Building A Heat-Resilient India: Exploring Super Cool Materials For Urban Development
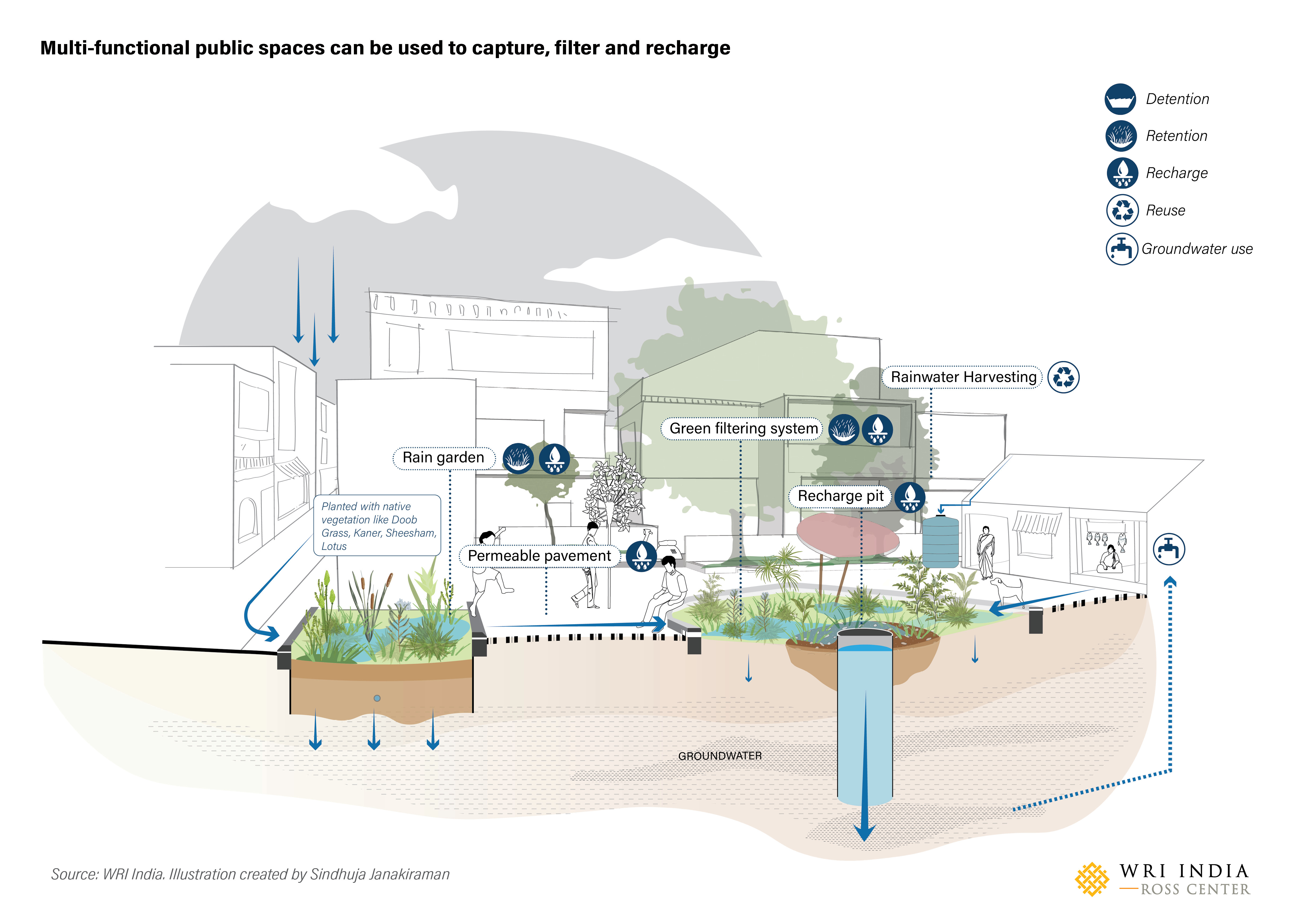
Table of Contents
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect and its Impacts
The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect is a significant concern in rapidly urbanizing India. It refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. This is due to factors like reduced vegetation, increased impervious surfaces (concrete and asphalt), and anthropogenic heat emissions from vehicles and industries. The consequences of the UHI effect in the Indian context are far-reaching:
- Increased energy consumption: Higher temperatures necessitate increased air conditioning use, leading to higher energy demands and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Health issues: Heat stress, heat stroke, respiratory problems, and cardiovascular diseases are exacerbated by the UHI effect, particularly impacting vulnerable populations.
- Reduced productivity: Extreme heat reduces worker productivity and overall economic output.
- Water scarcity: Increased evaporation rates due to higher temperatures worsen water scarcity issues in already water-stressed cities.
Addressing the UHI effect through climate change adaptation strategies is crucial for building sustainable and livable Indian cities. Understanding the complex interplay between urbanization, climate change, and heat stress is the first step towards implementing effective solutions.
