Japan's Steep Yield Curve: Investor Divisions And Economic Challenges
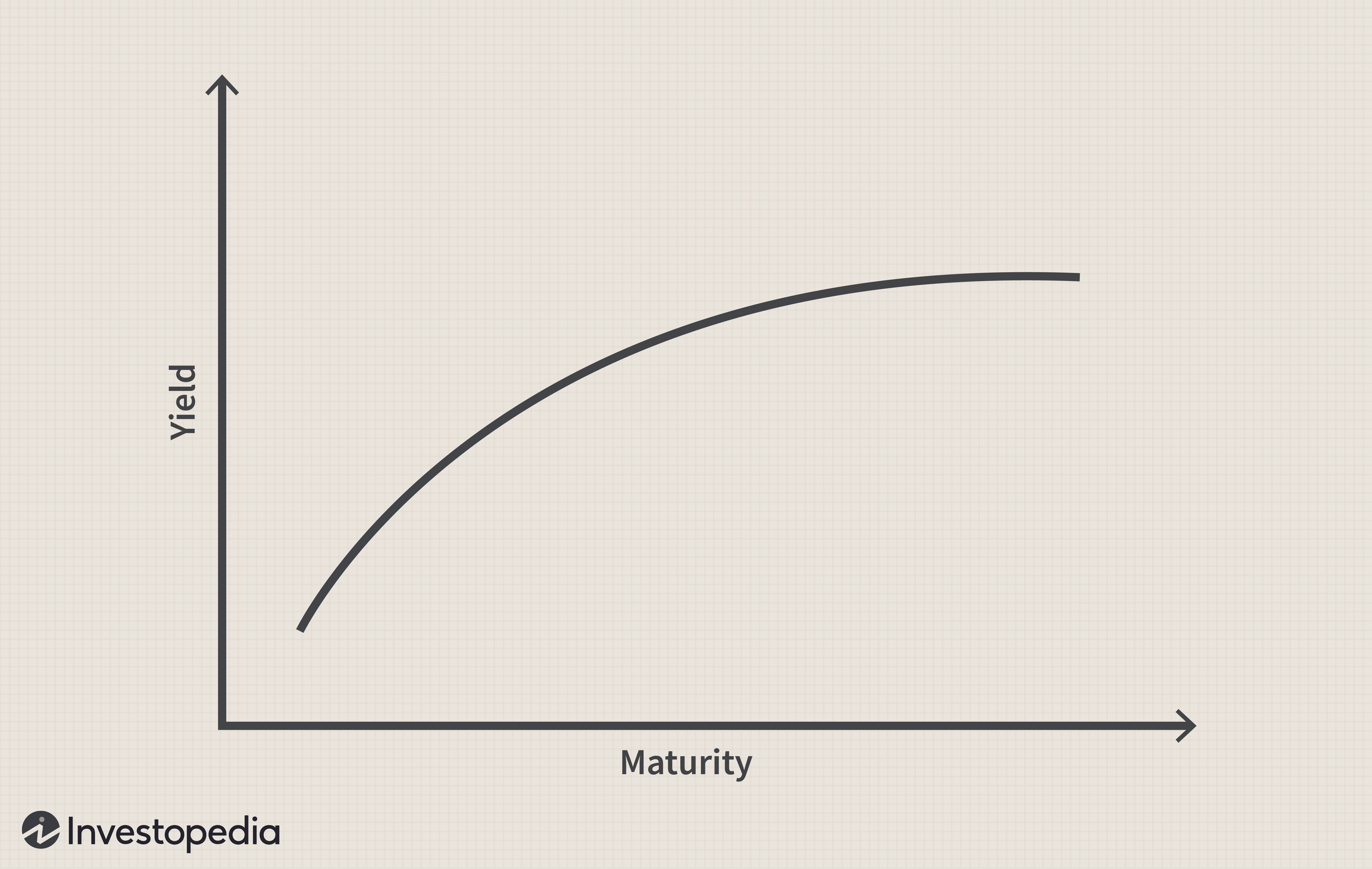
Table of Contents
Understanding Japan's Steep Yield Curve
A steep yield curve illustrates a large difference between short-term and long-term interest rates. In Japan's context, this means the yield on long-term Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs) is significantly higher than that of short-term JGBs. This unusual steepness is a direct result of several interacting factors.
The primary driver is the BOJ's Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy. YCC aims to keep short-term interest rates near zero while controlling the yield on 10-year JGBs. However, the policy's effectiveness has been questioned as inflation has begun to rise, exceeding the BOJ's initial projections.
