Harmful Fungi Flourishing In A Changing Climate: A Public Health Concern

Table of Contents
H2: The Expanding Habitat of Harmful Fungi
H3: Climate Change as a Catalyst
Rising temperatures, increased humidity, and more frequent extreme weather events are creating ideal conditions for the proliferation of harmful fungi. These changes act as a catalyst, accelerating fungal growth and spore dispersal. The warmer, wetter conditions extend the growing season for many fungal species, leading to increased spore production and a longer period of exposure for humans.
- Examples of fungi thriving in warmer climates: Aspergillus species, known for causing aspergillosis, are flourishing in warmer regions. Similarly, Candida species, responsible for candidiasis, are showing increased prevalence in humid environments.
- Geographically affected areas: Regions with historically temperate climates are experiencing an increase in fungal diseases, while tropical and subtropical areas are seeing an expansion of already prevalent fungal pathogens.
- Link between weather patterns and fungal outbreaks: Heavy rainfall followed by periods of high humidity often correlate with increased fungal spore counts in the air, leading to outbreaks of respiratory illnesses.
H3: Increased Geographic Range
Climate change is not only increasing the abundance of harmful fungi but also expanding their geographical reach. This means that populations previously unaffected are now exposed to these potentially dangerous organisms. The northward migration of several fungal species is a particularly concerning trend.
- Examples of expanding fungal ranges: Certain species of Coccidioides, causing valley fever, are spreading beyond their traditional ranges in the southwestern United States.
- Impact on vulnerable populations: Individuals in newly affected areas may lack immunity or access to appropriate healthcare, making them particularly vulnerable.
- Challenges of adapting public health infrastructure: Public health systems often need to adapt quickly to address emerging fungal threats, requiring increased surveillance, diagnostic capabilities, and treatment protocols.
H2: Health Impacts of Flourishing Harmful Fungi
H3: Respiratory Illnesses
The increased prevalence of harmful fungi in the environment directly correlates with a rise in respiratory illnesses. Inhaling fungal spores can trigger allergic reactions, worsen asthma, and cause serious fungal infections like aspergillosis and histoplasmosis.
- Statistics on the increase in respiratory illnesses: Studies show a significant increase in hospital admissions for respiratory conditions linked to fungal exposure in areas experiencing shifts in climate patterns.
- Vulnerable populations: Children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals are particularly susceptible to severe fungal respiratory infections.
- Economic burden of healthcare costs: The treatment of fungal infections, particularly invasive ones, is often expensive and resource-intensive, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems.
H3: Other Health Concerns
Beyond respiratory issues, harmful fungi pose a wide range of health risks. They cause skin infections, contaminate food supplies with mycotoxins, and contribute to emerging infectious diseases.
- Examples of fungal skin infections: Ringworm, athlete's foot, and other dermatophytoses are common fungal skin infections that can be exacerbated by warm, humid conditions.
- Mycotoxin contamination in food crops: Fungi produce mycotoxins, which are potent toxins that contaminate various food crops. Consumption of mycotoxin-contaminated food can result in various health problems, from mild gastrointestinal distress to serious organ damage.
- Emerging fungal pathogens and their potential for pandemics: The changing climate may favor the emergence of new fungal pathogens with the potential to cause widespread outbreaks.
H2: Mitigation and Public Health Strategies
H3: Early Warning Systems
Developing robust early warning systems to predict and monitor fungal outbreaks is crucial for effective public health management. These systems should leverage climate data, fungal spore counts, and other relevant factors to anticipate potential threats.
- Examples of existing monitoring systems: Some regions already employ fungal spore monitoring networks, but these often need to be improved in terms of coverage and data analysis.
- Technological advancements needed for improved predictions: Advanced modeling techniques, remote sensing technologies, and improved data sharing are vital to enhance predictive capabilities.
- The role of public health agencies: Public health agencies play a crucial role in coordinating surveillance, disseminating information, and implementing public health interventions.
H3: Prevention and Treatment
Prevention and treatment strategies are essential to mitigating the risks associated with harmful fungi. This includes improving indoor air quality, controlling humidity, and advancing antifungal treatments.
- Recommendations for improving indoor air quality: Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, ensuring proper ventilation, and controlling moisture levels can significantly reduce fungal spore exposure indoors.
- Guidelines for preventing fungal contamination of food: Proper food storage, timely harvest, and appropriate processing techniques can help minimize mycotoxin contamination.
- Development of new antifungal drugs and therapies: Research and development of novel antifungal drugs and therapies are needed to combat the increasing resistance to existing treatments.
3. Conclusion
The evidence clearly demonstrates a strong link between climate change and the proliferation of harmful fungi, resulting in significant public health consequences. The expanding range and increased prevalence of these dangerous fungi necessitate proactive mitigation strategies. Understanding the impact of harmful fungi on public health is crucial. By investing in research, improving preventative measures, and strengthening public health systems, we can mitigate the risks associated with these increasingly prevalent organisms in our changing climate. Continued global collaboration is key to addressing the escalating threat of climate-driven fungal outbreaks and protecting public health from these toxic fungi. Further research into the effects of climate change on various harmful fungi species, including those producing dangerous mycotoxins, is vital for future preparedness.

