April's U.S. Jobs Report: 177,000 New Jobs, 4.2% Unemployment Rate
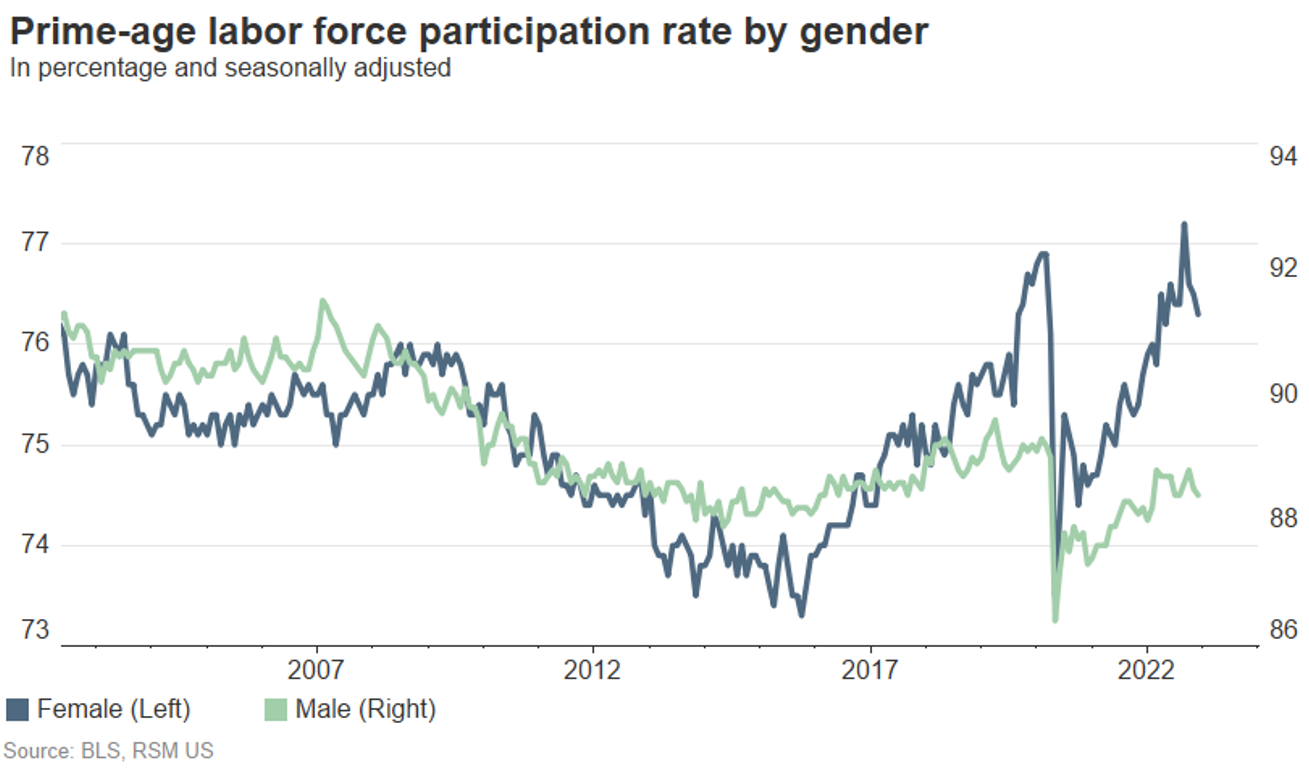
Table of Contents
Job Growth Breakdown: A Deeper Dive into the 177,000 New Jobs
The 177,000 new jobs added in April represent a slowdown compared to the previous month's figures. Understanding the composition of this job growth is crucial. While the overall number might seem modest, analyzing the sectors involved provides a clearer picture of the U.S. employment landscape.
-
Sector-Specific Performance: The service sector, as expected, continued to be a significant driver of job creation. However, the pace of growth in this sector showed some moderation compared to previous months. Manufacturing showed modest growth, while certain other sectors like construction experienced a slight decline. The professional and business services sector also contributed significantly to the overall job creation.
-
Geographical Distribution: Job growth wasn't evenly distributed across the country. Some regions experienced stronger growth than others, reflecting variations in local economic conditions and industry concentrations. Further analysis is needed to determine the specific regional disparities.
-
Month-Over-Month and Year-Over-Year Comparisons: April's job growth was notably lower than March's figures, indicating a potential slowdown in the pace of job creation. Year-over-year comparisons also need to be carefully analyzed to ascertain long-term trends.
-
Key Points:
- Strong growth in the healthcare and leisure and hospitality sectors.
