Ghana's Mental Health: Challenges And Solutions To The Psychiatrist Deficit

Table of Contents
Ghana faces a significant challenge in providing adequate mental healthcare due to a severe shortage of psychiatrists. This critical shortage impacts access to vital psychiatric care for millions of Ghanaians, exacerbating the burden of mental illness within the country. This article explores the multifaceted issues contributing to this deficit and proposes potential solutions to improve the mental health landscape in Ghana. We will delve into the root causes of the problem, examine existing initiatives, and propose strategies for building a more robust and accessible mental health system, ensuring that every Ghanaian has access to the care they need.
H2: The Magnitude of the Psychiatrist Deficit in Ghana
H3: Current Statistics and Prevalence of Mental Illness
Ghana suffers from a stark deficiency in psychiatrists. The current psychiatrist-to-population ratio is alarmingly low compared to international standards recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). While precise figures vary depending on the source, it's clear that the number of trained psychiatrists is far below what's needed to meet the demands of the population. This shortage directly impacts access to mental healthcare, creating a significant gap in the provision of essential services.
- Psychiatrist-to-population ratio: Estimates suggest a ratio significantly lower than the WHO recommended minimum, leaving large segments of the population without access to specialized care. (Source: Insert citation from a reputable source like the Ghana Health Service or WHO report).
- Prevalence of mental illness: Studies indicate a high prevalence of common mental health disorders in Ghana, including depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. These conditions often go undiagnosed and untreated due to the lack of accessible psychiatric care. (Source: Insert citation from a reputable study on mental health prevalence in Ghana).
- Specific examples: (Insert real-world examples illustrating the prevalence of untreated mental illness).
H3: Impact on Access to Care
The psychiatrist shortage severely restricts access to crucial mental healthcare services. This limitation extends beyond urban areas, significantly impacting rural populations. The consequences are far-reaching:
- Delayed diagnosis and treatment: Individuals experiencing mental health crises often face lengthy delays in receiving appropriate diagnosis and treatment, leading to worsening symptoms and potentially life-threatening situations.
- Limited access to specialized services: Many Ghanaians lack access to specialized psychiatric care, including psychotherapy, medication management, and hospitalization, when necessary.
- Geographical disparities: The disparity in access to mental health services between urban and rural areas is vast, with rural communities often being the most underserved. Lack of transportation, limited awareness, and scarcity of trained professionals further complicate the situation.
- Example: (Include a real-life example illustrating the difficulty in accessing mental health services in Ghana).
H2: Underlying Causes of the Psychiatrist Shortage
H3: Lack of Training and Educational Opportunities
The limited number of psychiatric training programs and residency positions in Ghana is a key factor contributing to the psychiatrist shortage.
- Few training institutions: Only a limited number of medical schools in Ghana offer comprehensive psychiatric training programs.
- Insufficient residency positions: The number of available residency positions for aspiring psychiatrists is far too low to meet the country's needs.
- Brain drain: Qualified Ghanaian psychiatrists often seek better opportunities abroad, contributing to a further decline in the number of professionals available domestically.
- Lack of resources: Insufficient funding and outdated infrastructure hinder the effective training and development of future psychiatrists.
H3: Socioeconomic Factors
Poverty, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and deeply ingrained societal stigma surrounding mental illness significantly compound the problem.
- Poverty's impact: Many Ghanaians cannot afford the cost of mental healthcare, preventing them from seeking professional help even when services are available.
- Stigma and discrimination: Widespread stigma associated with mental illness discourages individuals from seeking help, fearing social isolation, judgment, and discrimination.
- Cultural beliefs: Traditional beliefs and practices in some communities may attribute mental illness to supernatural causes, leading to reliance on traditional healers instead of seeking evidence-based medical care.
H3: Inadequate Funding and Resource Allocation
Insufficient government funding allocated to mental health initiatives further hampers efforts to address the psychiatrist shortage.
- Low budget allocation: The budget allocated to mental health services in Ghana is disproportionately low compared to other healthcare sectors.
- Lack of investment: There's a clear need for increased investment in mental health infrastructure, technology, and research.
H2: Potential Solutions to Address the Psychiatrist Deficit
H3: Investing in Psychiatric Training and Education
Expanding training opportunities for psychiatrists is paramount.
- Scholarships and funding: Providing scholarships and financial aid to medical students specializing in psychiatry can incentivize more individuals to pursue this career path.
- Increased residency positions: A significant increase in the number of residency positions is crucial for training a new generation of psychiatrists.
- International collaborations: Partnering with international organizations and institutions can provide valuable support in terms of training, resources, and expertise.
H3: Improving Community-Based Mental Health Services
Strengthening community-based mental health services is crucial for expanding access to care.
- Community health workers: Training and deploying community health workers to provide basic mental health services can help reach underserved populations.
- Psychosocial support programs: Implementing accessible and culturally appropriate psychosocial support programs can offer crucial support to individuals struggling with mental illness.
- Telehealth: Utilizing telehealth platforms can bridge geographical barriers and provide access to mental healthcare in remote areas.
H3: Addressing Stigma and Promoting Mental Health Awareness
Reducing stigma and promoting awareness are critical steps towards improving mental health outcomes.
- Public awareness campaigns: Launching large-scale public awareness campaigns can help educate the public about mental illness and encourage help-seeking behavior.
- Educational programs: Integrating mental health education into school curriculums and community programs can address misconceptions and promote understanding.
- Community engagement: Working with religious and community leaders to address stigma and promote mental health awareness is essential.
