Justice Department Ends School Desegregation Order: What's Next?
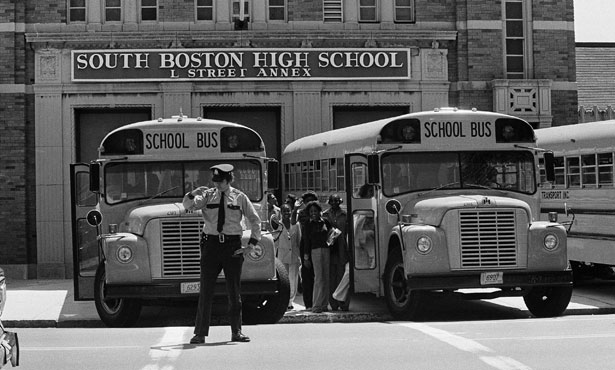
Table of Contents
The History and Context of the Ended Desegregation Order
Understanding the implications of the Justice Department's decision requires examining the history and context of the specific school desegregation order it terminated. While the exact order may vary depending on the specific case, many such orders stemmed from decades of legal battles aimed at dismantling racially segregated school systems. The landmark Supreme Court case, Brown v. Board of Education (1954), declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, the implementation of Brown v. Board proved slow and fraught with resistance, leading to numerous subsequent legal challenges and court-ordered desegregation plans.
- Specific details of the order's provisions: These orders often mandated specific actions like busing, redrawing school district boundaries, and implementing affirmative action programs to achieve racial balance in schools.
- The timeframe the order was in effect: Many desegregation orders remained in effect for decades, reflecting the persistent challenges in achieving meaningful integration.
- Significant legal precedents related to the order: Subsequent Supreme Court cases, such as Milliken v. Bradley (1974), further shaped the legal landscape surrounding school desegregation, often limiting the scope of court-ordered remedies.
- Key players and organizations involved in the case: The fight for school desegregation involved a wide range of actors, including civil rights organizations, local communities, and legal professionals.
Immediate Consequences of the Order's Termination
The termination of a long-standing school desegregation order has immediate and potentially profound consequences. The most concerning is the potential for increased racial segregation in schools. Without the oversight and mandated remedies, schools may revert to patterns of segregation, leading to a re-concentration of minority students in under-resourced schools.
- Potential increase in racial segregation in schools: This can exacerbate existing inequalities in access to quality education, resources, and opportunities.
- Impact on student achievement and opportunity: Studies consistently demonstrate a link between school segregation and disparities in academic achievement. Re-segregation could widen achievement gaps.
- Concerns about equitable resource allocation: Racially segregated schools often face unequal resource distribution, leading to disparities in teacher quality, facilities, and programs.
- Reactions from affected communities and organizations: The termination of these orders is likely to elicit strong reactions from affected communities and civil rights organizations, who may challenge the decision through legal channels or public advocacy.
Long-Term Implications for School Diversity and Equity
The long-term effects of ending school desegregation orders extend beyond immediate impacts, potentially shaping the educational landscape for generations to come. The decision could significantly impact school demographics and exacerbate existing inequalities in educational opportunities. Achieving racial integration remains a significant challenge nationwide, demanding persistent efforts to address systemic inequities.
- The potential for increased achievement gaps: The lack of diverse learning environments can hinder academic progress and limit opportunities for students from minority backgrounds.
- The need for continued federal oversight and intervention: While the Justice Department’s action represents a shift, federal legislation like the Elementary and Secondary Education Act continues to play a role in promoting equal educational opportunities.
- The role of local and state governments in promoting school desegregation: Local and state initiatives are crucial in fostering inclusive school environments and countering the effects of re-segregation.
- The importance of community involvement in maintaining diverse schools: Active community engagement can drive positive change and foster diverse and equitable schools.
The Role of Federal and Local Government in Addressing School Segregation
The responsibility for ensuring equal educational opportunities rests on both federal and local government entities. The federal government plays a vital role in setting national standards and providing resources to support school districts in their desegregation efforts. However, state and local governments also bear significant responsibility for implementing policies and programs that promote integration and equity.
