Declining Measles Cases In The United States: Understanding The Recent Trends
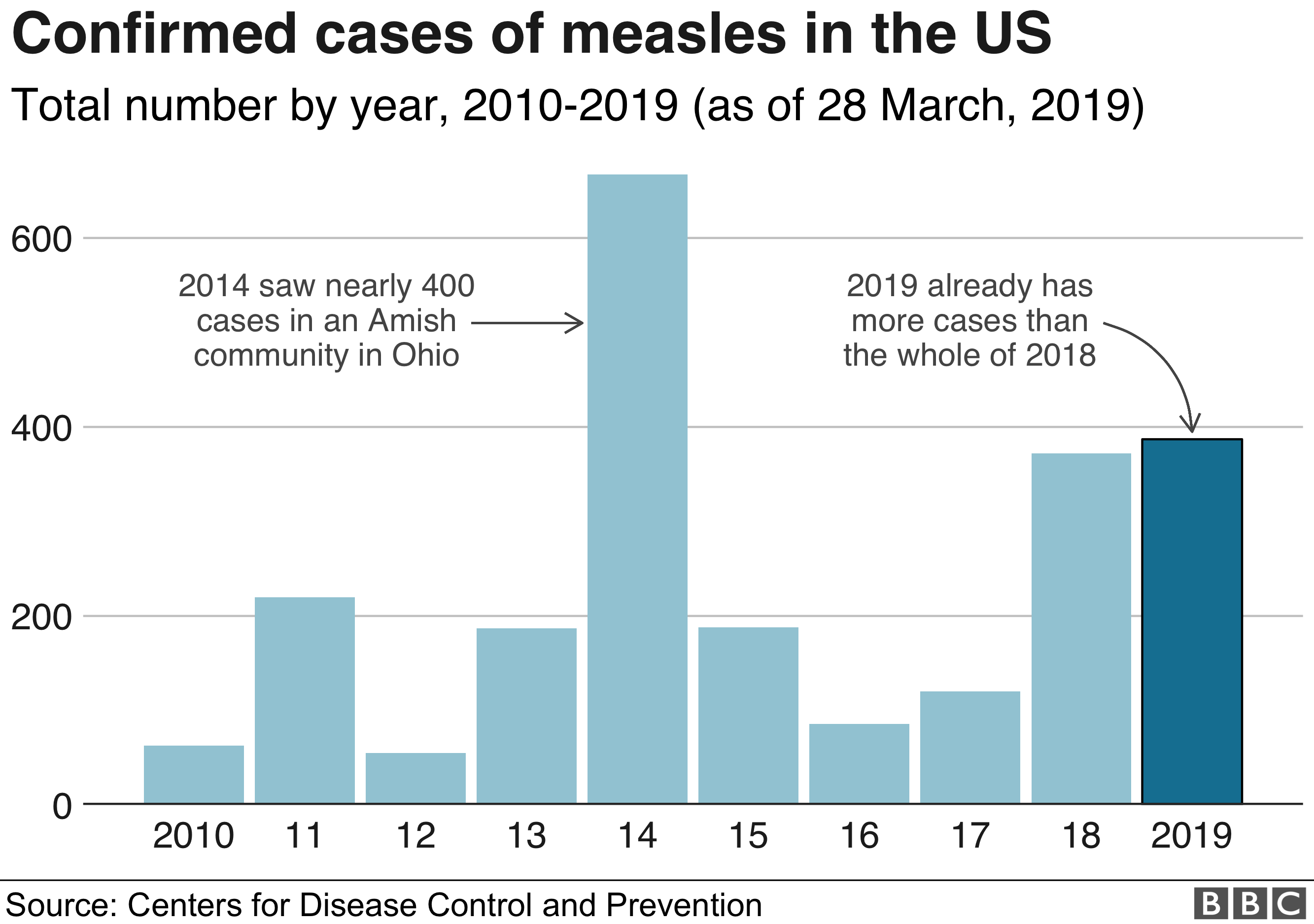
Table of Contents
The Impact of the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The MMR vaccine stands as a cornerstone in the fight against measles. Its effectiveness in preventing measles is exceptionally high, with studies consistently showing a greater than 97% efficacy rate after two doses. This high efficacy directly correlates with the decreased number of measles cases observed in the US. Vaccination rates have been a significant predictor of measles outbreaks.
- Data Correlation: Areas with higher MMR vaccination rates consistently demonstrate significantly lower incidence of measles. Conversely, communities with lower vaccination rates experience a greater risk of outbreaks.