H3: Policy and Advocacy
Strong government policies and robust advocacy efforts are crucial for driving meaningful change.
- Increased funding: Advocating for increased government funding dedicated to mental health services is vital.
- National mental health policy: The development and implementation of a comprehensive national mental health policy is necessary to guide resource allocation and service delivery.
- Collaboration: Effective collaboration among government agencies, NGOs, and civil society organizations is critical for a coordinated approach.
3. Conclusion:
Ghana's psychiatrist deficit presents a significant challenge, hindering progress towards ensuring adequate mental healthcare for all citizens. Addressing this complex issue demands a comprehensive and collaborative approach, incorporating strategic investments in training, infrastructure, community-based services, and public awareness campaigns. By tackling the multifaceted challenges of funding, training, stigma, and access, Ghana can significantly improve its mental health system. Let's work together to advocate for better mental health solutions in Ghana and build a future where everyone has access to the care they need. Join the conversation and become a champion for improved mental healthcare in Ghana.

Featured Posts
-
 Limited Time Captain America Items Available In The Fortnite Item Shop
May 02, 2025
Limited Time Captain America Items Available In The Fortnite Item Shop
May 02, 2025 -
 The Fortnite Item Shop Update Thats Angering Players
May 02, 2025
The Fortnite Item Shop Update Thats Angering Players
May 02, 2025 -
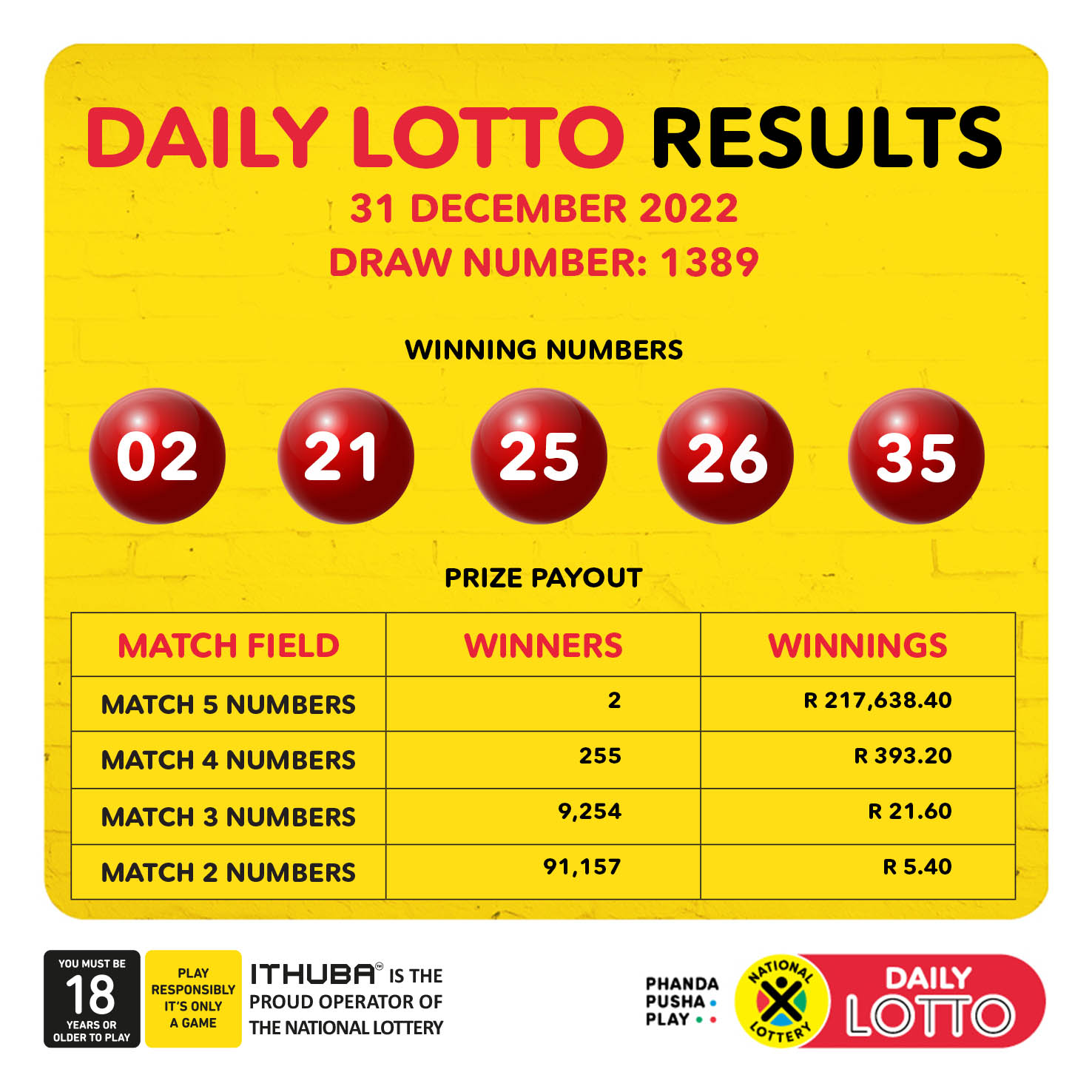 Find The Winning Numbers Lotto Lotto Plus 1 Lotto Plus 2 Results
May 02, 2025
Find The Winning Numbers Lotto Lotto Plus 1 Lotto Plus 2 Results
May 02, 2025 -
 Last Minute Host Change On Talk Tv Show
May 02, 2025
Last Minute Host Change On Talk Tv Show
May 02, 2025 -
 1 26 000
May 02, 2025
1 26 000
May 02, 2025
