Falling Demand For Electric Vehicles In Canada
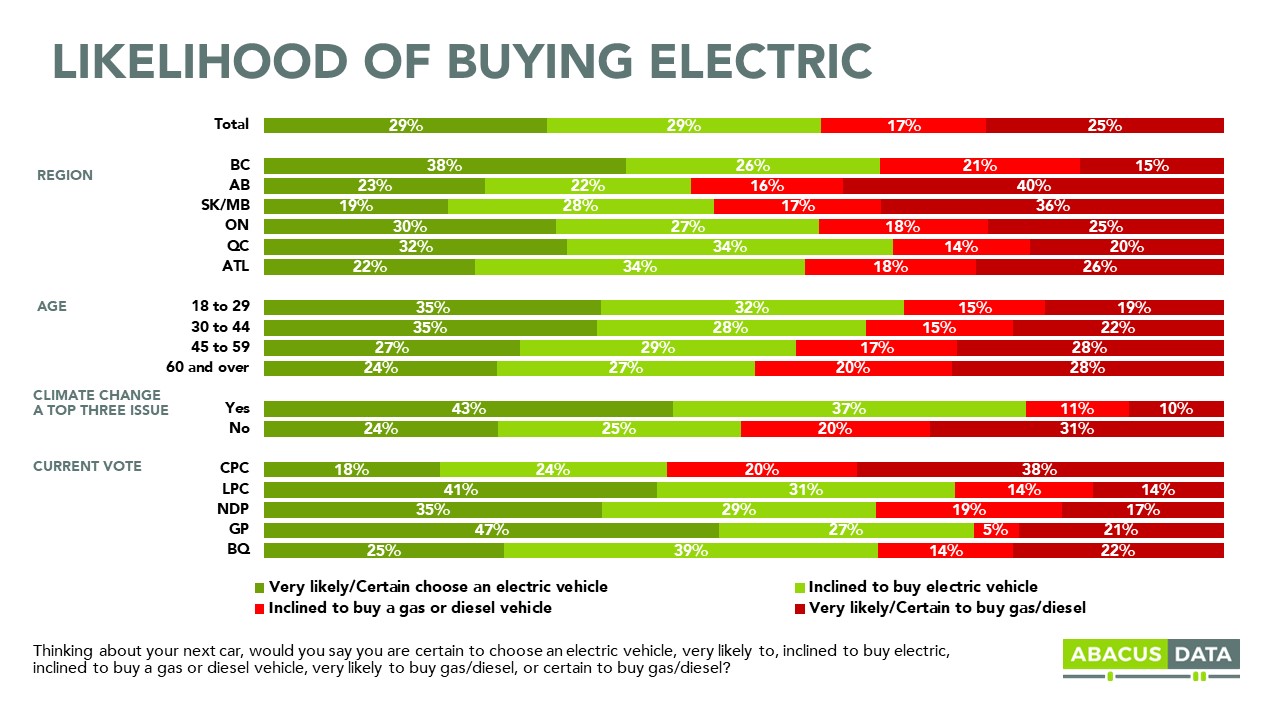
Table of Contents
Economic Factors Contributing to the Decline
Several economic headwinds are significantly impacting the affordability and desirability of electric vehicles in Canada.
Rising Inflation and Interest Rates
The current economic climate, characterized by soaring inflation and subsequent interest rate hikes by the Bank of Canada, is making it significantly more expensive for Canadians to purchase big-ticket items, including electric vehicles.
- Increased loan payments: Higher interest rates translate to substantially larger monthly payments for EV loans, making them less accessible to many potential buyers.
- Reduced disposable income: Inflation is eroding purchasing power, forcing consumers to prioritize essential spending over discretionary purchases like EVs.
- Prioritization of essential spending: With the rising cost of groceries, housing, and other necessities, many Canadians are simply unable to afford the upfront cost of an EV, regardless of potential long-term savings.
