Investor Guide: Understanding And Addressing High Stock Market Valuations (BofA)
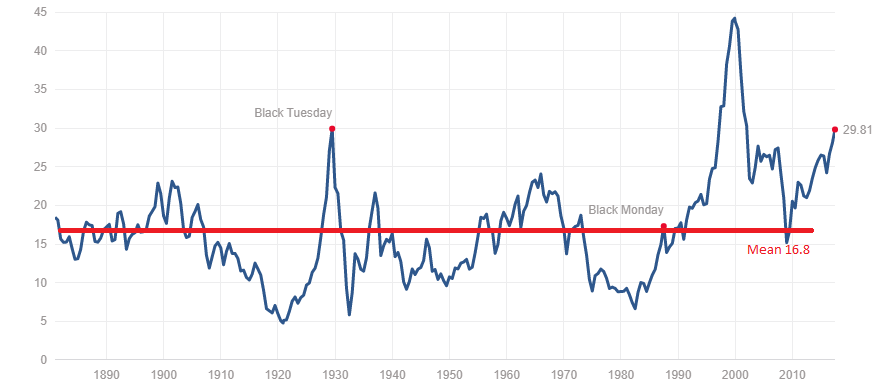
Table of Contents
Identifying High Stock Market Valuations
Determining whether the stock market is overvalued requires a careful analysis of various valuation metrics and a thorough understanding of market dynamics. Here's how to identify potential overvaluation:
Key Valuation Metrics
Several key ratios help gauge market valuation. Understanding their strengths and limitations is crucial:
-
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E): This compares a company's stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio might suggest overvaluation, while a low P/E might indicate undervaluation. For example, a P/E ratio of 30 indicates investors are willing to pay $30 for every $1 of earnings. However, a high P/E ratio can also reflect high growth expectations.
-
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S): This compares a company's stock price to its revenue per share. It's useful for valuing companies with negative earnings, but it doesn't consider profitability. A high P/S ratio might suggest overvaluation, especially if revenue growth is not substantial.
-
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B): This compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). A high P/B ratio might indicate overvaluation, while a low P/B ratio could suggest undervaluation. This ratio is particularly relevant for asset-heavy industries.
Limitations: These ratios should not be used in isolation. Consider using them in conjunction with other metrics and qualitative factors.
-
Comparable Company Analysis: Compare the valuation ratios of a company to its peers within the same industry. This helps to identify whether a company is relatively overvalued or undervalued compared to its competitors.
-
Industry Benchmarks: Use industry average valuation ratios as a benchmark to assess whether a particular stock or sector is overvalued or undervalued.
Spotting Overvalued Sectors and Stocks
Identifying overvalued sectors and individual stocks requires a deeper dive into company financials and market trends:
-
Sector Analysis: Analyze sectors based on growth prospects versus current market prices. Rapidly growing sectors often command higher valuations, but excessively high valuations relative to future growth potential can signal a bubble.
-
Company Financial Analysis: Examine a company's income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to identify potential overvaluation. Look for factors such as high debt levels, declining profitability, and slowing revenue growth.
-
Future Earnings Potential: Consider future earnings potential and growth forecasts. Analysts' estimates should be considered but critically evaluated, as these are just projections.
-
Qualitative Factors: Consider qualitative factors such as management quality, competitive landscape, and regulatory risks, which can impact a company's long-term prospects and valuation.
Understanding the Drivers of High Valuations
Several macroeconomic and market factors contribute to high stock market valuations. Understanding these drivers is crucial for effective investment strategy:
Low Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
Low interest rates and accommodative monetary policies significantly influence asset prices:
-
Impact of Low Interest Rates: Low interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of investing in stocks, pushing investors towards higher-yielding assets, thereby inflating stock prices.
-
Quantitative Easing (QE): QE programs, where central banks inject liquidity into the market, can further inflate asset prices, including stocks.
-
Investor Sentiment: Monetary policy significantly impacts investor sentiment. Easy monetary policy generally leads to increased risk appetite and higher valuations.
Technological Innovation and Growth Stocks
Technological innovation fuels the growth of certain sectors and drives high valuations:
-
Disruptive Technologies: Disruptive technologies can create companies with rapid growth potential, leading to high valuations despite limited current profitability.
