Decades-Long School Desegregation Order Terminated: A Turning Point?
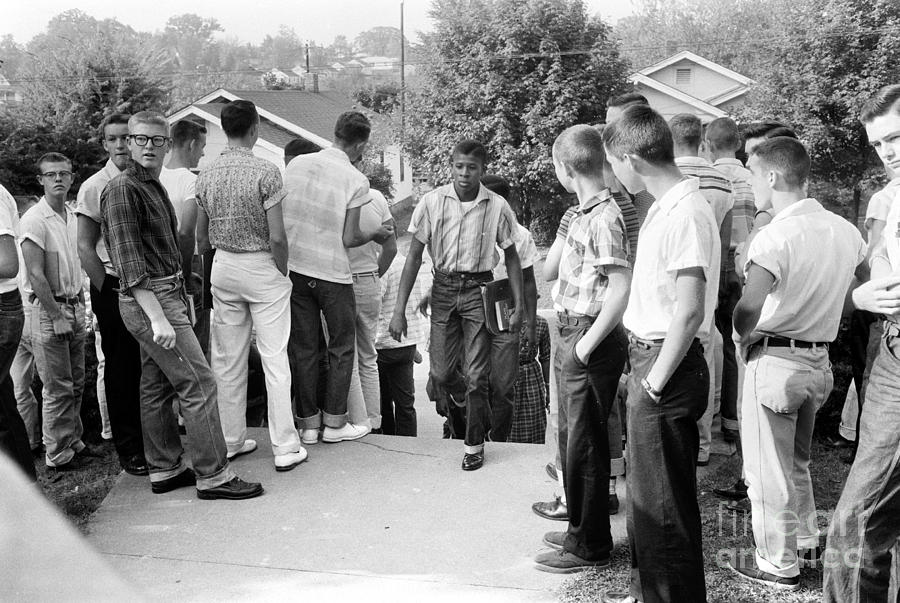

Table of Contents
The recent termination of a decades-long school desegregation order in Mississippi marks a significant moment in the ongoing struggle for racial equality in education. This event raises crucial questions about the progress made since Brown v. Board of Education, the challenges that remain, and the potential implications for the future of school integration across the nation. This article examines the termination, its historical context, and its possible impact on students and communities, exploring the complexities of school desegregation and its ongoing relevance.
<h2>The History of the Desegregation Order</h2>
The desegregation order, in effect for over [insert number] years, stemmed from a long and arduous legal battle to dismantle the Jim Crow South's system of racial segregation in schools. The landmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court decision in 1954 declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, implementation was slow and met with significant resistance, particularly in the South. The Mississippi desegregation order, like many others across the region, faced numerous legal challenges and delays.
- Specifics about the length of the order and the jurisdiction it covered: The order encompassed [specific school districts/counties] in Mississippi, impacting thousands of students.
- Key milestones in the implementation and challenges faced: Initial resistance included [mention specific examples of resistance, e.g., school closures, defiance of court orders]. Subsequent milestones involved [mention court-ordered busing, integration plans, etc.].
- The role of the federal courts in overseeing the desegregation process: Federal courts played a crucial role in monitoring compliance, issuing further orders, and addressing violations of the desegregation order.
- Mention any significant resistance to the order: The resistance ranged from subtle forms of discrimination to overt acts of defiance, highlighting the deeply entrenched nature of segregationist attitudes.
<h2>The Arguments For and Against Termination</h2>
The termination of the desegregation order has sparked a heated debate. Proponents argue that the order has outlived its purpose, citing progress in school integration and the belief that local school districts should have more autonomy in managing their affairs. Opponents, however, express deep concern about the potential for resegregation and the persistence of racial disparities in educational outcomes.
- Arguments supporting termination: These include claims of successful integration efforts in certain areas, a desire for increased local control over schools, and shifting demographics. Proponents point to the idea of school choice as a means to ensure equal opportunities.