-
YCC's Impact: The BOJ's continued purchases of JGBs to maintain its yield target have suppressed short-term yields. However, market forces, driven by inflation expectations and global interest rate hikes, have pushed up long-term yields, leading to the steepening of the curve.
-
Inflationary Pressures: Japan, experiencing its highest inflation in decades, is seeing increased pressure on prices. This rising inflation has led to market expectations of future interest rate hikes, even if the BOJ maintains its current policy stance. This expectation is a key factor contributing to the higher yields on longer-term JGBs.
-
Global Monetary Policy Tightening: The global tightening of monetary policy by central banks worldwide, including the Federal Reserve, has also impacted Japanese yields. Higher global interest rates increase the attractiveness of foreign bonds relative to JGBs, putting upward pressure on long-term Japanese yields.
[Insert chart here illustrating the steepness of the Japanese yield curve over time]
Investor Divisions and Strategies
Japan's steep yield curve has created a significant divide among investors. Their strategies are directly linked to their outlook on the future direction of the BOJ's policy and the Japanese economy.
-
Bullish on JGBs (BOJ Intervention): Some investors remain bullish on JGBs, betting that the BOJ will continue its aggressive bond-buying program to maintain its YCC target. They believe the central bank will prevent a significant rise in long-term yields.
-
Bearish on JGBs (Policy Shift): Others are bearish, anticipating a shift in the BOJ's policy, potentially involving the abandonment or modification of YCC. These investors expect long-term JGB yields to rise substantially.
-
Hedging Strategies: Many investors employ sophisticated hedging strategies to mitigate the risks associated with the uncertainty surrounding the yield curve. These strategies might involve using derivatives or diversifying across different asset classes.
-
Asset Class Impact: The steep yield curve significantly impacts various asset classes. The uncertainty affects JGB prices, impacting fixed-income portfolios. It also influences Japanese equities, as higher interest rates can affect corporate profitability and valuations.
Economic Challenges and Implications
The steepening yield curve presents significant challenges to the Japanese economy. The widening gap between short-term and long-term rates has broader implications for economic health.
-
Higher Borrowing Costs: A sustained steep yield curve translates to higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially hindering economic growth and investment. This can dampen consumer spending and business expansion plans.
-
Japanese Yen Exchange Rate: The yield curve's dynamics can influence the Japanese yen's exchange rate. A steeper curve, indicating higher long-term yields, might initially attract foreign investment, strengthening the yen. However, longer-term effects could be more complex and depend on other economic factors.
-
Sudden Yield Curve Shifts: A sudden and significant shift in the yield curve could trigger substantial market volatility, impacting asset prices and investor confidence. This underscores the inherent risks associated with the current situation.
-
BOJ Policy Response: The BOJ's response to the steepening curve will be crucial. Any policy adjustments could have significant ramifications for the Japanese economy and financial markets.
Conclusion
Japan's steep yield curve is a complex issue reflecting the interplay between the BOJ's monetary policy, global economic conditions, and domestic inflationary pressures. This has created a significant divergence in investor strategies, with some anticipating further BOJ intervention while others predict a shift towards higher yields. The sustained steepness of the curve poses significant challenges to the Japanese economy, impacting borrowing costs and potentially impacting economic growth.
Understanding the nuances of Japan's steep yield curve is crucial for investors navigating the Japanese market. Further research and analysis of Japan's steep yield curve are essential to make informed investment decisions. Stay informed on the latest developments regarding the BOJ's policy and the evolving economic landscape to effectively manage risk and capitalize on opportunities presented by this dynamic situation.

Featured Posts
-
 Angel Reese Shares Moving Message About Mom At Brothers Ncaa Game
May 17, 2025
Angel Reese Shares Moving Message About Mom At Brothers Ncaa Game
May 17, 2025 -
 Drakes Ben Mc Collum New Assistant Coach For Iowa
May 17, 2025
Drakes Ben Mc Collum New Assistant Coach For Iowa
May 17, 2025 -
 Palmeiras 2 0 Bolivar Resultado Resumen Y Goles Del Partido
May 17, 2025
Palmeiras 2 0 Bolivar Resultado Resumen Y Goles Del Partido
May 17, 2025 -
 Reddit Outage Global Service Disruption Impacts Thousands
May 17, 2025
Reddit Outage Global Service Disruption Impacts Thousands
May 17, 2025 -
 Federal Student Loan Refinancing What You Need To Know
May 17, 2025
Federal Student Loan Refinancing What You Need To Know
May 17, 2025