-
High-Growth, Unprofitable Companies: Valuing high-growth but unprofitable companies is particularly challenging. Investors often focus on future potential, leading to potentially inflated valuations.
-
Growth vs. Value Stocks: The distinction between growth and value stocks becomes more crucial in a high-valuation environment. Value stocks, often overlooked during periods of exuberance, might offer better risk-adjusted returns.
Increased Market Speculation and Sentiment
Investor psychology plays a significant role in driving up valuations:
-
Investor Psychology: Market sentiment, driven by investor psychology, can significantly impact stock prices. Periods of optimism can inflate valuations, while pessimism can lead to sharp declines.
-
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): FOMO can lead to impulsive investment decisions, pushing prices higher even beyond rational valuations.
-
Market Bubbles: Excessive speculation and FOMO can create market bubbles, where prices deviate significantly from fundamental values. These bubbles eventually burst, leading to sharp market corrections.
Strategies for Addressing High Stock Market Valuations
Several strategies can help investors mitigate risks associated with high stock market valuations:
Diversification and Portfolio Rebalancing
Diversification and rebalancing are crucial risk management tools:
-
Asset Class Diversification: Diversify across asset classes, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments to reduce overall portfolio risk.
-
Portfolio Rebalancing: Regularly rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation. This involves selling some overvalued assets and buying undervalued ones.
-
Reducing Exposure: Reduce exposure to overvalued sectors or individual stocks to limit potential losses during a market correction.
Value Investing and Contrarian Strategies
Value investing and contrarian strategies can help identify undervalued assets:
-
Value Investing Principles: Focus on identifying companies trading below their intrinsic value. This approach requires thorough fundamental analysis and patience.
-
Contrarian Strategies: Profit from market corrections by buying assets when others are selling. This requires courage and a long-term perspective.
-
Successful Value Investors: Study the strategies of successful value investors like Warren Buffett and Benjamin Graham to learn how to identify undervalued opportunities.
Defensive Investment Strategies
Defensive investment strategies focus on preserving capital during market volatility:
-
Defensive Stocks: Increase your allocation to defensive stocks (e.g., consumer staples, utilities) which tend to be less sensitive to economic downturns.
-
Increase Cash Holdings: Increase your cash holdings to take advantage of potential buying opportunities during market corrections.
-
Fixed-Income Securities: Consider investing in high-quality fixed-income securities, such as government bonds, to provide stability and income during periods of uncertainty.
-
Hedging Strategies: Explore hedging strategies, such as options or short selling, to mitigate potential losses in a volatile market.
Conclusion
High stock market valuations present both challenges and opportunities for investors. By understanding the key valuation metrics, the drivers behind high valuations, and employing appropriate investment strategies, you can navigate this complex environment more effectively. Remember to regularly monitor your portfolio, rebalance as needed, and remain disciplined in your investment approach. Don't hesitate to seek professional financial advice if you need further assistance in understanding and addressing high stock market valuations within the context of your individual investment goals and risk tolerance. A well-informed approach is crucial for achieving long-term financial success in navigating these market conditions.

Featured Posts
-
 Bryan Cranstons Take How A Malcolm In The Middle Reboot Would Differ
May 29, 2025
Bryan Cranstons Take How A Malcolm In The Middle Reboot Would Differ
May 29, 2025 -
 Indonesias Openness To Israel Conditional On Palestine Recognition
May 29, 2025
Indonesias Openness To Israel Conditional On Palestine Recognition
May 29, 2025 -
 Perfekt Badevaer Finn De Beste Stedene Og Tidspunktene
May 29, 2025
Perfekt Badevaer Finn De Beste Stedene Og Tidspunktene
May 29, 2025 -
 Opvallende Naam Ajax Twijfels Over Simonis En De Hoge Positie Van Kroes
May 29, 2025
Opvallende Naam Ajax Twijfels Over Simonis En De Hoge Positie Van Kroes
May 29, 2025 -
 O Tramp Epilegei Tin Tzanin Piro Gia Eisaggelea Tis Oyasingkton
May 29, 2025
O Tramp Epilegei Tin Tzanin Piro Gia Eisaggelea Tis Oyasingkton
May 29, 2025
