Analysis: Trump's 30% Tariffs On Chinese Imports Projected To 2025
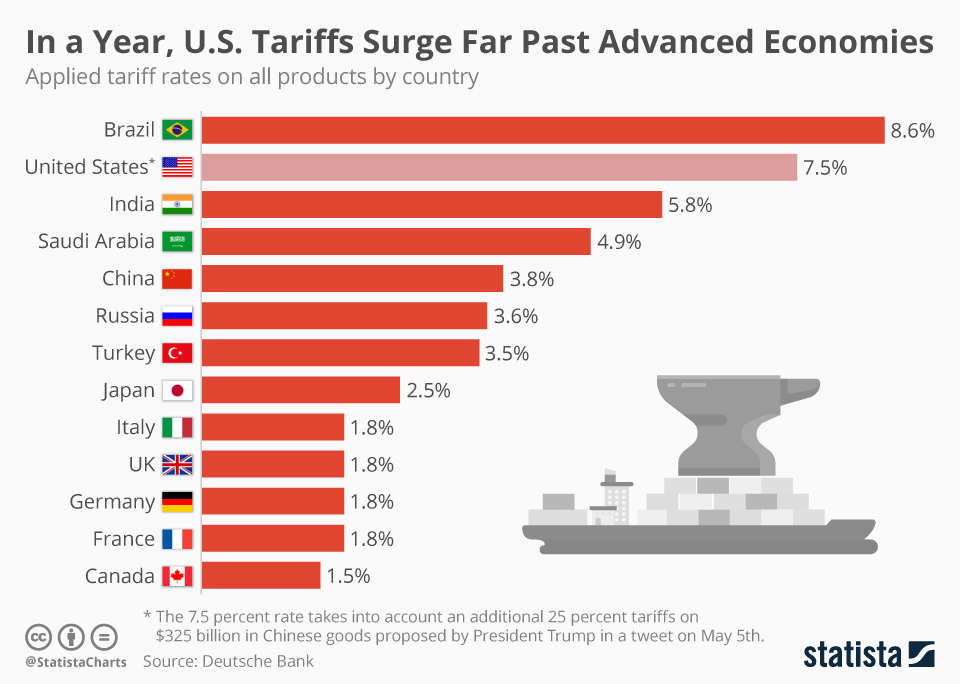
Table of Contents
The Initial Impact of the 30% Tariffs (2018-2020)
Immediate Economic Effects
The immediate impact of the 30% tariffs on Chinese imports was multifaceted and significant. The sudden increase in import costs led to:
- Increased prices for consumers: Many everyday goods, from electronics to clothing, experienced price hikes, directly impacting consumer purchasing power and potentially slowing consumer spending.
- Significant disruption to specific sectors: The agricultural sector, particularly soybean farmers, faced substantial losses due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by China. The manufacturing and technology sectors also experienced significant disruptions to supply chains and increased production costs.
- Retaliatory tariffs from China: China responded with its own tariffs on US goods, escalating the trade war and impacting various US industries. This tit-for-tat exchange created uncertainty and volatility in global markets.
- Reduced trade volume: The tariffs led to a noticeable decrease in bilateral trade volume between the US and China, impacting both economies. Precise figures varied by sector, but overall trade shrank significantly in the initial period.
- Impact on US GDP growth: The tariffs are estimated to have contributed to a slight decrease in US GDP growth during this period. However, isolating their exact impact from other economic factors remains challenging. Studies have offered varied estimations.
Shifting Trade Dynamics
The initial shock spurred a significant shift in global trade dynamics. Businesses began:
- Diversifying supply chains: Companies actively sought alternative sourcing countries to reduce their reliance on Chinese imports. This process was driven by the need to mitigate tariff risks and ensure business continuity.
- Reshoring and nearshoring: The tariffs accelerated the trend of companies moving production back to the US (reshoring) or to neighboring countries (nearshoring), such as Mexico and Vietnam.
- Impact on US-China trade relations: The tariffs severely strained US-China trade relations, leading to increased geopolitical tensions and uncertainty in the global economic landscape.
