Air Traffic Safety Crisis: Internal Warnings Ignored Before Newark System Failure

Table of Contents
H2: Pre-existing System Vulnerabilities and Internal Warnings
The Newark ATC system failure wasn't a sudden, unforeseen event; rather, it was the culmination of long-standing, documented weaknesses and ignored internal warnings. Numerous reports and internal communications indicated potential problems that, if addressed proactively, could have prevented the crisis.
- Outdated Software: Internal memos dating back several years flagged the outdated software as a significant risk factor, citing compatibility issues and increasing vulnerability to system failures. These concerns were consistently documented but seemingly ignored.
- Insufficient Redundancy: Reports highlighted a lack of sufficient backup systems, meaning a single point of failure could cripple the entire operation. This lack of redundancy was repeatedly identified as a critical vulnerability.
- Understaffing Reports: Documented evidence points to consistent understaffing within the Newark ATC control center. These reports detailed overworked controllers facing increasing pressure and a higher risk of human error. The potential for fatigue-related mistakes was consistently raised but not adequately addressed.
- Inadequate Training Documentation: Internal reviews revealed deficiencies in training materials and the overall training program for air traffic controllers. This lack of up-to-date, comprehensive training contributed to a potential for operational errors and a reduced ability to react efficiently to system failures.
Experts in air traffic management have voiced serious concerns about the disregard of these warnings. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading aviation safety researcher, stated, "The documented internal warnings were clear and unambiguous. The failure to act on these warnings demonstrates a systemic problem within the FAA's approach to safety management." This pattern of ignoring pre-existing vulnerabilities highlights a critical need for improved internal communication and a greater emphasis on preventative maintenance.
H2: The Breakdown: A Detailed Account of the System Failure
The Newark Airport system failure unfolded over a period of approximately [Insert Duration]. The sequence of events started with [Describe the initiating event, e.g., a power surge]. This triggered [Describe the subsequent technical issues, e.g., a cascading software failure]. The system’s lack of redundancy meant that the failure quickly spread, causing a complete shutdown of the air traffic control system.
- Technical Issues: The primary contributing factor appears to be [Specific technical issues: hardware failure, software glitch, etc.]. The aged infrastructure and lack of recent upgrades exacerbated the impact of the initial failure.
- Impact on Flights: The outage resulted in widespread flight disruptions, including hundreds of delays, dozens of diversions to neighboring airports, and numerous cancellations. This led to significant passenger inconvenience, stranded travelers, and massive economic losses for airlines and businesses.
- Safety Risks: The near-miss incidents that occurred during the ATC system outage highlight the serious safety risks associated with such failures. The potential for mid-air collisions, though thankfully avoided, underscores the gravity of the situation.
The economic impact was substantial, with estimates reaching [Insert estimated economic losses]. The human cost, however, is immeasurable, emphasizing the urgent need for robust and resilient air traffic control systems.
H2: The Role of Budget Cuts and Resource Allocation
The Newark ATC system failure may be directly linked to years of budget cuts and insufficient resource allocation within the FAA and airport authorities. This underfunding may have directly contributed to the inadequate maintenance, outdated equipment, and understaffing identified as contributing factors.
- Understaffing: The FAA has experienced budget cuts that led to hiring freezes and attrition, resulting in a chronic shortage of air traffic controllers. This directly impacts the ability to provide safe and efficient air traffic management.
- Lack of Equipment Upgrades: Insufficient funding likely hampered the timely replacement of outdated equipment and implementation of modern, more resilient systems. The reliance on aging technology increased the vulnerability to failures.
- Delayed Maintenance: Budget limitations may have forced the postponement of crucial maintenance procedures, further contributing to the system's vulnerability and increasing the risk of failure.
Examining the correlation between these resource limitations and the severity of the Newark system failure is crucial to understanding the systemic issues that need addressing. The data on funding cuts to the FAA in recent years paints a concerning picture and strengthens the case for increased investment in aviation safety.
H2: Post-Failure Response and Investigation
The immediate response to the Newark Airport system failure involved [Describe the immediate actions taken, e.g., diverting flights, deploying emergency protocols]. A comprehensive investigation, led by [Mention the investigating body], is underway to determine the root causes of the outage.
