Global Forest Destruction: A Record Year Fueled By Wildfires
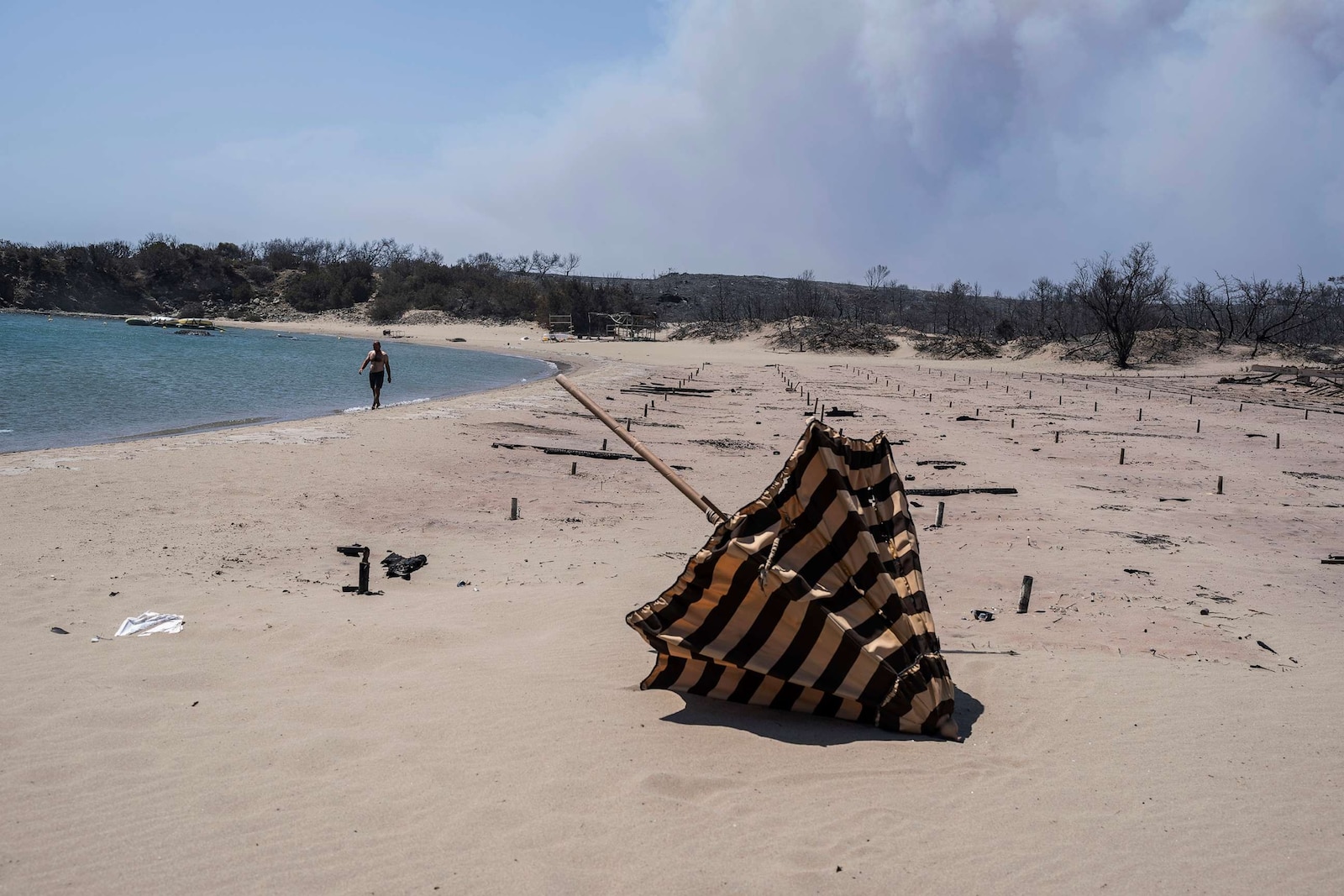

Table of Contents
The Role of Wildfires in Global Forest Destruction
The increased frequency and intensity of wildfires globally are significantly contributing to global forest destruction. Climate change, characterized by rising global temperatures and prolonged drought conditions, is creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Areas once considered relatively fire-resistant are now highly susceptible, leading to larger and more destructive blazes.
Devastating examples abound: the Amazon rainforest, the lungs of the planet, has experienced record-breaking fire seasons in recent years. Similarly, Siberia and Australia have witnessed catastrophic wildfires that have consumed millions of hectares of forest, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide and devastating biodiversity.
- Increased temperatures and dry conditions: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, creating readily available fuel for fires.
- Deforestation reduces natural firebreaks: The removal of trees reduces natural barriers that can slow or stop the spread of wildfires.