Exploring Super Cool Materials for Building Construction
The use of "Super Cool Materials" offers a promising avenue for mitigating the UHI effect and building heat-resilient infrastructure. These materials are designed to reflect solar radiation and reduce surface temperatures, thus contributing to a cooler urban environment.
Cool Roofs
Cool roofs, characterized by high albedo (reflectivity), play a significant role in reducing surface temperatures. They minimize heat absorption and thus reduce the amount of heat transferred to the building and the surrounding environment.
- Types of cool roof materials: Reflective paints, cool roofing tiles (made from materials like ceramic or metal with high reflectivity), and specialized coatings.
- Effectiveness: Studies have shown that cool roofs can significantly reduce building temperatures and energy consumption.
- Cost-effectiveness: While the initial investment might be higher, the long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance costs make cool roofs a cost-effective solution.
- Lifecycle analysis: A comprehensive lifecycle analysis, considering material production, installation, maintenance, and disposal, is crucial for evaluating the overall environmental impact and cost-effectiveness of cool roof systems. Keywords: Cool roofs, high albedo, reflective coatings, thermal emissivity, energy savings.
Cool Pavements
Cool pavements, similar to cool roofs, aim to reduce surface temperatures and mitigate the UHI effect. They utilize materials with high reflectivity and/or porosity.
- Materials: Permeable pavements (allowing water infiltration), light-colored concrete, and other innovative solutions incorporating porous materials.
- Impact on stormwater management: Permeable pavements improve stormwater management by reducing runoff and recharging groundwater. This is particularly important in cities facing increasing rainfall intensity and flooding.
- Keywords: Cool pavements, permeable pavements, porous concrete, stormwater management, urban drainage.
Building Envelope Materials
Improving building insulation and reducing heat transfer through the building envelope is crucial for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption. Advanced materials offer significant improvements in thermal performance.
- Examples: Aerogel, vacuum insulation panels, and high-performance insulation materials (e.g., mineral wool, expanded polystyrene).
- Thermal performance: These materials offer superior thermal resistance, significantly reducing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter.
- Cost implications: While these materials might have a higher initial cost, their long-term energy savings and improved comfort levels make them a worthwhile investment.
- Keywords: Building envelope, thermal insulation, aerogel, vacuum insulation panels, energy efficiency.
Green Infrastructure and its Role
Green infrastructure, encompassing green walls, green roofs, and urban trees, plays a vital role in mitigating the UHI effect.
- Impact on temperature reduction: Vegetation helps reduce surface temperatures through evapotranspiration (cooling effect of water evaporation).
- Air quality improvement: Plants absorb pollutants, improving air quality and contributing to a healthier urban environment.
- Biodiversity enhancement: Green infrastructure promotes biodiversity and creates more aesthetically pleasing urban spaces.
- Keywords: Green infrastructure, green walls, green roofs, urban greenery, biodiversity, air quality.
Policy and Implementation Strategies for Widespread Adoption of Super Cool Materials
Widespread adoption of "Super Cool Materials" requires supportive government policies and incentives.
- Tax breaks: Tax incentives can make these materials more financially attractive to builders and developers.
- Subsidies: Government subsidies can help offset the higher initial cost of "Super Cool Materials."
- Building codes: Updating building codes to mandate or incentivize the use of these materials is essential for long-term impact.
- Awareness campaigns: Public awareness campaigns can educate stakeholders about the benefits of these materials and encourage their adoption.
- Keywords: Government policies, building codes, sustainability, climate action, incentives.
Conclusion
By embracing "Super Cool Materials" and implementing effective policies, India can create more livable and sustainable urban environments. The key takeaways from this article highlight the significant benefits of cool roofs, cool pavements, advanced building envelope materials, and green infrastructure in mitigating the UHI effect. These materials offer a pathway towards creating heat-resilient cities, reducing energy consumption, improving public health, and building a more sustainable future for India. Learn more about "Super Cool Materials" and advocate for their wider adoption in urban planning and construction to help build a cooler, more sustainable India.
 Udstilling Ditte Okman Praesenterer Kare Quist Han Taler Udenom
Udstilling Ditte Okman Praesenterer Kare Quist Han Taler Udenom
 Six New Ai Data Centres Coming To British Columbia From Bell
Six New Ai Data Centres Coming To British Columbia From Bell
 Exploring The Nintendo Switchs Impact On The Indie Game Landscape
Exploring The Nintendo Switchs Impact On The Indie Game Landscape
 Talking Pictures Tvs Z Cars Episodes Cast And Legacy
Talking Pictures Tvs Z Cars Episodes Cast And Legacy
 Dolberg 25 Mal I Saesonen Et Realistisk Chokskifte
Dolberg 25 Mal I Saesonen Et Realistisk Chokskifte
