Investigation Into Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following Ohio Train Derailment
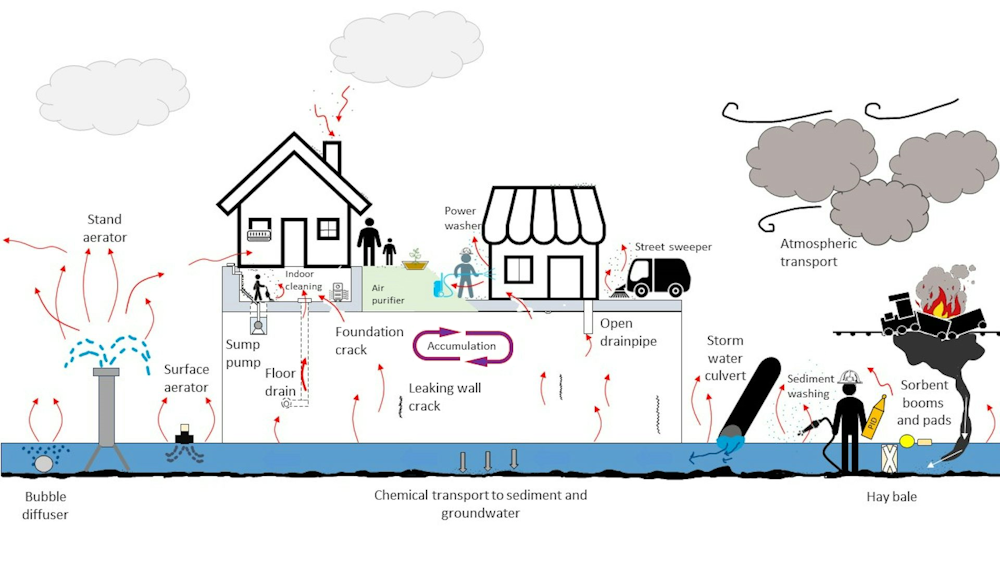
Table of Contents
Types of Persistent Toxic Chemicals Released
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous materials, many of which are known persistent toxic chemicals. Key among these were vinyl chloride (C₂H₃Cl) and butyl acrylate (C₈H₁₂O₂).
-
Vinyl Chloride: This colorless gas is a known carcinogen, meaning it can cause cancer. Exposure can lead to a range of health problems, including liver damage, respiratory issues, and neurological disorders. Its volatility means it can readily spread through the air, contaminating both indoor and outdoor environments. Furthermore, vinyl chloride's persistence in certain materials poses a long-term risk.
-
Butyl Acrylate: This colorless liquid with a pungent odor is also highly toxic. It's an irritant to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system, and prolonged exposure can cause serious health problems. Like vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate's volatility contributes to its potential for widespread contamination, particularly within buildings near the derailment site. Its persistence in building materials further complicates remediation efforts.
Pathways of Contamination in Buildings
The spread of persistent toxic chemicals from the derailment into buildings occurred through several pathways:
-
Air Infiltration: The initial release created a large plume that infiltrated buildings via HVAC systems, open windows, and cracks in building structures. This airborne contamination can lead to long-term exposure for occupants.
-
Surface Deposition: Chemicals settled on building exteriors and interiors, leading to surface contamination. This contamination can persist for extended periods, particularly on porous materials such as fabrics and drywall. Cleaning and decontamination may not completely eliminate the threat.
-
Water Contamination: Depending on the extent of the spill, groundwater and drinking water supplies could be compromised, leading to potential ingestion exposure. This represents a serious and persistent threat requiring thorough testing and remediation.
-
Long-Term Persistence: Some of the released chemicals can persist within building materials for years, slowly releasing vapors and posing a chronic exposure risk. This necessitates careful consideration of remediation strategies involving material replacement in affected buildings.
Assessing and Mitigating Building Contamination
Detecting and mitigating contamination requires a multi-pronged approach:
-
Environmental Testing: Professional environmental testing is crucial to accurately assess the extent of contamination. This includes air sampling to measure airborne concentrations of persistent toxic chemicals, and surface sampling to identify contaminated areas. Sophisticated analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), are needed to accurately identify and quantify the chemicals present.
-
Remediation Strategies: Remediation may involve a combination of methods including thorough cleaning and decontamination of surfaces, specialized air purification systems to remove airborne contaminants, and in severe cases, replacement of contaminated building materials.
-
Safety Protocols: Remediation efforts must adhere to strict safety protocols to protect workers and prevent further spread of contamination. This includes the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), proper waste disposal, and adherence to established safety guidelines.
-
Cost Considerations: The cost of comprehensive testing and remediation can be substantial, depending on the extent of contamination and the chosen remediation strategies. Funding mechanisms and support for affected property owners are crucial to ensuring adequate response and recovery.
Long-Term Health Impacts and Public Health Concerns
The long-term health effects of exposure to these persistent toxic chemicals are a major concern:
-
Chronic Illnesses: Exposure may lead to various respiratory illnesses, cancers, neurological disorders, and other chronic health conditions. The long latency periods for some of these diseases mean that the full impact may not be apparent for years to come.
-
Health Monitoring: Ongoing health monitoring of affected populations is essential to detect and manage any health problems related to exposure. This requires robust public health surveillance and access to healthcare resources.
-
Transparent Communication: Open and transparent communication from authorities about the risks and ongoing monitoring is crucial to build public trust and ensure informed decision-making.
Prevention and Future Preparedness
Preventing future incidents requires significant improvements:
-
Strengthened Regulations: Regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials need to be significantly strengthened to prevent similar accidents from occurring. This includes stricter enforcement and investment in improved safety measures.
-
Improved Emergency Response: Emergency response protocols for chemical spills must be improved, ensuring rapid and effective containment and mitigation efforts. This includes better training for first responders and improved coordination between agencies.
-
Chemical-Resilient Building Codes: Building codes should be updated to incorporate features that enhance resilience to chemical contamination, minimizing the impact of future accidental releases.
Conclusion:
The Ohio train derailment underscores the critical need for comprehensive investigation and remediation efforts concerning persistent toxic chemicals in affected buildings. The potential long-term health and environmental consequences demand immediate action. Thorough testing, effective remediation strategies, and robust preventative measures are essential to safeguard the health and well-being of the community. Further research into the long-term effects of these persistent toxic chemicals is crucial. We must learn from this tragedy to prevent future incidents and mitigate the risks associated with the release of persistent toxic chemicals. Continued monitoring and investigation into the presence of persistent toxic chemicals are vital to ensure the safety of residents and prevent further exposure. We urge continued investigation into persistent toxic chemicals and their impact on buildings and communities affected by the Ohio train derailment.

Featured Posts
-
 Katie Nolans Response To Charlie Dixons Claims
May 05, 2025
Katie Nolans Response To Charlie Dixons Claims
May 05, 2025 -
 Get Anna Kendricks Look The Perfect Glittering Shell Crop Top For Summer
May 05, 2025
Get Anna Kendricks Look The Perfect Glittering Shell Crop Top For Summer
May 05, 2025 -
 Addressing The Slow Traffic Movement In Darjeeling
May 05, 2025
Addressing The Slow Traffic Movement In Darjeeling
May 05, 2025 -
 2025 Kentucky Derby Betting Focusing On Chunk Of Gold
May 05, 2025
2025 Kentucky Derby Betting Focusing On Chunk Of Gold
May 05, 2025 -
 Year Long Hiatus Ends Ufc Champ Fights Bantamweight Veteran May 3rd
May 05, 2025
Year Long Hiatus Ends Ufc Champ Fights Bantamweight Veteran May 3rd
May 05, 2025