- Slight decline in construction and manufacturing employment.
- Job growth fell short of analyst predictions.
- Seasonal adjustments played a moderate role in the final figures.
Unemployment Rate Holds Steady at 4.2%: What Does It Mean?
The unemployment rate remaining stable at 4.2% might appear positive, but a comprehensive analysis is necessary. This figure doesn't tell the whole story.
-
Labor Force Participation Rate: Analyzing the labor force participation rate is crucial. Has the number of people actively seeking employment increased or decreased? A stagnant unemployment rate with a declining participation rate might mask underlying issues.
-
Types of Unemployment: Understanding the different types of unemployment (frictional, structural, cyclical) is key to interpreting the 4.2% figure. Frictional unemployment, related to temporary job transitions, is normal. Structural unemployment, arising from skills mismatches, and cyclical unemployment, tied to economic downturns, are more concerning.
-
Historical Context: Comparing the current 4.2% rate to historical trends provides valuable context. Is this unemployment rate higher or lower than in previous years? Analyzing historical data alongside economic forecasts gives a clearer picture.
-
Key Points:
- The unemployment rate remains relatively low compared to historical averages.
- Potential for increased inflationary pressure due to low unemployment.
- Further analysis is required to determine the types of unemployment dominating the current figures.
- Long-term implications for social welfare programs and economic growth need further examination.
Average Hourly Earnings: Wage Growth and Inflation
Average hourly earnings are a crucial economic indicator reflecting the relationship between wage growth and inflation.
-
Percentage Change and Real Wage Growth: The April jobs report revealed a specific percentage change in average hourly earnings. However, it's crucial to assess real wage growth, which adjusts for inflation. Real wage growth reflects the actual purchasing power of wages.
-
Impact on Consumer Spending: Wage growth influences consumer spending, a key driver of economic growth. Higher wages can lead to increased consumer confidence and spending, boosting economic activity.
-
Relationship to Inflation: The relationship between wage growth and inflation is complex. Rapid wage growth could fuel inflation, while stagnant wage growth might hinder consumer spending.
-
Key Points:
- Average hourly earnings increased by X% in April (replace X with the actual percentage).
- Real wage growth needs careful analysis to account for inflation.
- Wage growth impacts consumer confidence and spending.
- The potential for future wage increases needs careful consideration.
The Bigger Picture: Implications for the US Economy
The April U.S. jobs report has significant implications for the overall U.S. economy.
-
Federal Reserve's Monetary Policy: The report's data will influence the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions, particularly regarding interest rates. Low unemployment might prompt the Fed to consider raising interest rates to combat potential inflation.
-
Economic Outlook: The report provides valuable insights into the overall health of the U.S. economy. Sustained job growth and a stable unemployment rate generally signal a positive economic outlook.
-
Potential Concerns: Despite the positive aspects, certain sectors showed weakness, indicating potential areas of concern.
-
Key Points:
- Potential for interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve.
- Positive economic growth outlook but with potential challenges.
- Impact on the stock market and investor sentiment.
- Long-term projections depend on future economic indicators.
Conclusion: Understanding the April U.S. Jobs Report and its Future Implications
The April U.S. jobs report presented a mixed picture of the U.S. economy. While job growth was positive, the slower-than-expected pace and nuanced unemployment rate require careful consideration. Wage growth, in relation to inflation, remains a key factor to watch. The implications for the Federal Reserve's monetary policy and the overall economic outlook are significant. Stay updated on the latest U.S. jobs reports and economic indicators to make informed decisions. Follow [Your Website/Platform] for future analyses and insights into the U.S. employment landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Nba Scoring Update Westbrook Moves Past Garnett Into Top 20
May 05, 2025
Nba Scoring Update Westbrook Moves Past Garnett Into Top 20
May 05, 2025 -
 Emma Stones Popcorn Dress Viral Sensation From Snls 50th
May 05, 2025
Emma Stones Popcorn Dress Viral Sensation From Snls 50th
May 05, 2025 -
 Westbrooks Play In Nuggets Vs Warriors Fan Opinions And Social Media Buzz
May 05, 2025
Westbrooks Play In Nuggets Vs Warriors Fan Opinions And Social Media Buzz
May 05, 2025 -
 Berlangas Future Hearn Offers Plant Or Charlo Bout
May 05, 2025
Berlangas Future Hearn Offers Plant Or Charlo Bout
May 05, 2025 -
 The Private Credit Boom 5 Dos And Don Ts To Get Hired
May 05, 2025
The Private Credit Boom 5 Dos And Don Ts To Get Hired
May 05, 2025