- Arguments opposing termination: These center on the fear of a return to de facto segregation, the continued existence of significant racial achievement gaps, and the ongoing need for federal oversight to ensure educational equity. They argue that the achievement gap, despite progress, requires continued intervention.
- Statistical data on school demographics and achievement gaps in the affected area: [Insert relevant statistics on racial demographics in schools, test scores, graduation rates, and access to resources. Cite sources appropriately]. This data is crucial to understanding the context of the debate.
<h3>The Impact on Affected Students and Communities</h3>
The termination of the desegregation order carries potentially profound consequences for students and communities. The most immediate concern is the potential for increased school segregation, leading to unequal access to resources and opportunities.
- Potential increase in school segregation: The removal of federal oversight could lead to a gradual or rapid resegregation of schools, mirroring patterns seen in other areas after similar orders were lifted.
- Impact on student access to quality education and resources: Resegregation often leads to disparities in funding, teacher quality, and access to advanced courses, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities.
- Effects on interracial relationships and social cohesion within the community: Integrated schools can foster positive interracial relationships and promote social cohesion, while segregated schools can reinforce existing social divisions.
- Long-term implications for social mobility and economic opportunity: Unequal educational opportunities can have long-lasting impacts on students' future prospects, affecting social mobility and economic opportunities.
<h2>The Future of School Integration and the Role of Federal Oversight</h2>
The termination of this desegregation order raises important questions about the future of school integration and the role of federal intervention. While the Supreme Court's decision in Brown v. Board of Education remains legally binding, the practical implementation of school integration continues to be a challenge.
- The potential for future legal challenges to school segregation: The termination of this order may set a precedent for challenges to other desegregation orders and potentially lead to renewed litigation regarding school segregation.
- The effectiveness of existing civil rights laws and their enforcement: The effectiveness of existing civil rights laws depends heavily on their enforcement, requiring ongoing vigilance and commitment from federal agencies.
- Policy recommendations for promoting school integration and addressing racial disparities: Policy recommendations could include targeted funding for schools in underserved communities, initiatives promoting diversity in schools, and strengthened enforcement of existing civil rights laws.
- The ongoing need for federal funding and support for equitable education: Federal funding remains essential for ensuring equitable educational opportunities for all students, regardless of race or socioeconomic status.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
The termination of this decades-long school desegregation order is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While proponents celebrate local control and perceived progress, opponents express valid concerns about the potential for resegregation and the continued existence of significant racial achievement gaps. The long-term effects on students and communities remain to be seen, but the need for continued vigilance and commitment to school desegregation is undeniable. The debate surrounding school desegregation is far from over. We need continued discussion, thoughtful policy changes, and sustained commitment to ensuring equal educational opportunities for all students. Let's continue the conversation about school desegregation and work towards achieving true racial equality in education.

Featured Posts
-
 Ajtmae Wzyr Altjart Alsewdy Me Mswwlyn Adhrbyjanyyn Lbhth Tezyz Alteawn
May 02, 2025
Ajtmae Wzyr Altjart Alsewdy Me Mswwlyn Adhrbyjanyyn Lbhth Tezyz Alteawn
May 02, 2025 -
 Florida And Wisconsin Election Turnout Key Insights And Interpretations
May 02, 2025
Florida And Wisconsin Election Turnout Key Insights And Interpretations
May 02, 2025 -
 Is Fortnite Offline Checking Server Status And Update 34 30 Details
May 02, 2025
Is Fortnite Offline Checking Server Status And Update 34 30 Details
May 02, 2025 -
 Gewinnzahlen Lotto 6aus49 Mittwoch 9 April 2025
May 02, 2025
Gewinnzahlen Lotto 6aus49 Mittwoch 9 April 2025
May 02, 2025 -
 Bbcs Financial Crisis 1 Billion Loss And Unprecedented Difficulties
May 02, 2025
Bbcs Financial Crisis 1 Billion Loss And Unprecedented Difficulties
May 02, 2025
