G-7 To Discuss De Minimis Tariff Thresholds For Chinese Goods
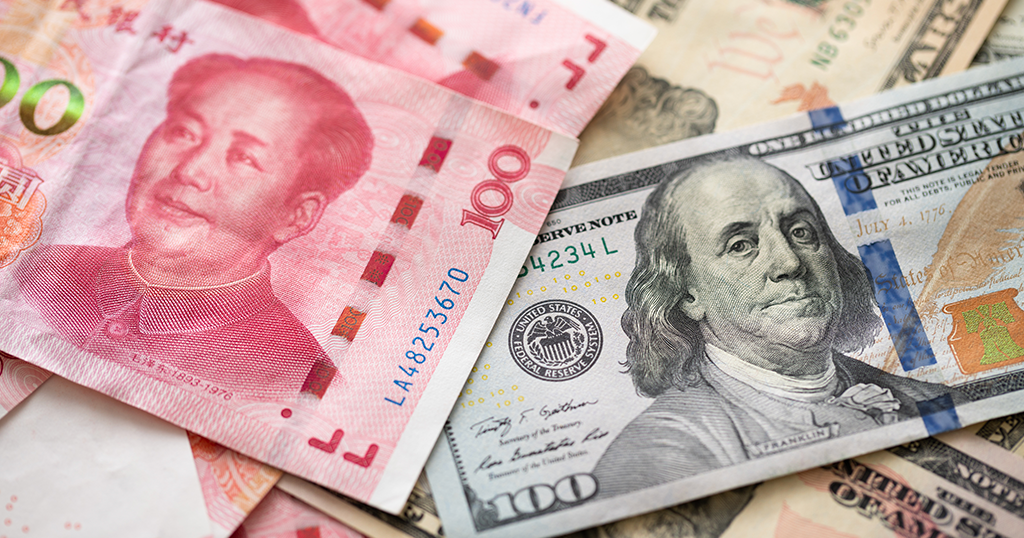

Table of Contents
Understanding De Minimis Tariff Thresholds
Definition and Importance
"De minimis," in the context of international trade, refers to the value below which imported goods are exempt from import duties or other tariffs. These thresholds significantly impact the ease and cost of importing goods, particularly for smaller businesses and online retailers. Currently, these thresholds vary considerably across G7 nations, creating an uneven playing field for importers. For instance, a lower de minimis threshold makes it easier for businesses in countries with lower thresholds to import low-value goods from China, giving them a competitive edge over businesses in countries with higher thresholds. This disparity directly affects the competitiveness of domestic industries and influences consumer pricing.
- Current Thresholds: The current de minimis thresholds vary widely among G7 countries, ranging from a few dollars to several hundred dollars per shipment. This inconsistency contributes to unequal competition among businesses.
- Impact on Small Businesses & E-commerce: Lower thresholds greatly benefit small businesses and e-commerce platforms reliant on importing inexpensive goods from China. These businesses often operate on thin margins and benefit from lower import costs. Higher thresholds can cripple their competitiveness.
- Competitive Advantage: Countries with lower de minimis thresholds for Chinese goods enjoy a competitive advantage in attracting both importers and consumers, potentially leading to market share gains.
The G7's Consideration of Changes
Reasons for the Discussion
The G7's review of de minimis thresholds for Chinese goods is driven by several factors:
-
Unfair Trade Practices: Concerns persist about potential unfair trade practices and the need for a more balanced trade relationship with China.
-
Domestic Industry Pressure: Domestic industries in G7 countries have lobbied for adjustments to protect themselves from cheaper imports from China.
-
Level Playing Field: The current inconsistencies in de minimis thresholds create an uneven playing field globally, demanding a more harmonized approach.
-
Goods Affected: The review specifically targets numerous goods imported from China, including electronics, clothing, textiles, toys, and numerous other consumer products.
-
Potential Scenarios: The G7 could raise, lower, or maintain the current thresholds. Each outcome will have far-reaching implications. Raising them could protect domestic industries but might increase consumer prices. Lowering them could boost competitiveness but could lead to concerns about unfair trade practices.
-
Bilateral Trade Relations: The G7's decision will inevitably affect bilateral trade relations between China and its member nations, potentially leading to negotiations and potential trade disputes.
Potential Impacts of Changing Thresholds
Impact on Businesses
Changes to de minimis tariff thresholds will have a significant impact on businesses:
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses will need to adapt their pricing strategies to reflect potential changes in import costs.
- Supply Chains: Businesses may need to restructure their supply chains to adapt to new tariff implications, possibly sourcing from alternative countries.
- Profit Margins: Profit margins will likely be impacted by changes in import costs, potentially requiring businesses to reassess their operational efficiency.
- Consumer Prices: Changes in import costs can translate directly to changes in consumer prices, affecting demand and purchasing power.
Impact on Consumers
The effects on consumers will be equally significant:
- Price Fluctuation: Consumers can expect price fluctuations for various goods imported from China, depending on the G7's decision.
- Availability of Goods: Changes in thresholds could impact the availability of affordable goods, potentially reducing consumer choice.
- Smuggling and Grey Market: Higher thresholds may encourage smuggling and grey market activities, undermining legitimate businesses.
Conclusion
The G7's decision regarding de minimis tariff thresholds for Chinese goods is a critical juncture for global trade. The current inconsistencies create an uneven playing field, affecting businesses of all sizes and consumers alike. The potential impacts—on pricing, supply chains, and even consumer choice—are substantial and far-reaching. The review underscores the complex interplay between trade policy, economic competitiveness, and international relations. To stay informed about the final decision and its ongoing implications, subscribe to trade publications and follow relevant news sources closely. The long-term impact of the G7’s decisions on de minimis tariff thresholds and Chinese goods will undoubtedly shape the future of global commerce.

Featured Posts
-
 Ai In Healthcare Key Findings From The Philips Future Health Index 2025
May 25, 2025
Ai In Healthcare Key Findings From The Philips Future Health Index 2025
May 25, 2025 -
 Lion Kings Land Of Sometimes Tim Rices Lyrical Contribution
May 25, 2025
Lion Kings Land Of Sometimes Tim Rices Lyrical Contribution
May 25, 2025 -
 La Primera Comunion De Los Gemelos De Alberto De Monaco
May 25, 2025
La Primera Comunion De Los Gemelos De Alberto De Monaco
May 25, 2025 -
 From 0 6 To Victory Swiateks Resilience Earns Madrid Semifinal Spot Against Gauff
May 25, 2025
From 0 6 To Victory Swiateks Resilience Earns Madrid Semifinal Spot Against Gauff
May 25, 2025 -
 90mph Refueling Stunt During Police Chase Texting Duos Reckless Escape
May 25, 2025
90mph Refueling Stunt During Police Chase Texting Duos Reckless Escape
May 25, 2025
