Inside Our ADHD Minds: A Guide To Self-Understanding
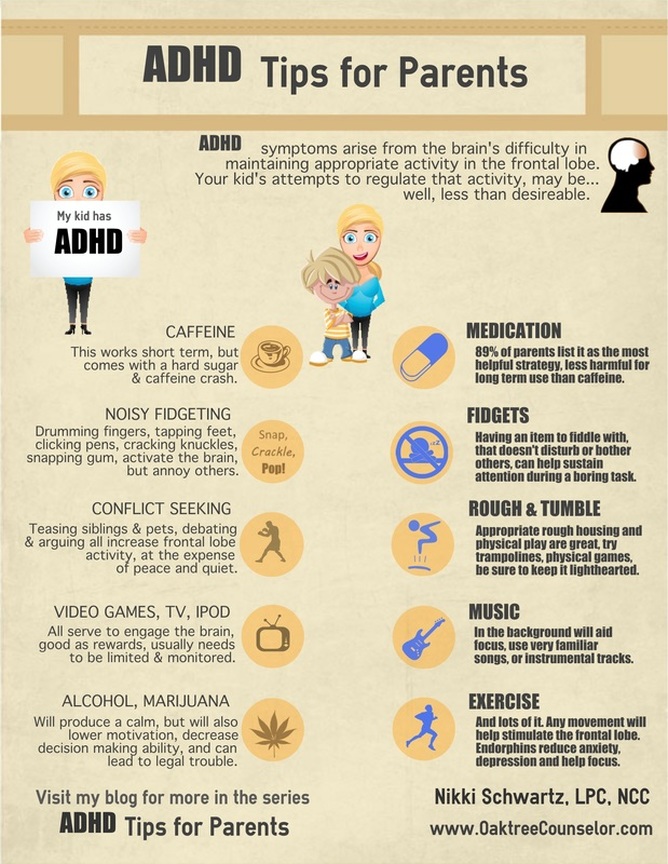
Table of Contents
Understanding the Neurological Differences of ADHD
The ADHD Brain: Structure and Function
The neurobiology of ADHD significantly impacts brain structure and function, leading to the characteristic symptoms of this neurodevelopmental disorder. Key areas involved include the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions like planning and organization; and the neurotransmitter systems involving dopamine and norepinephrine, crucial for attention and focus.
- Prefrontal Cortex Dysfunction: Differences in the prefrontal cortex's structure and activity can affect executive functions, leading to difficulties with planning, working memory, and inhibitory control. This explains challenges with task initiation, organization, and impulse control often seen in ADHD.
- Dopamine and Norepinephrine Imbalances: These neurotransmitters play a vital role in attention, motivation, and reward processing. Imbalances can result in difficulties sustaining attention, experiencing low motivation, and seeking immediate gratification.
- Misconceptions about Willpower: It's crucial to debunk the myth that ADHD is simply a "lack of willpower." The neurological differences in the ADHD brain make focusing, organizing, and self-regulating significantly more challenging, not a matter of personal failing.
Common ADHD Symptoms and Presentations
ADHD presents differently in individuals, making it essential to understand the wide spectrum of symptoms. The primary presentations include inattentive, hyperactive/impulsive, and a combined type, encompassing symptoms from both.
- Inattentive ADHD Symptoms: Difficulty sustaining attention, easily distracted, forgetful, disorganized, struggles with following instructions, poor time management.
- Hyperactive/Impulsive ADHD Symptoms: Fidgeting, restlessness, excessive talking, interrupting, difficulty waiting their turn, acting without thinking.
- Symptoms in Adults vs. Children: While core symptoms remain consistent, their manifestation changes with age. Children may exhibit more overt hyperactivity, while adults may experience primarily inattentive symptoms or subtle hyperactivity. Adult ADHD often presents as chronic disorganization, procrastination, and emotional dysregulation.
- ADHD Symptoms Checklist: If you suspect you or a loved one might have ADHD, consulting a professional for a proper diagnosis is crucial. They can provide a thorough assessment and determine the appropriate course of action.
The Impact of ADHD on Daily Life
Challenges Faced by Individuals with ADHD
The challenges posed by ADHD extend across various life domains, significantly impacting daily functioning and overall well-being.
