Inflation Persists: ECB Links Post-Pandemic Fiscal Measures
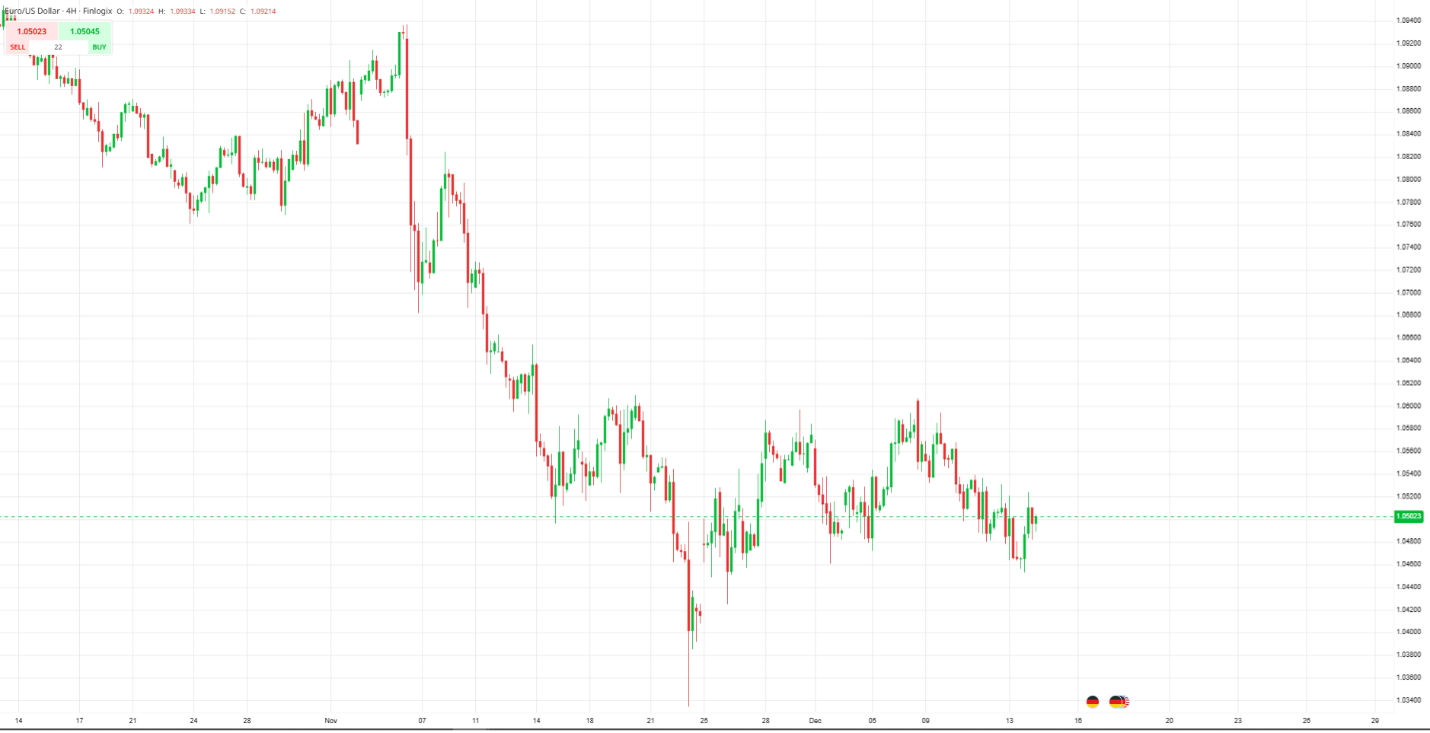
Table of Contents
The ECB's Stance on Post-Pandemic Fiscal Policy and Inflation
The ECB's primary mandate is to maintain price stability within the Eurozone, aiming for inflation of 2% over the medium term. However, current inflation rates significantly exceed this target, prompting the ECB to actively address the situation. The bank has expressed significant concerns regarding the impact of the substantial fiscal stimulus packages deployed during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. These measures, while necessary to mitigate the immediate economic fallout, are now viewed by the ECB as a contributing factor to the current inflationary pressures.
- High aggregate demand: The large-scale fiscal stimulus injected significant purchasing power into the economy, boosting aggregate demand substantially. This surge in demand outstripped the capacity of supply chains to meet it, creating inflationary pressures.
- Exacerbated supply chain disruptions: The increased demand, fueled by fiscal stimulus, further exacerbated already strained supply chains. This led to shortages of goods and services, driving up prices.
