Economists Forecast Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts In Response To Tariff Job Losses
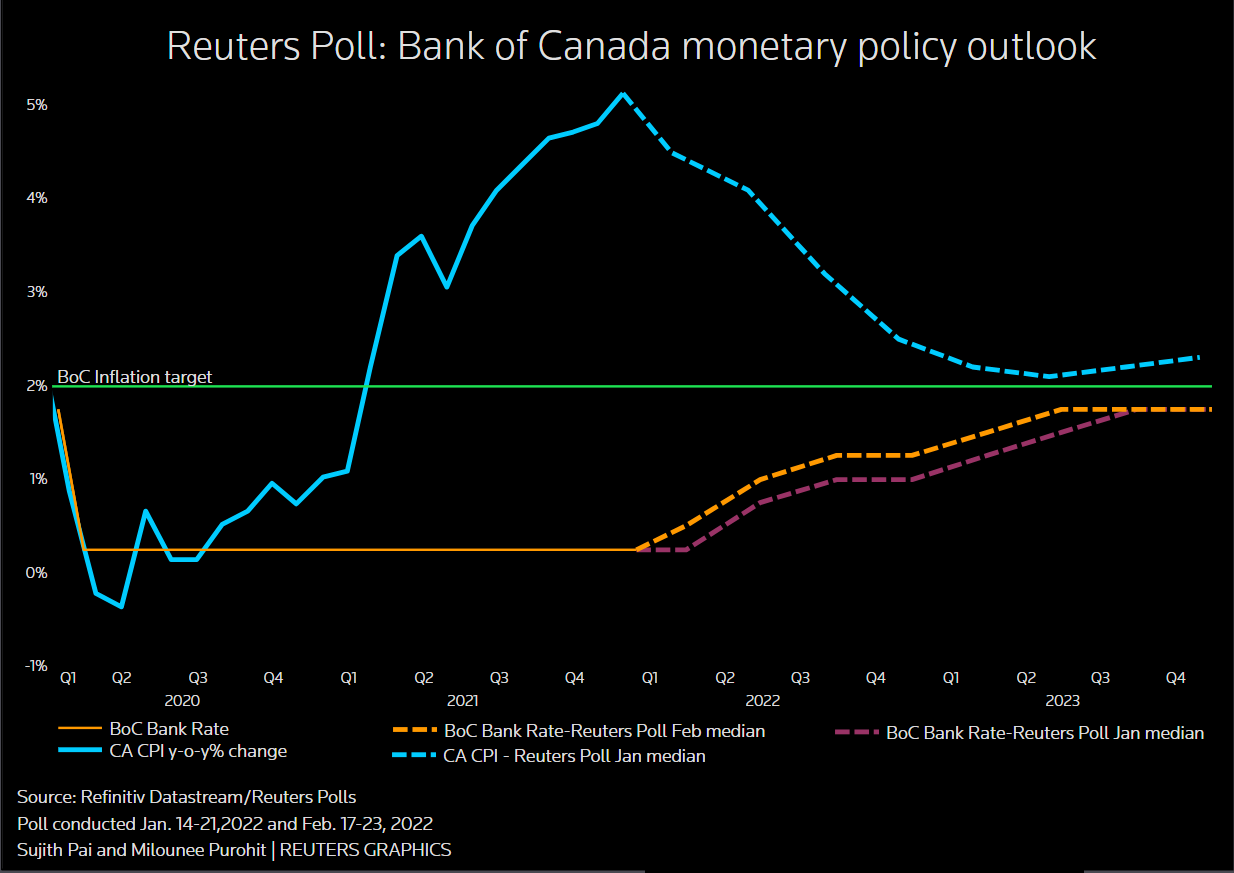
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on Canadian Employment
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, directly impact Canadian employment in several key sectors. The increased cost of imported materials and goods makes Canadian products less competitive globally, leading to reduced exports and potentially factory closures. This effect is particularly pronounced in industries heavily reliant on imports, such as:
- Manufacturing: Companies facing higher input costs may reduce production, leading to layoffs and plant closures. The automotive and steel industries, for example, are particularly vulnerable.
- Agriculture: Tariffs on agricultural products can severely impact farmers' ability to export their goods, resulting in decreased revenue and potential job losses across the agricultural value chain.
