Child Soldiers In Yemen: Driving Amidst Conflict And Crisis
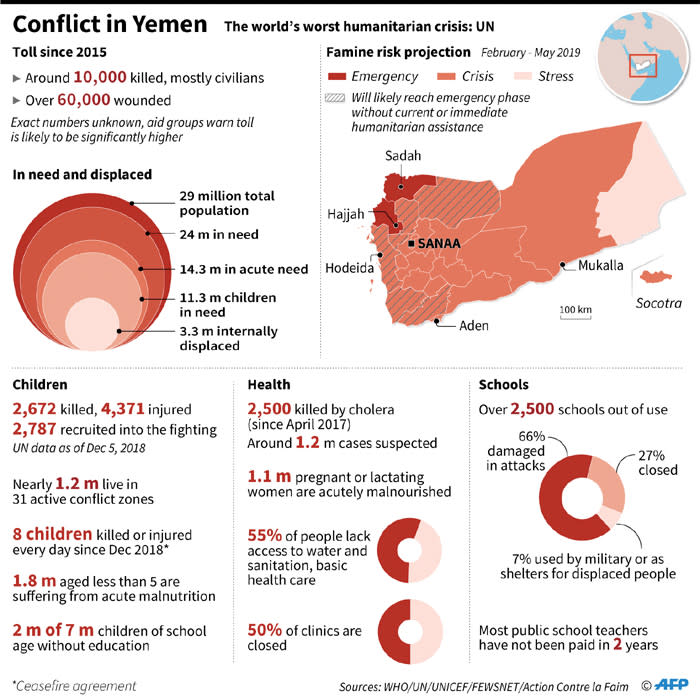
Table of Contents
The Root Causes of Child Soldier Recruitment in Yemen
The recruitment of child soldiers in Yemen is a multifaceted problem stemming from a confluence of devastating circumstances. Understanding these root causes is crucial to effectively combating the issue.
Poverty and Economic Hardship
Widespread poverty and the near-total collapse of Yemen's economy have created a breeding ground for child soldier recruitment. Families, desperate to survive, are often left with no choice but to send their children to armed groups in exchange for meager financial support, food, or shelter.
- Examples of economic hardship: Lack of access to clean water, food insecurity, widespread unemployment, and hyperinflation.
- Statistics on poverty rates in Yemen: The World Bank reports extremely high poverty rates, exacerbated by the conflict, leaving millions vulnerable to exploitation.
- The allure of financial incentives offered by armed groups: Armed groups often offer relatively high salaries compared to what most families can earn, making them a seemingly attractive option.
Lack of Education and Opportunities
The ongoing conflict has decimated Yemen's education system, leaving countless children out of school and with limited prospects for the future. This lack of opportunities makes them exceptionally vulnerable to recruitment by armed groups, who often prey on their desperation and lack of alternatives.
- Statistics on out-of-school children: The number of out-of-school children has dramatically increased due to the conflict, creating a generation lacking basic education and life skills.
- The breakdown of the education system: Schools have been destroyed, teachers haven't been paid, and many children are too preoccupied with survival to attend school.
- The lack of alternative pathways for children: Without access to education or vocational training, children see limited options for escaping poverty and often turn to armed groups.
Exploitation and Coercion
Armed groups in Yemen employ various tactics to recruit children, including abduction, forced conscription, and manipulative promises. These tactics often exploit children's vulnerability and lack of access to protection.
- Examples of coercion tactics: Threats of violence against the child or their family, kidnapping, and forced indoctrination.
- Psychological manipulation: Children are often lured with false promises of adventure, belonging, and a better life.
- The role of family pressure: In some cases, families, facing extreme hardship, are pressured or coerced into allowing their children to join armed groups.
The Role of Tribal and Clan Structures
Yemen's complex tribal and clan structures play a significant role in the recruitment of child soldiers. Loyalty to a particular tribe or clan can often override concerns about human rights, leading to the normalization of child recruitment within certain communities.
- Examples of tribal loyalties influencing recruitment: Children may be pressured to join the armed group affiliated with their tribe or clan.
- The impact of customary law: Traditional norms and practices can sometimes legitimize or excuse the use of child soldiers.
- The challenges of intervention: The deeply entrenched nature of tribal structures makes it challenging for external actors to intervene and address the issue effectively.
The Devastating Impact on Child Soldiers
The experience of being a child soldier leaves deep and lasting scars on individuals and communities. The consequences are far-reaching and catastrophic.
Physical and Psychological Trauma
Child soldiers endure unimaginable physical and psychological trauma. They are often subjected to violence, injury, and witnessing horrific events, leading to severe mental health issues such as PTSD.
- Examples of injuries sustained: Gunshot wounds, shrapnel injuries, and severe malnutrition.
- PTSD: Many child soldiers suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder, characterized by nightmares, flashbacks, and anxiety.
