Export-Led Growth: Assessing China's Tariff Sensitivity
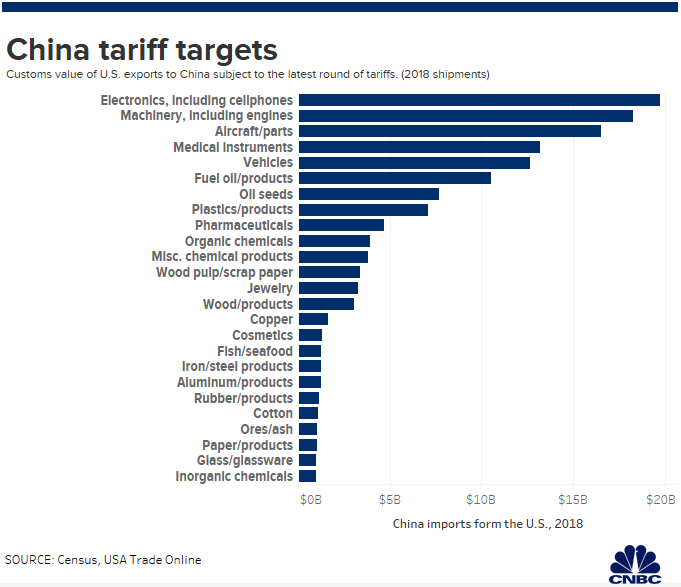
Table of Contents
China's Export Dependence and its Economic Structure
China's economic structure is heavily reliant on exports. For decades, export-led growth has been a cornerstone of its economic strategy, contributing significantly to GDP growth and employment. Key export sectors, such as electronics, textiles, machinery, and increasingly, high-tech manufacturing, have driven this growth. The country's massive trade surplus, a result of its substantial export volume, further underscores this dependence. Understanding this economic structure is critical to analyzing the impact of tariff sensitivity.
- Percentage of GDP attributed to exports over the past decade: While the exact percentage fluctuates yearly, exports consistently contributed a substantial portion (around 20% or more) to China's GDP over the past decade.
- Key export industries and their respective contributions: Electronics manufacturing alone accounts for a significant percentage of total exports, followed by textiles, machinery, and increasingly, high-value manufactured goods.
- Impact of export growth on employment figures: Millions of jobs across various sectors, from manufacturing to logistics and shipping, are directly or indirectly tied to export performance.
- Analysis of China's trade balance and surplus: China's persistent trade surplus highlights its strong export orientation and its position as a major player in global trade.
Impact of Tariffs on Key Chinese Export Sectors
The imposition of tariffs, particularly the trade war initiated by the US, significantly impacted several key Chinese export sectors. Import tariffs imposed by other countries, coupled with China's retaliatory tariffs, disrupted global supply chains and created uncertainty in the market. This led to price increases, decreased market share for some Chinese goods, and a slowdown in production in affected sectors. The impact varied across sectors; some, like electronics and agriculture, faced more significant challenges than others.
- Specific examples of tariff impacts on individual sectors (e.g., electronics, agriculture): Tariffs on electronics led to increased prices for consumer goods in importing countries, while tariffs on agricultural products disrupted supply chains and harmed Chinese farmers.
- Analysis of price changes and market share fluctuations: The imposition of tariffs led to observable price increases in affected sectors in both China and importing countries. Market share analysis revealed a drop in the global market share for some Chinese goods.
- Discussion of the effectiveness of retaliatory tariffs: While retaliatory tariffs aimed to leverage leverage against imposing countries, their effectiveness in mitigating the initial damage remains a subject of ongoing debate.
- Case studies of companies affected by tariffs: Numerous case studies highlight the struggles of Chinese companies affected by tariffs, illustrating the real-world consequences of trade disputes.
China's Strategies to Mitigate Tariff Sensitivity
In response to the challenges posed by tariff sensitivity, China has implemented several strategies to diversify its economy and reduce its reliance on exports. These include boosting domestic consumption, encouraging technological innovation, attracting foreign direct investment (FDI), and forging regional trade agreements. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) also plays a vital role, aiming to create new trade routes and enhance connectivity.
- Government policies aimed at stimulating domestic demand: The government has implemented various measures to increase domestic consumption, such as raising disposable incomes and investing in infrastructure.
- Investments in research and development and technological advancement: Significant investment in R&D aims to move China up the value chain, reducing its reliance on low-cost manufacturing.
- Progress in attracting foreign investment: China continues to attract significant foreign investment, particularly in high-tech sectors, further diversifying its economy.
- The impact and effectiveness of regional trade agreements: Agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) offer new opportunities to reduce dependence on individual markets.
The Role of the World Trade Organization (WTO)
The WTO plays a crucial role in regulating international trade and providing a framework for resolving trade disputes. Its rules and dispute settlement mechanisms are designed to promote free trade and prevent protectionist measures. However, the effectiveness of the WTO in addressing disputes like the US-China trade war is a subject of ongoing debate, highlighting the challenges of multilateralism in the face of geopolitical tensions. China's engagement with the WTO remains critical in navigating global trade rules and addressing tariff-related issues.
Conclusion
China's export-led growth model, while remarkably successful, has demonstrated significant vulnerability to tariff sensitivity. The impact of tariffs on key export sectors highlights the risks associated with over-reliance on global markets. However, China's proactive strategies to diversify its economy, boost domestic demand, and foster technological innovation offer a path toward mitigating these risks. Further research and analysis are crucial to understanding the long-term effects of tariff sensitivity on China's economic trajectory. Understanding China's export-led growth strategy and its vulnerabilities is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Stay informed about developments in China's tariff sensitivity and the evolving dynamics of global trade relations.

Featured Posts
-
 The English Leaders Debate 5 Important Economic Conclusions
Apr 22, 2025
The English Leaders Debate 5 Important Economic Conclusions
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Fsus Post Shooting Class Resumption Plan A Controversial Decision
Apr 22, 2025
Fsus Post Shooting Class Resumption Plan A Controversial Decision
Apr 22, 2025 -
 La Palisades Wildfires Which Celebrities Lost Their Homes
Apr 22, 2025
La Palisades Wildfires Which Celebrities Lost Their Homes
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Secret Service Closes Investigation Into White House Cocaine Discovery
Apr 22, 2025
Secret Service Closes Investigation Into White House Cocaine Discovery
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Saudi Aramco And Byd A New Ev Technology Partnership
Apr 22, 2025
Saudi Aramco And Byd A New Ev Technology Partnership
Apr 22, 2025