Statistics Canada reports inflation exceeding 7% in 2022, the highest rate in decades. Concurrently, the Bank of Canada increased its key interest rate multiple times, impacting borrowing costs across the board. This economic environment makes it harder for consumers to justify the higher price tag associated with electric vehicle ownership.
High Upfront Costs of EVs
The significant price difference between EVs and gasoline-powered vehicles remains a substantial barrier to entry for many Canadian consumers.
- Comparison of average EV prices vs. gasoline car prices: While the cost of gasoline vehicles has also increased, EVs generally command a considerably higher upfront price, often exceeding $40,000 even with government incentives.
- Government incentives and their effectiveness: While government incentives, such as rebates and tax credits, exist to lessen the financial burden, they are often insufficient to bridge the gap entirely for many potential buyers.
- Lack of affordable EV options: The market still lacks a wide selection of affordable EVs, leaving many consumers with limited choices.
Statistics from the Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers' Association (CVMA) show the average price of a new EV significantly exceeds that of a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle. This disparity remains a key obstacle to widespread EV adoption.
Uncertainty in the Used EV Market
The lack of clarity and uncertainty surrounding the resale value of used EVs also contributes to consumer hesitancy.
- Depreciation rates: EVs, particularly those with older battery technologies, can experience faster depreciation compared to gasoline cars. This concern affects consumers' willingness to invest heavily in a vehicle with potentially lower resale value.
- Battery life concerns: The lifespan and eventual replacement cost of EV batteries remain a source of anxiety for many potential buyers.
- Lack of readily available parts: The repair and maintenance of EVs can sometimes be more challenging due to limited parts availability and specialized expertise.
Infrastructure Challenges Hampering EV Adoption
Beyond the economic considerations, deficiencies in Canada's EV charging infrastructure are also hindering broader adoption.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
The lack of widespread and reliable charging stations, particularly outside of major urban centres, is a significant impediment.
- Statistics on charging station availability in urban vs. rural areas: While charging infrastructure is improving in urban areas, rural communities often lag far behind, creating a significant "range anxiety" barrier for potential EV owners.
- Range anxiety concerns: The fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station prevents many drivers from considering EVs, especially for long-distance travel.
- Charging times and costs: The time required to fully charge an EV and the associated costs also contribute to concerns about convenience and affordability.
Inconsistent Charging Standards
The lack of standardization in EV charging connectors and protocols adds further complexity and confusion for potential buyers.
- Different connector types: The proliferation of various charging connector types across different EV models creates incompatibility issues and limits the usability of charging stations.
- Lack of standardization: The absence of a widely adopted standard creates uncertainty and inconvenience for drivers.
- Difficulties with interoperability: The inability to seamlessly use different charging networks adds to the overall complexity and reduces consumer confidence.
Shifting Consumer Preferences and Perceptions
Beyond economic and infrastructure limitations, shifting consumer preferences and perceptions also play a crucial role in the declining EV demand.
Concerns about Battery Life and Range
Concerns remain about the longevity of EV batteries and their limited driving range, especially in colder Canadian climates.
- Battery lifespan: The actual lifespan of an EV battery and its impact on the vehicle's overall performance remains a key concern for many consumers.
- Range anxiety in different weather conditions: Cold weather significantly reduces the effective range of many EVs, adding to range anxiety in many parts of Canada.
- Myths vs. realities: Many misconceptions surrounding EV battery technology and performance persist, hindering informed decision-making.
Lack of Awareness and Education
A lack of adequate consumer education regarding the benefits, practicalities, and long-term cost-effectiveness of EV ownership further impedes wider adoption.
- Government initiatives to promote EV adoption: While the government is actively promoting EV adoption, these initiatives need to be more comprehensive and effective in reaching a broader audience.
- Educational campaigns: Targeted educational campaigns are needed to address misconceptions and highlight the benefits of EVs.
- Misconceptions surrounding EV technology: Many myths and misunderstandings surrounding charging times, battery life, and overall maintenance costs remain prevalent, hindering consumer confidence.
