Gas Prices Surge: Nearly 20-Cent Increase Per Gallon
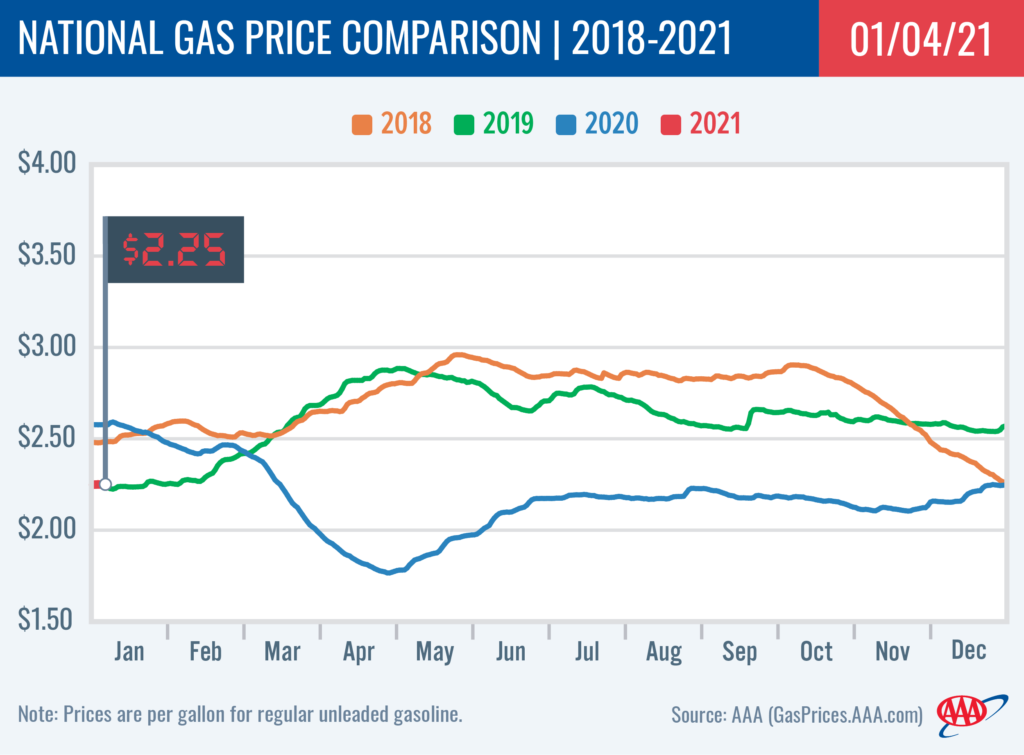
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the Recent Gas Price Surge
Several interconnected factors have contributed to the recent near 20-cent gas price increase. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to anticipating future price fluctuations and mitigating their impact.
Increased Global Demand
The global economy's recovery from the pandemic has led to a surge in demand for oil. This increased demand, coupled with robust economic growth in several key regions, has outpaced the current supply, pushing prices higher.
- Strong economic recovery in Asia and Europe: Post-pandemic travel and industrial activity have significantly boosted oil consumption.
- Increased travel demand: As travel restrictions ease, air travel and road trips are increasing, further fueling the demand for gasoline and other petroleum products.
- Geopolitical instability: Ongoing conflicts and uncertainties in various parts of the world disrupt supply chains and contribute to price volatility. The war in Ukraine, for example, significantly impacted global energy markets. Data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) shows a clear correlation between geopolitical events and oil price fluctuations. [Link to IEA data]
Reduced Oil Production
OPEC+ (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies), a significant player in global oil production, has implemented production quotas. These quotas, combined with unplanned maintenance shutdowns and unexpected supply disruptions from various producers, have constrained the overall supply of crude oil.
- OPEC+ production quotas: Deliberate limitations on oil production have tightened the market and contributed to higher prices.
- Maintenance shutdowns: Planned and unplanned outages at oil production facilities reduce the available supply and create price pressures.
- Unexpected supply disruptions: Natural disasters, political instability, and other unforeseen events can significantly impact oil production and exacerbate price increases. [Link to OPEC+ production data]
Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical events are major drivers of oil price volatility. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, for instance, has created significant uncertainty in global energy markets, leading to higher prices.
- Impact of sanctions: Sanctions imposed on oil-producing nations can disrupt supply chains and limit the availability of oil.
- Disruptions to supply routes: Conflicts and political instability can interrupt the transportation of oil, leading to shortages and higher prices.
- Uncertainty in global energy markets: Geopolitical tensions create uncertainty, which investors often respond to by increasing oil prices as a hedge against risk. [Link to relevant news articles on geopolitical impacts on oil prices]
Refinery Issues and Capacity Constraints
Refinery maintenance and limited capacity play a role in affecting the supply of gasoline. Planned and unplanned refinery outages, coupled with existing capacity constraints, can restrict the amount of gasoline produced, contributing to higher prices at the pump.