- Effects of witnessing violence: Exposure to extreme violence and death has devastating long-term impacts on mental and emotional well-being.
- Long-term mental health consequences: The trauma experienced can lead to depression, substance abuse, and difficulty forming healthy relationships.
Lost Childhood and Education
The stolen childhood of child soldiers is a tragedy. They are deprived of education, play, and the normal developmental experiences essential for healthy growth. This deprives them of opportunities for a better future.
- Impact on future prospects: The lack of education and skills makes it extremely difficult for former child soldiers to reintegrate into society and lead fulfilling lives.
- Social isolation: Many former child soldiers struggle to form relationships and connect with their peers due to their traumatic experiences.
- Difficulty reintegrating into society: Reintegrating into a community can be incredibly challenging for children who have witnessed and participated in extreme violence.
Violation of International Law
The recruitment and use of child soldiers is a grave violation of international human rights law, specifically the Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the involvement of children in armed conflict.
- Relevant international treaties and conventions: The UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) and its Optional Protocol explicitly prohibit the recruitment and use of child soldiers.
- Legal consequences for perpetrators: While holding perpetrators accountable is challenging, international law provides a framework for prosecuting those responsible for these crimes.
Efforts to Combat the Use of Child Soldiers in Yemen
Combating the use of child soldiers in Yemen requires a multi-pronged approach involving international organizations, governments, and local communities.
International Organizations' Role
Numerous UN agencies, NGOs, and other international organizations are working tirelessly to address the issue. Their efforts include providing humanitarian assistance, advocating for policy changes, and supporting the rehabilitation of former child soldiers.
- Specific examples of interventions: Providing psychosocial support, educational opportunities, and vocational training for former child soldiers.
- Challenges faced by humanitarian organizations: Access restrictions, security concerns, and the complexity of the conflict create immense challenges for humanitarian workers.
- Successes and failures: While significant progress has been made in some areas, the scale of the problem remains immense, and many challenges persist.
Governmental Initiatives (if any)
The Yemeni government, even amidst its internal divisions, has a responsibility to protect children and prevent their recruitment into armed conflict. However, the effectiveness of governmental initiatives remains significantly hampered by the ongoing conflict and limited resources.
- Specific government programs (if any): Limited initiatives focused on child protection and rehabilitation exist, but their impact has been largely constrained by the political context.
- Challenges in implementing such programs: Lack of funding, lack of control over certain areas, and the ongoing conflict drastically hinder the effectiveness of government programs.
- Effectiveness of government efforts: The effectiveness of government efforts is greatly diminished due to the severe limitations imposed by the ongoing war and political instability.
Community-Based Solutions
Community-based initiatives play a vital role in preventing child recruitment and supporting the rehabilitation of former child soldiers. By engaging with local communities, these programs can promote lasting change.
- Examples of community-based initiatives: Providing educational opportunities, vocational training, and psychosocial support through locally led programs.
- The importance of local participation: Community involvement is crucial to building trust and ensuring the sustainability of these efforts.
- Challenges in engaging communities: The insecurity and displacement caused by the conflict make it difficult to access and engage with communities effectively.
Conclusion
The recruitment and use of child soldiers in Yemen is a tragic consequence of the ongoing conflict and a profound violation of human rights. The root causes are complex, ranging from poverty and lack of opportunity to exploitation and ingrained social structures. The impact on these children is devastating, leaving lasting physical and psychological scars. While international organizations, governments, and local communities are working to address this issue, a concerted global effort is necessary to prevent the further exploitation of children and ensure their protection. Ending the exploitation of child soldiers in Yemen requires a concerted global effort, demanding sustained international pressure, increased humanitarian aid, and long-term investment in peacebuilding and development. Let's work together to prevent the horrors of child soldiers in Yemen and build a future where all children can thrive. To learn more and support organizations working to protect children, visit [insert links to relevant organizations].

Featured Posts
-
 Za Chto Geri Oldman Poprosil Proscheniya U Demi Mur
May 06, 2025
Za Chto Geri Oldman Poprosil Proscheniya U Demi Mur
May 06, 2025 -
 Indian Fashion News Trending Styles And Latest Designs
May 06, 2025
Indian Fashion News Trending Styles And Latest Designs
May 06, 2025 -
 Fortnite Competitive Scene Tournaments Players And Strategies
May 06, 2025
Fortnite Competitive Scene Tournaments Players And Strategies
May 06, 2025 -
 Kidnapped Father Of Crypto Entrepreneur Rescued Suffers Finger Amputation
May 06, 2025
Kidnapped Father Of Crypto Entrepreneur Rescued Suffers Finger Amputation
May 06, 2025 -
 Celebrity Family Goldblums At The Como Vs Torino Match
May 06, 2025
Celebrity Family Goldblums At The Como Vs Torino Match
May 06, 2025