Featured Posts
-
 Link Streaming Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Pukul 20 00 Wib Siaran Langsung
May 26, 2025
Link Streaming Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Pukul 20 00 Wib Siaran Langsung
May 26, 2025 -
 Hugo De Waha Remporte La Bourse Payot 2023
May 26, 2025
Hugo De Waha Remporte La Bourse Payot 2023
May 26, 2025 -
 Best Nike Running Shoes In 2025 Reviews And Recommendations
May 26, 2025
Best Nike Running Shoes In 2025 Reviews And Recommendations
May 26, 2025 -
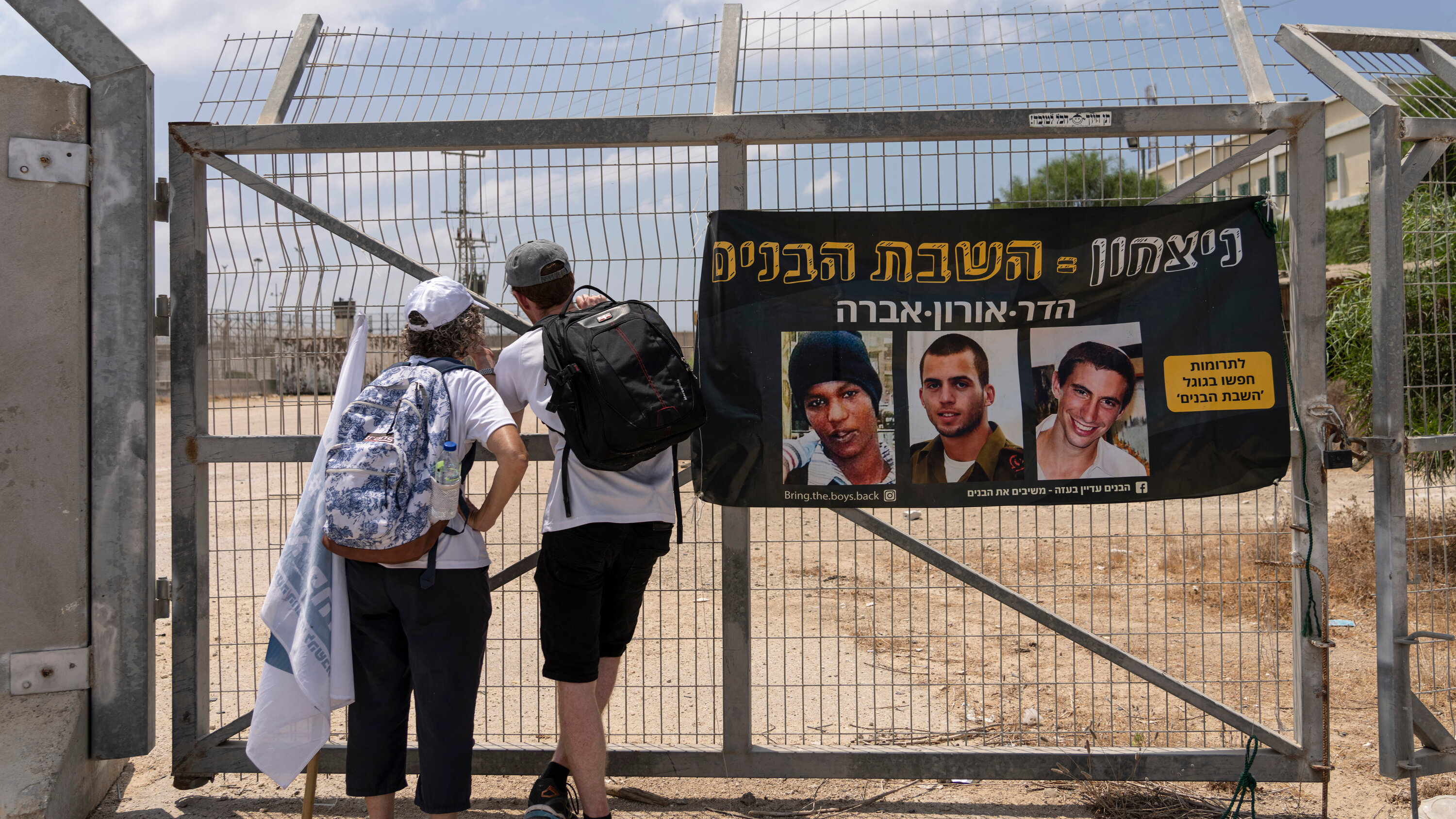 Ex Israeli Soldiers Plea Free Gaza Captives
May 26, 2025
Ex Israeli Soldiers Plea Free Gaza Captives
May 26, 2025 -
 Scene Du 128e Sexe Dans Le Grand Cactus Le Csa Regle Le Compte A La Rtbf
May 26, 2025
Scene Du 128e Sexe Dans Le Grand Cactus Le Csa Regle Le Compte A La Rtbf
May 26, 2025