- Wildfires release massive amounts of carbon dioxide: Burning forests release significant amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and creating a vicious cycle.
- Loss of habitat leads to biodiversity loss and extinction of species: Wildfires destroy habitats, leading to the displacement and death of countless plant and animal species.
Deforestation: A Major Driver of Global Forest Loss
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, is another major driver of global forest loss. This multifaceted issue stems from a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. Agricultural expansion, particularly for commodities like soy, palm oil, and cattle ranching, is a leading cause. Illegal logging and the unsustainable timber trade further contribute to the problem. Mining operations and the construction of infrastructure also result in significant forest clearing.
The Amazon rainforest and the Indonesian rainforests are particularly hard hit, experiencing alarming rates of deforestation. Weak governance, lack of effective law enforcement, and insufficient forest management practices exacerbate the situation.
- Agricultural expansion: The demand for agricultural products drives the conversion of forests into farmland.
- Illegal logging and timber trade: Illegal logging operations often operate with impunity, contributing significantly to forest loss.
- Mining operations and infrastructure development: Roads, mines, and other infrastructure projects often require clearing vast areas of forest.
- Lack of effective forest management and law enforcement: Weak governance and inadequate resources hamper efforts to protect forests.
The Environmental Consequences of Global Forest Destruction
The environmental consequences of global forest destruction are profound and far-reaching. Forests play a vital role in carbon sequestration, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Their loss contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating climate change and its associated impacts. Furthermore, forests support incredible biodiversity, providing habitats for countless plant and animal species. The loss of forests leads to habitat fragmentation, biodiversity loss, and even extinction.
Forests also provide essential ecosystem services, including clean water, pollination, and soil stabilization. Their destruction can lead to reduced rainfall, increased soil erosion, and water scarcity. The social and economic impacts on local communities that depend on forests for their livelihoods are equally devastating.
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions: Forest loss significantly increases the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Loss of biodiversity: Deforestation threatens countless plant and animal species, leading to biodiversity loss.
- Reduced rainfall and increased soil erosion: The removal of trees can disrupt local weather patterns and lead to soil erosion.
- Impact on indigenous communities and their livelihoods: Many indigenous communities rely on forests for their survival.
Combating Global Forest Destruction: Solutions and Strategies
Combating global forest destruction requires a multi-pronged approach involving sustainable forestry practices, reforestation efforts, stricter regulations, and increased international cooperation. Sustainable forestry certification schemes, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), promote responsible forest management. Reforestation and afforestation projects help restore degraded forests and create new ones.
Strengthening forest governance, improving law enforcement, and tackling illegal logging are crucial. Promoting sustainable agriculture, reducing deforestation drivers, and supporting alternative livelihoods for communities dependent on forests are also essential. Consumer awareness and responsible consumption, avoiding products linked to deforestation, play a vital role.
- Sustainable forestry certification schemes (e.g., FSC): These schemes promote responsible forest management practices.
- Reforestation and afforestation projects: Planting trees helps restore degraded forests and create new ones.
- Strengthening forest governance and law enforcement: Effective governance and law enforcement are crucial to protecting forests.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing deforestation drivers: Sustainable agricultural practices can help reduce the pressure on forests.
Conclusion: Addressing the Urgent Issue of Global Forest Destruction
The record-breaking levels of global forest loss, driven by devastating wildfires and rampant deforestation, pose a severe threat to our planet's environmental health and human well-being. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting climate change, biodiversity, and the livelihoods of millions. We are at a critical juncture, and inaction will have catastrophic consequences.
We must act now to halt global forest destruction and protect our planet's vital forests. Learn more about the issue, support organizations working to protect forests, and adopt sustainable practices to reduce your environmental footprint. Get involved in combating global forest loss today!

Featured Posts
-
 Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Ocean City Rehoboth And Sandy Point Beach Forecast
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day Weekend 2025 Ocean City Rehoboth And Sandy Point Beach Forecast
May 23, 2025 -
 Top 7 Netflix Shows To Stream This Week May 18 24
May 23, 2025
Top 7 Netflix Shows To Stream This Week May 18 24
May 23, 2025 -
 My Sharjah Rent Double The Space Same Price A Dubai Familys Relocation Story
May 23, 2025
My Sharjah Rent Double The Space Same Price A Dubai Familys Relocation Story
May 23, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers April 8 2025 Tuesday
May 23, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Answers April 8 2025 Tuesday
May 23, 2025 -
 Alhryt Lflstyn Sda Emlyt Washntn Wsrakh Rwdryghyz Yhzan Alealm Alrqmy
May 23, 2025
Alhryt Lflstyn Sda Emlyt Washntn Wsrakh Rwdryghyz Yhzan Alealm Alrqmy
May 23, 2025