- Challenges to Vaccination: Despite the vaccine's effectiveness, challenges remain. Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and unfounded concerns, continues to pose a threat. Furthermore, access to healthcare, particularly in underserved communities, remains a barrier to achieving universal vaccination.
- Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated: Statistical analyses consistently show that the overwhelming majority of measles cases occur in unvaccinated individuals. The protection offered by the MMR vaccine is clearly demonstrable.
- Herd Immunity: High vaccination rates create herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. This collective protection is crucial for maintaining a measles-free environment.
Improved Public Health Surveillance and Response
Enhanced public health infrastructure has played a vital role in the decline of measles cases. Modern surveillance systems enable rapid detection of outbreaks, allowing for swift and targeted interventions.
- Early Detection and Containment: Improved diagnostic capabilities and reporting mechanisms ensure quicker identification of measles cases, facilitating prompt containment measures.
- Contact Tracing and Quarantine: Effective contact tracing and quarantine strategies have been instrumental in preventing further spread within communities.
- Public Health Education: Public health campaigns have significantly improved awareness regarding measles symptoms, prevention, and the importance of vaccination. These campaigns actively combat misinformation and promote responsible health behaviors.
Changes in Immigration Policies and Global Measles Trends
US immigration policies, particularly vaccination requirements for entry, have contributed to preventing the importation of measles cases.
- Vaccination Requirements: Stricter vaccination requirements for immigrants and travelers help prevent the introduction and spread of measles from areas with higher incidence rates.
- Global Context: Global measles trends significantly influence the US. Outbreaks in other countries can lead to imported cases, highlighting the interconnectedness of global health.
- International Travel: International travel continues to be a potential pathway for measles importation, emphasizing the need for robust surveillance and prevention measures at points of entry.
- Global Vaccination Efforts: The success of global vaccination initiatives plays a crucial role in reducing the overall burden of measles worldwide, indirectly contributing to a decline in imported cases to the US.
Challenges and Future Outlook for Measles Eradication
While the decline in measles cases is encouraging, challenges persist. Pockets of low vaccination rates remain, creating vulnerabilities for outbreaks.
- Persistent Low Vaccination Rates: Addressing persistent pockets of low vaccination rates, particularly in certain communities, requires targeted interventions and addressing underlying concerns regarding vaccine safety and access.
- Potential for Resurgence: Waning immunity in older populations and reduced vaccination coverage in younger generations create a potential risk for resurgence. Sustained high vaccination rates are crucial for long-term protection.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Continued efforts are needed to address vaccine hesitancy through evidence-based communication, community engagement, and collaboration with healthcare providers.
- Continued Surveillance and Preparedness: Maintaining robust public health surveillance and preparedness is essential to detect and respond rapidly to any future outbreaks.
Conclusion: Maintaining the Decline of Measles Cases in the United States
The decline in measles cases in the United States is a testament to the effectiveness of the MMR vaccine, improved public health surveillance, and proactive prevention strategies. Sustaining this downward trend requires continued commitment to high vaccination rates, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and maintaining vigilance against potential outbreaks. To ensure the continued decline of measles cases in the United States and ultimately achieve eradication, learn more about the MMR vaccine and protect yourself and your community. Contact your healthcare provider to schedule your measles vaccination today. Protecting our collective health necessitates proactive engagement with public health initiatives aimed at eliminating measles completely.

Featured Posts
-
 Agassi Rios Uno De Mis Mas Grandes Rivales En Sudamerica
May 30, 2025
Agassi Rios Uno De Mis Mas Grandes Rivales En Sudamerica
May 30, 2025 -
 Alcarazs Comeback Victory Monte Carlo Masters Triumph
May 30, 2025
Alcarazs Comeback Victory Monte Carlo Masters Triumph
May 30, 2025 -
 New Discovery Strange Pulsating Object Unlike Anything Seen Before
May 30, 2025
New Discovery Strange Pulsating Object Unlike Anything Seen Before
May 30, 2025 -
 Casper Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him Roland Garros Match Against Nuno Borges
May 30, 2025
Casper Ruuds Knee Injury Costs Him Roland Garros Match Against Nuno Borges
May 30, 2025 -
 Kawasaki Z900 Dan Z900 Se Harga Resmi Di Bawah Rp 200 Juta
May 30, 2025
Kawasaki Z900 Dan Z900 Se Harga Resmi Di Bawah Rp 200 Juta
May 30, 2025