The impact isn't limited to these directly affected sectors. The ripple effect extends throughout the economy. Job losses in manufacturing, for instance, lead to reduced consumer spending, impacting service industries and creating a domino effect of economic hardship. Keywords: Tariff impact, job market, employment rate, Canadian workforce, specific sectors affected. Statistics Canada data on sector-specific employment changes following tariff implementations will provide further quantitative support.
Inflationary Pressures and the Bank of Canada's Mandate
Tariffs directly contribute to inflationary pressures. Increased import costs are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for goods and services. This erosion of purchasing power directly affects the Bank of Canada's primary mandate: maintaining price stability and controlling inflation. The Bank of Canada's target inflation rate is typically around 2%. If tariffs push inflation significantly above this target, the Bank may feel compelled to intervene through monetary policy adjustments. Keywords: Inflation rate, price stability, Bank of Canada mandate, monetary policy, interest rate targets. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) will be a key indicator to watch in this context.
Economic Slowdown and the Need for Stimulus
The combined effect of tariff-induced job losses and rising inflation is a significant threat to economic growth. A decline in consumer confidence, coupled with reduced investment and potentially reduced GDP growth, could signal an economic slowdown or even a recession. To counter this, the Bank of Canada might implement stimulative monetary policy, including rate cuts. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers, encouraging investment and spending, ultimately boosting economic activity. Keywords: Economic growth, GDP, recession, stimulus package, monetary easing, economic indicators. Monitoring key economic indicators like GDP growth and consumer spending will be crucial in assessing the need for stimulus.
Expert Opinions and Market Predictions
Leading economists and financial analysts are increasingly vocal about the likelihood of Bank of Canada rate cuts. Many predict that the central bank will respond to the economic pressures created by tariffs with a series of interest rate reductions. While the timing and magnitude of these cuts remain subject to debate, the general consensus points towards a loosening of monetary policy. For instance, [Quote from a prominent economist on the expected rate cuts]. The market is already anticipating potential rate cuts, reflected in fluctuations in the Canadian dollar and bond yields. Keywords: Economist predictions, market analysis, financial forecasts, rate cut expectations.
Potential Government Interventions Beyond Rate Cuts
The Bank of Canada's rate cuts are likely to be complemented by government interventions. Fiscal policies, such as targeted retraining programs for workers displaced by tariff-related job losses, and financial aid packages for struggling businesses, could help cushion the blow. These initiatives would work in tandem with the Bank's monetary policy to provide a comprehensive approach to economic stabilization. Keywords: Government intervention, fiscal policy, economic support, job creation initiatives. The government’s budget and subsequent policy announcements will be crucial in this regard.
Conclusion: Bank of Canada Rate Cuts: A Necessary Response to Tariff-Induced Job Losses?
In summary, the confluence of tariff-induced job losses, inflationary pressures, and the potential for an economic slowdown strongly suggests that the Bank of Canada will likely implement rate cuts. Economists' forecasts point to this as a necessary response to mitigate the negative consequences of tariffs on the Canadian economy. The impact of these rate cuts remains to be seen, but they represent a key tool in navigating the challenges posed by the current economic climate. To understand the evolving situation and the impact of Bank of Canada decisions, stay informed by following reputable financial news sources and carefully analyzing the Bank's official statements and economic data releases. Understanding Bank of Canada rate cuts and their implications is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Severe Hailstorms Cause Damage To Pools And Gardens
May 12, 2025
Severe Hailstorms Cause Damage To Pools And Gardens
May 12, 2025 -
 Doom The Dark Ages Launch Times A Global Countdown
May 12, 2025
Doom The Dark Ages Launch Times A Global Countdown
May 12, 2025 -
 Nba Betting Cavaliers Vs Knicks Odds And Prediction February 21st
May 12, 2025
Nba Betting Cavaliers Vs Knicks Odds And Prediction February 21st
May 12, 2025 -
 Sekret Pokhudeniya Dzhessiki Simpson Ee Put K Novoy Figure
May 12, 2025
Sekret Pokhudeniya Dzhessiki Simpson Ee Put K Novoy Figure
May 12, 2025 -
 Le Parcours De Jose Aldo Une Lecon D Adaptation Et De Perseverance
May 12, 2025
Le Parcours De Jose Aldo Une Lecon D Adaptation Et De Perseverance
May 12, 2025
