ECB Rate Cuts: Economists Warn Against Delays
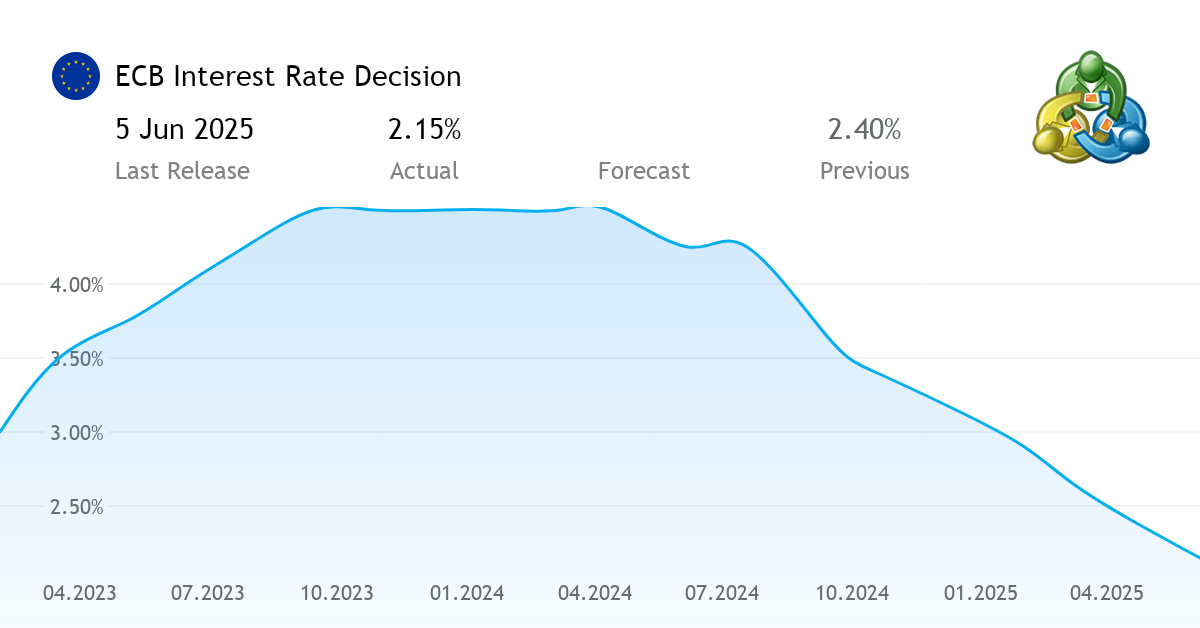
Table of Contents
H2: The Urgent Need for ECB Rate Cuts
Economists are increasingly convinced that immediate ECB intervention through monetary easing is crucial to avert a full-blown economic crisis. Current economic indicators paint a concerning picture. Inflation, while showing signs of easing, remains significantly above the ECB's target, eroding purchasing power and dampening consumer confidence. Simultaneously, GDP growth is slowing across the Eurozone, indicating a weakening economy. Unemployment figures, while relatively stable, could surge if the economic slowdown deepens. The risk of a deeper recession, coupled with a potential loss of investor confidence, necessitates swift action.
- High inflation eroding purchasing power: Persistent high inflation reduces consumer spending power, hindering economic growth.
- Slowing economic growth across the Eurozone: Several key Eurozone economies are showing signs of significant slowdown, impacting overall economic health.
- Risk of a deeper recession if action is delayed: Inaction risks a self-reinforcing cycle of economic contraction, leading to a prolonged and severe recession.
- Potential for a loss of investor confidence: Uncertainty surrounding the ECB's response can trigger capital flight and further destabilize the financial markets.
H2: Risks of Delaying ECB Rate Cuts
The potential consequences of delaying ECB rate cuts are severe. Procrastination risks exacerbating existing economic challenges and creating new ones. A prolonged period of economic stagnation could lead to a deflationary spiral, where falling prices discourage spending and investment, further depressing economic activity. This could destabilize financial markets, leading to increased market volatility and potentially impacting the stability of the Euro. Delaying necessary stimulus will negatively impact businesses, leading to decreased investment and job losses.
- Increased risk of prolonged recession: Delaying rate cuts increases the likelihood of a deeper and more prolonged recession.
- Potential for deflationary pressures: Stagnant demand in a high-inflation environment can lead to deflation, a very difficult situation to overcome.
- Negative impact on business investment and consumer spending: Uncertainty discourages both businesses and consumers from investing and spending.
- Weakening of the Euro: A weakening economy can put downward pressure on the Euro's exchange rate.
H2: Alternative Economic Policies and Their Limitations
While fiscal policy, such as increased government spending, and quantitative easing (liquidity injection) are alternative policy tools, they have limitations in the current context. Many Eurozone member states face fiscal constraints, limiting their ability to significantly increase government spending. Quantitative easing, while effective in injecting liquidity, has shown limited success in stimulating economic activity in the past, particularly in boosting investment and consumer confidence. Large-scale government borrowing also carries significant risks. In this situation, rate cuts offer a targeted and swift response mechanism.
- Fiscal constraints within Eurozone member states: Many countries have limited fiscal space for significant stimulus packages.
- Limitations of quantitative easing in boosting economic activity: QE has shown mixed results in stimulating economic activity and can lead to asset bubbles.
- Potential risks associated with large-scale government borrowing: Excessive borrowing can lead to higher interest rates and increased debt burden.
- Rate cuts as a targeted and swift response mechanism: Interest rate cuts offer a relatively quick and efficient way to stimulate economic activity.
H3: The Debate Surrounding the Magnitude of Rate Cuts
The debate surrounding the appropriate size of the ECB rate cuts is intense. Economists hold differing views on the optimal interest rate target and the effectiveness of various levels of monetary easing. Some advocate for aggressive rate cuts to swiftly stimulate the economy, while others prefer a more cautious approach to avoid unforeseen consequences such as excessive inflation or asset bubbles down the line. Accurate economic forecasting remains challenging, adding another layer of complexity to the decision-making process.
3. Conclusion
The evidence overwhelmingly supports the urgent need for the ECB to implement rate cuts. Delaying this crucial action carries significant risks, including a deeper recession, deflationary pressures, and increased financial market volatility. Alternative policies have limitations and may not be sufficient to address the current economic challenges. The time for decisive action on ECB rate cuts is now. Delaying these cuts risks a deeper economic crisis. Stay informed about further developments regarding ECB monetary policy and its implications for the Eurozone economy. The future economic health of the Eurozone depends on timely intervention.

 Iran Nuclear Deal And Israels Strategic Vulnerability
Iran Nuclear Deal And Israels Strategic Vulnerability
 101 Million In Dei Funding Eliminated Musks Cost Cutting Measures Highlighted By Trump
101 Million In Dei Funding Eliminated Musks Cost Cutting Measures Highlighted By Trump
 Trump And Musk Oval Office Press Conference Scheduled For Friday
Trump And Musk Oval Office Press Conference Scheduled For Friday
 Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Everything We Know
Tudor Pelagos Fxd Chrono Pink Release Everything We Know
 Detroit Anticipates 150 000 Visitors For Busy Memorial Day Weekend
Detroit Anticipates 150 000 Visitors For Busy Memorial Day Weekend
