End Of An Era: Justice Department Concludes Louisiana School Desegregation Case
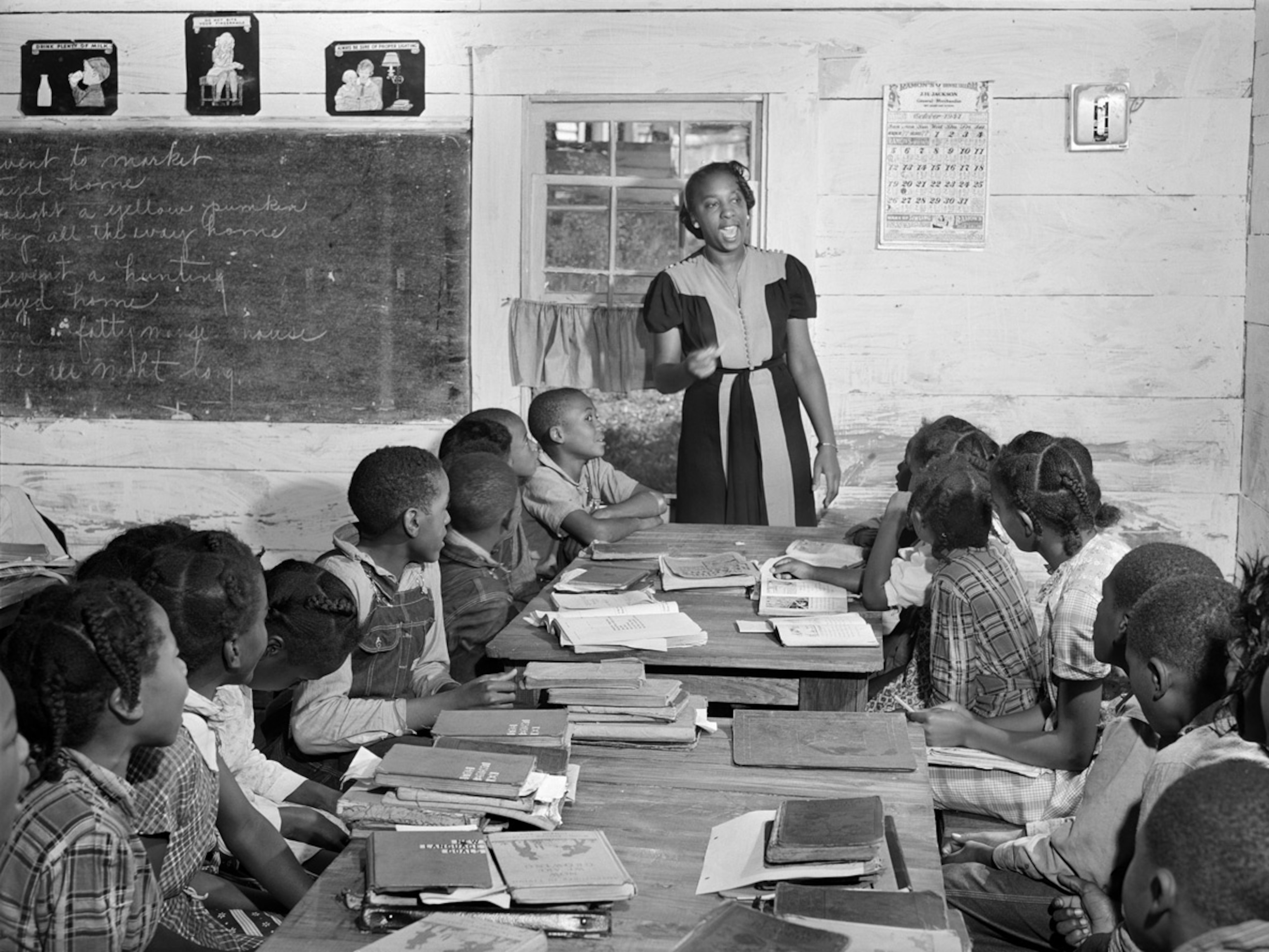

Table of Contents
The History of the Louisiana School Desegregation Case
The fight for desegregation in Louisiana schools has been a long and arduous journey, marked by significant legal challenges and setbacks. The roots of this particular case stretch back to the aftermath of Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which declared state-sponsored segregation in public schools unconstitutional. However, implementation was far from swift or seamless in Louisiana, leading to protracted legal battles to enforce the landmark Supreme Court decision.
- Year of initial lawsuit filing: While pinpointing the exact "initial" lawsuit is complex due to numerous related cases, significant legal action began in the late 1960s and early 1970s, focusing on specific school districts' resistance to integration.
- Key rulings and appeals: Several key court rulings throughout the decades shaped the trajectory of the desegregation efforts, including appeals to federal courts and even the Supreme Court. These rulings often dealt with issues of busing, school district restructuring, and the ongoing monitoring of integration progress.