- Federal legislation related to school desegregation: Legislation such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Elementary and Secondary Education Act provides a legal framework for addressing school segregation.
- State-level policies impacting school integration: States play a significant role in funding education and setting policies that can either promote or hinder school integration efforts.
- Local initiatives aimed at promoting diversity in schools: Local school districts can implement magnet programs, open enrollment policies, and other initiatives to attract diverse student populations.
- The effectiveness of current laws and policies: The effectiveness of current laws and policies in preventing and addressing school segregation remains a subject of ongoing debate and evaluation.
Advocacy and Future Strategies for Promoting School Desegregation
Advocacy groups play a critical role in monitoring school desegregation efforts and pushing for policy changes to ensure equitable educational opportunities for all students. Future strategies may include legal challenges to discriminatory practices, increased public awareness campaigns, and the development of innovative programs to foster inclusive school environments.
- Key advocacy organizations working on school desegregation: Organizations like the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund continue to champion school desegregation through litigation and advocacy.
- Potential legal strategies to challenge segregation: Legal action can be taken to challenge policies and practices that lead to or perpetuate school segregation.
- The importance of public awareness and engagement: Raising public awareness about the continuing challenges of school segregation is critical to galvanizing support for change.
- Recommendations for future policy changes: Policy changes may include strengthening federal oversight, providing additional resources for under-resourced schools, and implementing programs to promote school diversity.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's decision to end the school desegregation order marks a significant shift, raising serious concerns about the future of racial integration in schools. The potential for increased segregation, widening achievement gaps, and inequitable resource distribution necessitates continued vigilance and proactive measures from all stakeholders. The fight for school desegregation is far from over; it requires sustained efforts from federal, state, and local governments, as well as community involvement and advocacy to ensure equitable access to education for all students, regardless of race. The challenges are immense, but so is the potential for creating truly inclusive and equitable learning environments. Stay informed on the latest developments in school desegregation and participate in advocating for equitable educational opportunities for all children. Learn more about school desegregation and how you can make a difference.
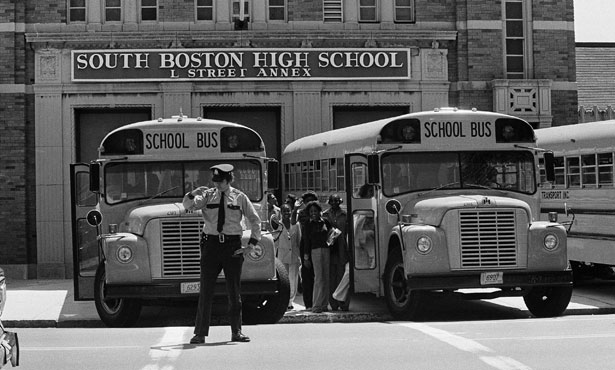
Featured Posts
-
 Rechtszaak Kampen Enexis Gevecht Om Stroomnetaansluiting
May 02, 2025
Rechtszaak Kampen Enexis Gevecht Om Stroomnetaansluiting
May 02, 2025 -
 Beijings Economic Vulnerability The Untold Story Of The Us Trade War
May 02, 2025
Beijings Economic Vulnerability The Untold Story Of The Us Trade War
May 02, 2025 -
 Pubg Mobile Studios Next Project A Valorant Mobile Adaptation
May 02, 2025
Pubg Mobile Studios Next Project A Valorant Mobile Adaptation
May 02, 2025 -
 Sony Play Station Beta Program Registration Now Open Check Requirements
May 02, 2025
Sony Play Station Beta Program Registration Now Open Check Requirements
May 02, 2025 -
 Severe Storm Watch Tulsa Area At Highest Risk After 2 Am
May 02, 2025
Severe Storm Watch Tulsa Area At Highest Risk After 2 Am
May 02, 2025