- Temporary Solutions: [Describe temporary solutions implemented, e.g., manual control procedures]. These temporary measures highlight the complexities of managing air traffic without the aid of advanced systems.
- Long-Term Solutions: Proposed long-term solutions include [List proposed solutions, e.g., system upgrades, improved redundancy, increased staffing]. These preventative measures aim to mitigate the risk of future incidents.
- Regulatory Oversight: The FAA's role in the investigation and its subsequent actions will be crucial in determining whether adequate measures are implemented to prevent similar incidents from occurring.
Conclusion:
The Newark Airport air traffic control system failure serves as a stark warning. Ignoring internal warnings and prioritizing short-term cost savings over long-term safety has dire consequences. Addressing systemic vulnerabilities, improving resource allocation for critical infrastructure, and implementing robust safety protocols are not just advisable—they are paramount to prevent future air traffic safety crises. We must demand increased transparency and accountability from regulatory bodies and airport authorities. Failure to prioritize air traffic safety risks jeopardizing the lives of passengers and the integrity of our national airspace. Let’s work together to prevent a future air traffic safety crisis and ensure a safer future for air travel.

Featured Posts
-
 High Potential The Surprising Choice For The Actor Playing David In Episode 13
May 10, 2025
High Potential The Surprising Choice For The Actor Playing David In Episode 13
May 10, 2025 -
 Pakistans Imf Bailout 1 3 Billion Package Under Review Amidst India Tensions
May 10, 2025
Pakistans Imf Bailout 1 3 Billion Package Under Review Amidst India Tensions
May 10, 2025 -
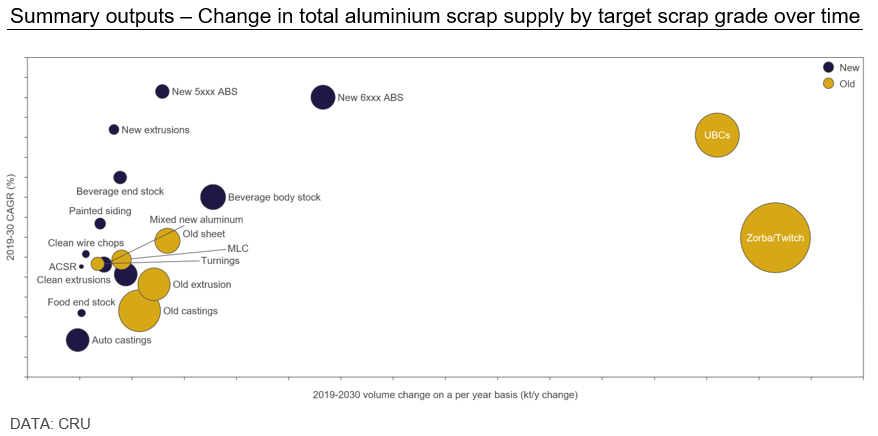 Growth Opportunities Pinpointing The Countrys Best Business Locations
May 10, 2025
Growth Opportunities Pinpointing The Countrys Best Business Locations
May 10, 2025 -
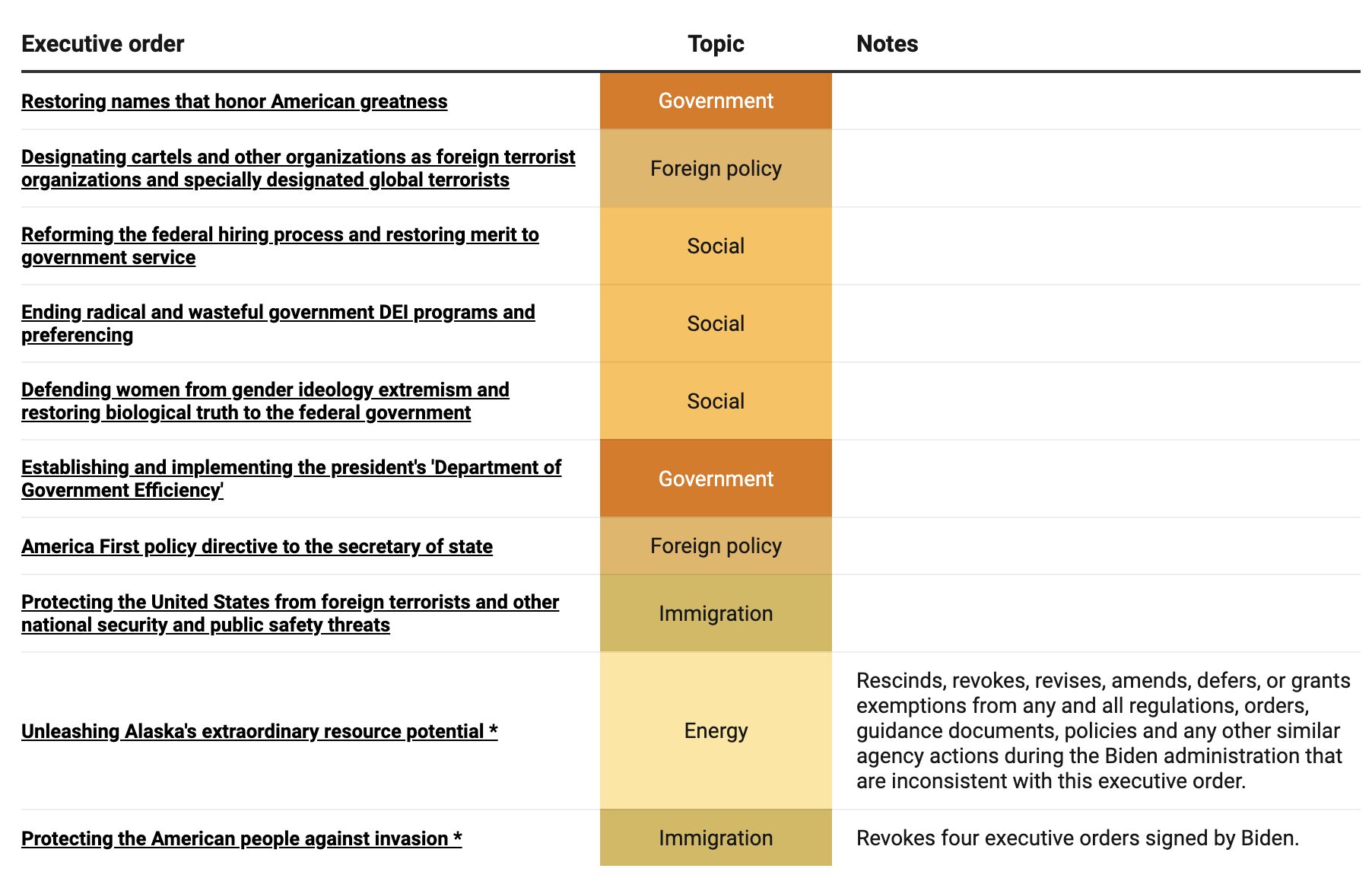 Sharing Your Story How Trumps Executive Orders Affected Transgender Lives
May 10, 2025
Sharing Your Story How Trumps Executive Orders Affected Transgender Lives
May 10, 2025 -
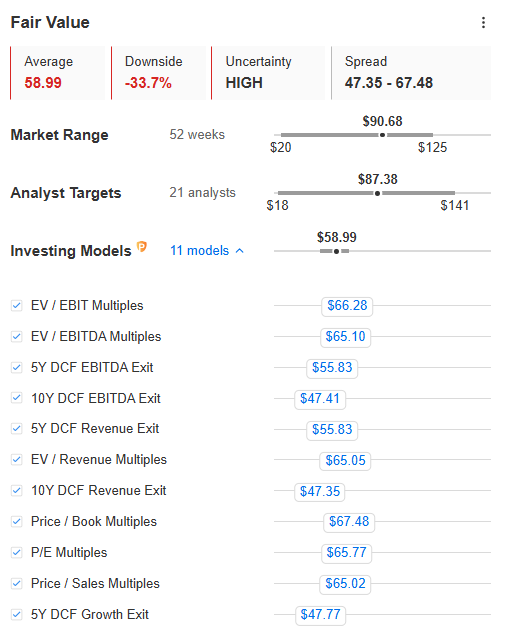 Palantir Stock 30 Down Investment Strategy Considerations
May 10, 2025
Palantir Stock 30 Down Investment Strategy Considerations
May 10, 2025