- Significant figures involved: The case involved numerous key players, including federal judges, attorneys representing the state and plaintiffs, and civil rights activists who played a crucial role in pushing for desegregation.
- Major obstacles encountered during the desegregation process: Obstacles included resistance from some school districts, lack of funding for equitable resources in previously underserved schools, and deeply ingrained social and cultural prejudices. White flight to private schools was also a significant challenge.
- Mention any specific school districts involved: Specific districts heavily involved in this protracted legal battle varied over time, but often included those with a history of significant racial imbalance.
The Justice Department's Role in the Case
The Justice Department (DOJ) played a critical role throughout the Louisiana school desegregation case. Their involvement encompassed enforcing court orders, monitoring school districts' compliance, and intervening when necessary to ensure progress toward integration. This oversight involved years of monitoring and enforcement actions.
- Specific actions taken by the DOJ to enforce desegregation: The DOJ utilized various methods, including filing motions to compel compliance, initiating contempt proceedings against non-compliant districts, and working collaboratively with local authorities to implement desegregation plans.
- Monitoring methods used: The DOJ used data analysis to track student demographics, teacher assignments, and resource allocation across school districts. Site visits were also conducted to observe school environments and assess compliance with court orders firsthand.
- Reasons for the Justice Department's decision to conclude the case: The decision to conclude the case reflects a determination that sufficient progress has been made towards desegregation and that the ongoing involvement of the DOJ is no longer necessary to ensure continued compliance. This does not, however, imply that the fight for educational equity is over.
Implications and Future of Louisiana Schools
The conclusion of this long-standing school desegregation case has profound implications for Louisiana's education system. While it marks a formal end to federal oversight, the challenge of achieving genuine racial equity remains.
- Potential for increased segregation in certain districts: There are concerns that without federal oversight, some districts might revert to patterns of de facto segregation, where racial segregation arises through housing patterns and other socioeconomic factors rather than official policy.
- Need for continued monitoring and support for diverse schools: Ongoing monitoring and support are essential to ensure that the progress achieved is sustained and that disparities in resources and educational opportunities are addressed.
- Opportunities for improved educational outcomes for all students: The conclusion of the case opens the opportunity to focus efforts on improving educational outcomes for all students, irrespective of race, by focusing on resource allocation and equitable funding.
- Role of state and local governments in maintaining desegregation efforts: State and local governments now bear the primary responsibility for ensuring that desegregation efforts continue and that any emerging challenges are met swiftly and effectively.
- Ongoing need for addressing systemic inequalities in education: Addressing systemic inequalities requires a multi-pronged approach that tackles issues beyond mere school assignment, including disparities in access to quality teachers, advanced coursework, and extra-curricular activities.
The Ongoing Fight for Educational Equity
The Louisiana school desegregation case is a microcosm of the larger national conversation surrounding racial equity in education. The fight for true educational equality is far from over. While this case concludes a specific chapter, the broader struggle demands continued advocacy, systemic change, and a relentless commitment to ensuring all students have equal access to a quality education, regardless of race or socioeconomic background. This requires ongoing dialogue, engagement, and policy reforms at all levels of government.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's conclusion of the Louisiana school desegregation case marks a significant, albeit bittersweet, milestone. While it signifies a formal end to decades of legal battles, the fight for genuine racial equality in Louisiana schools remains an ongoing process. Continued vigilance and proactive efforts are crucial to ensure that the progress made is maintained and further advancements are achieved. Understanding the history and implications of the Louisiana school desegregation case is critical to fostering a future where all students have equitable access to quality education. Stay informed about ongoing efforts to ensure school integration and continue the conversation about Louisiana school desegregation and its impact on the future of education. The legacy of this case must serve as a catalyst for continued progress towards true educational equity for all students in Louisiana.

Featured Posts
-
 Problemen Met Enexis Aansluitingen Meer Dan 1000 Limburgse Bedrijven Wachten
May 02, 2025
Problemen Met Enexis Aansluitingen Meer Dan 1000 Limburgse Bedrijven Wachten
May 02, 2025 -
 Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Jan 6 Falsehoods Alleged
May 02, 2025
Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Lawsuit Against Fox News Jan 6 Falsehoods Alleged
May 02, 2025 -
 Frimpong Talks Dismissed Liverpools Transfer Stance Explained
May 02, 2025
Frimpong Talks Dismissed Liverpools Transfer Stance Explained
May 02, 2025 -
 The Unpredictability Of Trumps Tariffs And Their Effect On Auto Production
May 02, 2025
The Unpredictability Of Trumps Tariffs And Their Effect On Auto Production
May 02, 2025 -
 The Fortnite Item Shop Update Thats Angering Players
May 02, 2025
The Fortnite Item Shop Update Thats Angering Players
May 02, 2025
