on datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases, the algorithms will perpetuate and potentially amplify these biases. This can lead to unfair or inaccurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations, particularly for marginalized communities.
- Examples of algorithmic bias: Similar biases seen in facial recognition technology can manifest in AI therapy, leading to inaccurate assessments.
- Importance of diverse datasets: Training algorithms on representative datasets is crucial for mitigating bias.
- Strategies for mitigating bias: Regular audits, transparency in algorithm design, and continuous monitoring are essential.
Lack of Transparency and Explainability
Many AI systems operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions. This lack of transparency hinders accountability and erodes trust.
- The need for clear explanations: Users should be able to understand the reasoning behind AI's recommendations.
- User control over data usage: Patients should have control over how their data is utilized.
- The role of regulatory oversight: Independent oversight is necessary to ensure responsible development and deployment of AI therapy tools.
Conclusion
AI therapy presents a powerful tool with the potential to revolutionize mental healthcare access. However, realizing this potential requires prioritizing data security, addressing algorithmic bias, and ensuring robust mechanisms for protecting patient privacy. The ethical considerations outlined above—data security, surveillance, and algorithmic bias—must be carefully addressed to ensure responsible innovation in this field. As AI therapy continues to evolve, it's crucial to advocate for strong regulations and ethical guidelines to protect patient privacy and prevent misuse. Let's work together to ensure that the benefits of AI therapy are realized without compromising the fundamental right to confidentiality and privacy in mental healthcare. Learn more about advocating for responsible AI therapy development and participate in the ongoing conversation about ethical AI in mental health.

Featured Posts
-
 Nbas 50 000 Fine Anthony Edwards And The Fan Incident
May 15, 2025
Nbas 50 000 Fine Anthony Edwards And The Fan Incident
May 15, 2025 -
 Dodgers Offense Muted In Loss To Cubs
May 15, 2025
Dodgers Offense Muted In Loss To Cubs
May 15, 2025 -
 Draymond Greens Honest Assessment Of Jimmy Butler After Warriors Kings Game
May 15, 2025
Draymond Greens Honest Assessment Of Jimmy Butler After Warriors Kings Game
May 15, 2025 -
 Evaluating Trumps Stance On Oil Prices A Goldman Sachs Report
May 15, 2025
Evaluating Trumps Stance On Oil Prices A Goldman Sachs Report
May 15, 2025 -
 Crystal Palace Vs Nottingham Forest Minuto A Minuto Y Estadisticas
May 15, 2025
Crystal Palace Vs Nottingham Forest Minuto A Minuto Y Estadisticas
May 15, 2025