Long-Term Effects of the Tariffs (2021-2025)
Persistent Inflationary Pressures
The impact of Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese imports extended beyond the initial period. The increased costs of goods continue to contribute to:
- Ongoing inflationary pressures: The tariffs acted as a persistent inflationary force, pushing up prices for various goods and services. This impact is still being felt and has been compounded by other global economic factors.
- Reduced consumer purchasing power: Higher prices for imported goods directly reduced consumer purchasing power, affecting demand and potentially hindering economic growth.
- Increased cost of goods sold for businesses: Businesses faced higher input costs, impacting their profitability and potentially leading to price increases for consumers.
- Projections for future inflation rates: Forecasting future inflation rates is complex and depends on numerous factors. However, the lingering effects of these tariffs are likely to contribute to inflationary pressure in the years to come.
Restructuring of Global Supply Chains
The long-term implications of the tariffs extend to a fundamental restructuring of global supply chains:
- Long-term implications of reshoring and nearshoring: The shift away from China is expected to be a long-term trend, reshaping global manufacturing landscapes.
- Impact on global manufacturing: The re-allocation of manufacturing capacity has significant implications for global competitiveness and the distribution of economic activity.
- Role of automation and technology: The increased focus on efficiency and cost reduction is accelerating the adoption of automation and advanced technologies in manufacturing and supply chain management.
Geopolitical Implications
The geopolitical consequences of Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese imports are far-reaching:
- Ongoing impact on US-China relations: The trade war has had a lasting impact on the relationship between the two economic superpowers, shaping their geopolitical strategies and international alliances.
- Broader implications for global trade and economic governance: The experience has raised questions about the effectiveness of existing global trade agreements and the need for updated governance mechanisms.
- Strategic implications for other nations: Other countries have had to adapt to the changing global trade landscape, seeking to capitalize on new opportunities or mitigate the risks associated with the ongoing trade tensions.
Modeling and Forecasting Techniques Used in this Analysis
This analysis utilizes econometric modeling techniques, incorporating data from various sources, including:
- Official trade statistics: Data from the US Census Bureau and other international organizations provided baseline information on trade volumes and values.
- Consumer price indices: Inflation data was used to assess the impact of tariffs on consumer prices.
- Industry-specific data: Data from industry associations and research firms were used to analyze sector-specific impacts.
The models incorporate various assumptions about future economic conditions and policy changes, including assumptions about global growth rates and exchange rates. The limitations of the models include the inherent uncertainty in predicting future economic events and the complexity of disentangling the impact of tariffs from other economic factors. Charts and graphs visualize the projected data, illustrating the anticipated trends in trade, inflation, and GDP growth.
Conclusion
Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese imports had a profound and lasting impact on the global economy. The initial shock resulted in increased prices for consumers, disrupted supply chains, and escalated trade tensions. In the long term, the tariffs have contributed to persistent inflationary pressures, reshaped global supply chains, and altered geopolitical relationships. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors requires a nuanced approach, recognizing the long-term adjustments underway in global trade and the lingering influence of these policies.
For a deeper understanding of the complex implications of Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese imports and their projected effects until 2025, further research into specific sectors and economic modeling is recommended. Continue exploring the lasting impact of these trade policies and their influence on the global economy by accessing relevant resources and expert opinions on Trump's 30% tariffs on Chinese imports.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Hints Sunday May 11th
May 18, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Hints Sunday May 11th
May 18, 2025 -
 O Maik Magiers Ensarkonei Ton Ilon Mask Sto Saturday Night Live
May 18, 2025
O Maik Magiers Ensarkonei Ton Ilon Mask Sto Saturday Night Live
May 18, 2025 -
 Projecting The Spring Breakout 2025 Rosters
May 18, 2025
Projecting The Spring Breakout 2025 Rosters
May 18, 2025 -
 Monday April 28th 2025 Daily Lotto Results Announced
May 18, 2025
Monday April 28th 2025 Daily Lotto Results Announced
May 18, 2025 -
 Wednesdays Daily Lotto Results April 16 2025
May 18, 2025
Wednesdays Daily Lotto Results April 16 2025
May 18, 2025