- Planned and unplanned refinery outages: Regular maintenance and unexpected shutdowns at refineries can temporarily reduce gasoline production.
- Limited refining capacity: Existing refining capacity might not be sufficient to meet the current demand, leading to supply shortages and price increases. [Link to news articles on specific refinery issues, if available]
Impact of the Gas Price Surge on Consumers and the Economy
The near 20-cent gas price increase has wide-ranging consequences for consumers and the economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate to increased transportation costs for individuals and businesses.
- Higher commuting costs: Daily commutes become more expensive, impacting household budgets.
- Increased prices for goods: Higher transportation costs for businesses lead to increased prices for consumers across various goods and services.
- Impact on small businesses: Small businesses reliant on transportation, such as delivery services, are particularly vulnerable to higher fuel costs.
Inflationary Pressure
Increased fuel costs contribute significantly to overall inflation.
- Connection between gas prices and CPI: Higher gas prices directly impact the Consumer Price Index (CPI), a key measure of inflation.
- Impact on consumer spending: Higher gas prices reduce disposable income, potentially impacting consumer spending on other goods and services.
- Potential for wage increases to compensate: To offset the impact of higher fuel costs, workers may demand wage increases, potentially leading to a wage-price spiral. [Link to CPI data and charts showing the relationship between gas prices and inflation]
Impact on Different Demographics
The impact of the gas price increase is not felt equally across all demographics.
- Higher percentage of income spent on fuel by lower-income families: Lower-income households spend a larger proportion of their income on fuel, making them more vulnerable to price increases.
- Impact on trucking and delivery industries: The trucking industry, a cornerstone of the supply chain, faces substantial cost increases, which can further impact the prices of goods. [Link to statistics on income distribution and fuel consumption]
What Can Consumers Do?
While the gas price surge is largely beyond individual control, consumers can take steps to mitigate its impact.
Fuel Efficiency Tips
Improving fuel economy can help reduce the impact of higher gas prices.
- Proper tire inflation: Maintaining correct tire pressure improves fuel efficiency.
- Regular vehicle maintenance: Regular servicing ensures optimal engine performance and fuel economy.
- Driving habits: Smooth acceleration and braking, avoiding aggressive driving, can significantly improve fuel efficiency.
- Choosing fuel-efficient vehicles: Consider fuel-efficient vehicles when purchasing a new car.
Alternatives to Driving
Reducing reliance on gasoline-powered vehicles can lessen the impact of price increases.
- Public transportation: Utilize public transport options whenever feasible.
- Cycling: Cycling is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative for short distances.
- Carpooling: Sharing rides with colleagues or friends reduces individual fuel consumption.
- Working from home: Working remotely, when possible, reduces commuting costs.
Monitoring Gas Prices
Staying informed about gas prices and finding the best deals can save money.
- Using gas price tracking apps: Many apps track real-time gas prices in your area.
- Comparing prices at different stations: Prices can vary significantly between gas stations, so comparison shopping is worthwhile.
- Utilizing loyalty programs: Gas station loyalty programs often offer discounts and rewards.
Conclusion
The near 20-cent gas price surge is a complex issue driven by increased global demand, reduced oil production, geopolitical factors, and refinery issues. This surge significantly impacts consumers and the economy, leading to increased transportation costs, inflationary pressure, and disproportionate effects on various demographics. Key takeaways include the need to understand the multifaceted causes of this price hike, its cascading effects on the economy, and the importance of adopting fuel-efficient practices and exploring alternative transportation options. Stay informed about fluctuating gas prices and take steps to manage their impact on your budget.

Featured Posts
-
 Turning Trash Into Treasure An Ai Powered Poop Podcast From Repetitive Documents
May 22, 2025
Turning Trash Into Treasure An Ai Powered Poop Podcast From Repetitive Documents
May 22, 2025 -
 The Latest Peppa Pig News Mummy Pig Announces Babys Gender
May 22, 2025
The Latest Peppa Pig News Mummy Pig Announces Babys Gender
May 22, 2025 -
 Adam Ramey Dropout Kings Vocalist Dies By Suicide At 31 Go Fund Me Launched
May 22, 2025
Adam Ramey Dropout Kings Vocalist Dies By Suicide At 31 Go Fund Me Launched
May 22, 2025 -
 The Impact Of The Hollywood Strike Actors And Writers Unite
May 22, 2025
The Impact Of The Hollywood Strike Actors And Writers Unite
May 22, 2025 -
 Experiencing Coldplay Live A Night Of Music Lights And Powerful Messages
May 22, 2025
Experiencing Coldplay Live A Night Of Music Lights And Powerful Messages
May 22, 2025