- Entrenched inflationary pressures: The ECB worries that the current inflationary pressures could become entrenched, leading to a wage-price spiral where rising prices lead to higher wages, further fueling inflation. This poses a significant challenge to long-term price stability.
- Balancing economic growth and inflation control: The ECB faces a difficult balancing act: it needs to control inflation without triggering a sharp economic slowdown or recession. This delicate balancing act requires careful calibration of monetary policy tools.
Analyzing the Data: Evidence Linking Fiscal Measures and Inflation
The ECB utilizes a variety of economic indicators to assess the relationship between fiscal policy and inflation. This includes analyzing inflation rates across different sectors, government spending figures, and other macroeconomic data.
- Correlation between spending and inflation spikes: Data analysis reveals a strong correlation between periods of increased government spending and subsequent spikes in inflation. This correlation, while not definitive proof of causation, strongly suggests a link.
- Sector-specific analysis: The ECB's analysis has identified specific sectors, such as energy and hospitality, that were both heavily impacted by fiscal stimulus and experienced significant price increases.
- Inflation persistence and fiscal support: The persistence of inflation is also linked to the timing and scale of fiscal support. Prolonged and expansive fiscal measures contributed to longer-lasting inflationary pressures.
- International comparisons: Comparing the Eurozone's experience with other regions that implemented different fiscal responses to the pandemic provides further insights into the relationship between fiscal policy and inflation. These comparisons help isolate the impact of specific policy choices.
The Role of Supply-Side Bottlenecks
The inflationary pressures weren't solely caused by increased demand. Supply-side shocks played a critical role, interacting with the surge in demand from fiscal stimulus to amplify inflationary pressures. This phenomenon is often referred to as cost-push inflation.
- Energy price increases: The sharp increase in energy prices, exacerbated by geopolitical factors, significantly contributed to overall inflation. This increased production costs across various sectors.
- Labor market shortages: Labor market shortages, in part due to demographic shifts and pandemic-related disruptions, constrained production capacity and pushed up wages, further fueling inflation.
- Global supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain disruptions, lingering from the pandemic, limited the availability of goods and services, contributing to higher prices.
Potential Policy Responses and Future Outlook
In light of its assessment, the ECB is considering various policy adjustments to combat persistent inflation. This includes navigating the complexities of balancing economic stability with inflation control.
- Interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing: Adjustments to interest rates and quantitative easing (QE) programs are potential tools to manage inflation. Raising interest rates can curb borrowing and spending, while reducing QE can decrease the money supply.
- Fiscal and monetary policy balance: The ongoing debate regarding the optimal balance between fiscal and monetary policy is crucial. Coordination between fiscal authorities and the ECB is essential for effective inflation control.
- Long-term implications for economic growth: The ECB must carefully consider the long-term implications of its policy responses on economic growth and price stability. A premature tightening of monetary policy could trigger a recession.
- Inflation rate predictions: The ECB provides forecasts for future inflation rates, based on current trends and expected policy adjustments. These forecasts are crucial for businesses and consumers to make informed decisions.
Conclusion
The ECB's analysis strongly suggests a link between persistent inflation and the expansive post-pandemic fiscal measures implemented in the Eurozone. The data analysis reveals a correlation between increased government spending and subsequent inflation spikes, exacerbated by supply-side bottlenecks. The ECB faces the challenging task of balancing inflation control with the need to support economic growth. Understanding this complex interplay is vital for navigating the current economic environment. To stay informed about the ECB's ongoing efforts to manage "inflation persists" and its implications, continue to follow their pronouncements and analyses. Learn more about the ECB's monetary policy and its implications for controlling inflation by visiting [link to relevant ECB website/resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Hagia Sophia From Byzantine Glory To Ottoman Grandeur And Beyond
Apr 29, 2025
Hagia Sophia From Byzantine Glory To Ottoman Grandeur And Beyond
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Harnessing The Power Of Group Support For Adhd
Apr 29, 2025
Harnessing The Power Of Group Support For Adhd
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Kentucky Flood Warning State Of Emergency In Effect
Apr 29, 2025
Kentucky Flood Warning State Of Emergency In Effect
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Speedboats Record Attempting Flip At Arizona Boating Competition
Apr 29, 2025
Speedboats Record Attempting Flip At Arizona Boating Competition
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Willie Nelson Honors His King Of The Road Crew In New Documentary
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelson Honors His King Of The Road Crew In New Documentary
Apr 29, 2025