- Academic Struggles: Difficulty concentrating in class, completing assignments, and organizing study materials often lead to academic underachievement.
- Workplace Difficulties: Challenges with time management, prioritizing tasks, and maintaining focus can affect job performance and career progression.
- Relationship Issues: Impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, and communication difficulties can strain personal relationships.
- Financial Challenges: Poor financial planning, impulsive spending, and difficulty managing bills can lead to financial instability.
- Organizational Difficulties: Challenges with organizing belongings, maintaining a clean space, and managing schedules contribute to stress and frustration.
The Strengths of the ADHD Mind
While challenges are significant, it's vital to recognize the inherent strengths often associated with ADHD. These strengths can be harnessed to achieve remarkable success and fulfillment.
- Creativity and Innovation: Individuals with ADHD often possess exceptional creativity, innovative thinking, and the ability to approach problems from unique perspectives.
- Hyperfocus: The ability to intensely concentrate on tasks of personal interest can lead to remarkable achievements in chosen fields.
- Intense Passion: Often characterized by a deep passion for their interests, individuals with ADHD can demonstrate remarkable dedication and drive.
- Strong Empathy: Many individuals with ADHD possess a remarkable capacity for empathy and understanding of others' emotions.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Their ability to think outside the box often leads to innovative and effective problem-solving strategies.
Strategies for Self-Understanding and Management
Self-Compassion and Acceptance
Self-compassion is paramount in managing ADHD. Accepting ADHD as a part of your identity and practicing self-kindness is crucial for building self-esteem and reducing self-criticism.
- Combatting Self-Criticism: Challenge negative self-talk and replace it with positive affirmations. Acknowledge that struggles are a consequence of the neurological condition, not personal failings.
- Cultivating Self-Kindness: Treat yourself with the same understanding and compassion you would offer a friend facing similar challenges.
Effective Coping Mechanisms and Strategies
Effective management of ADHD requires a multi-faceted approach that often involves a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs.
- Medication: Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can help regulate neurotransmitter levels, improving focus, attention, and impulse control.
- Therapy: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can teach coping skills, address emotional regulation issues, and improve self-management strategies. ADHD coaching offers specialized support and guidance.
- Organizational Tools: Employing planners, calendars, apps, and other organizational tools can aid in time management, task prioritization, and reducing overwhelm.
- Time Management Techniques: Learn and implement techniques like time blocking, the Pomodoro Technique, and breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Mindfulness Practices: Mindfulness meditation and other mindfulness exercises can help improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and enhance emotional regulation.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques are crucial for overall well-being and symptom management.
Conclusion
Understanding your ADHD mind is a journey of self-discovery, not a destination. By acknowledging the neurological differences, understanding the impact on daily life, and implementing effective coping strategies, you can develop a greater sense of self-acceptance and build a fulfilling life. Remember, you are not alone, and with the right knowledge and support, you can successfully manage your ADHD and live a thriving life. Continue exploring resources and support networks to deepen your understanding of ADHD and empower yourself on this journey. Seek professional help from a psychologist or psychiatrist specializing in ADHD to develop a personalized management plan.

Featured Posts
-
 Natural Fiber Composites Market 2029 Global Market Size Share And Forecast
May 13, 2025
Natural Fiber Composites Market 2029 Global Market Size Share And Forecast
May 13, 2025 -
 Live Efl Highlights Streaming And Tv Coverage
May 13, 2025
Live Efl Highlights Streaming And Tv Coverage
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprio And Vittoria Ceretti A Surprise Met Gala Appearance
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprio And Vittoria Ceretti A Surprise Met Gala Appearance
May 13, 2025 -
 Kra Targetiranja Roma Otvoreno Pismo Uni E Roma Srbi E Mariniki Tepi
May 13, 2025
Kra Targetiranja Roma Otvoreno Pismo Uni E Roma Srbi E Mariniki Tepi
May 13, 2025 -
 Kostyuk Trebuet Ot Sandu Otmeny Zapreta Na Vyezd Simiona V Moldovu
May 13, 2025
Kostyuk Trebuet Ot Sandu Otmeny Zapreta Na Vyezd Simiona V Moldovu
May 13, 2025