Conclusion
The falling demand for electric vehicles in Canada is a multifaceted issue, stemming from a combination of economic headwinds, infrastructure limitations, and evolving consumer perceptions. Addressing the high upfront costs, improving charging infrastructure, clarifying charging standards, and effectively addressing consumer concerns surrounding battery life and range are crucial steps towards achieving the ambitious targets for EV adoption in Canada.
Understanding the factors contributing to the falling demand for electric vehicles in Canada is crucial. Learn more about the challenges and opportunities in this evolving market and contribute to the discussion on how to overcome these obstacles to foster a successful transition to electric mobility. The future of sustainable transportation in Canada depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Nosferatu The Vampyre A Now Toronto Detour Worth Taking
Apr 27, 2025
Nosferatu The Vampyre A Now Toronto Detour Worth Taking
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Former Dubai Champ Svitolinas Strong Us Open Start
Apr 27, 2025
Former Dubai Champ Svitolinas Strong Us Open Start
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ariana Grandes Dramatic Hair And Tattoo Transformation A Professionals Perspective
Apr 27, 2025
Ariana Grandes Dramatic Hair And Tattoo Transformation A Professionals Perspective
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Controversial Autism Study Head An Anti Vaxxers Appointment
Apr 27, 2025
Controversial Autism Study Head An Anti Vaxxers Appointment
Apr 27, 2025 -
 World No 1 Sinners Doping Case Resolved
Apr 27, 2025
World No 1 Sinners Doping Case Resolved
Apr 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Proposed Starbucks Raise Rejected By Union
Apr 28, 2025
Proposed Starbucks Raise Rejected By Union
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Starbucks Unions Rejection Of Companys Wage Guarantee
Apr 28, 2025
Starbucks Unions Rejection Of Companys Wage Guarantee
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Unionized Starbucks Employees Turn Down Companys Pay Raise Proposal
Apr 28, 2025
Unionized Starbucks Employees Turn Down Companys Pay Raise Proposal
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Pace Of Rent Increases Slows In Metro Vancouver Housing Costs Still High
Apr 28, 2025
Pace Of Rent Increases Slows In Metro Vancouver Housing Costs Still High
Apr 28, 2025 -
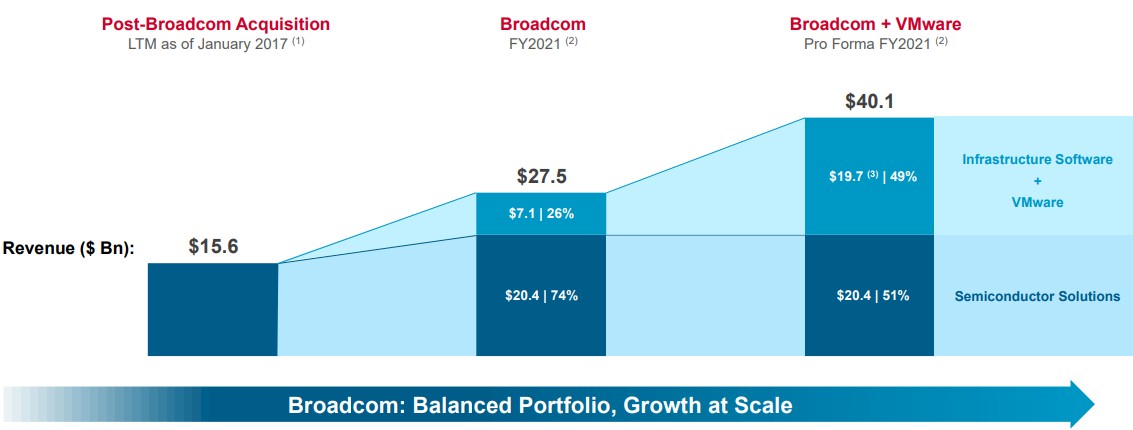 The V Mware Price Shock At And T Highlights A 1 050 Increase From Broadcom
Apr 28, 2025
The V Mware Price Shock At And T Highlights A 1 050 Increase From Broadcom
Apr 28, 2025
