Landslide Threat Forces Evacuations In Swiss Village
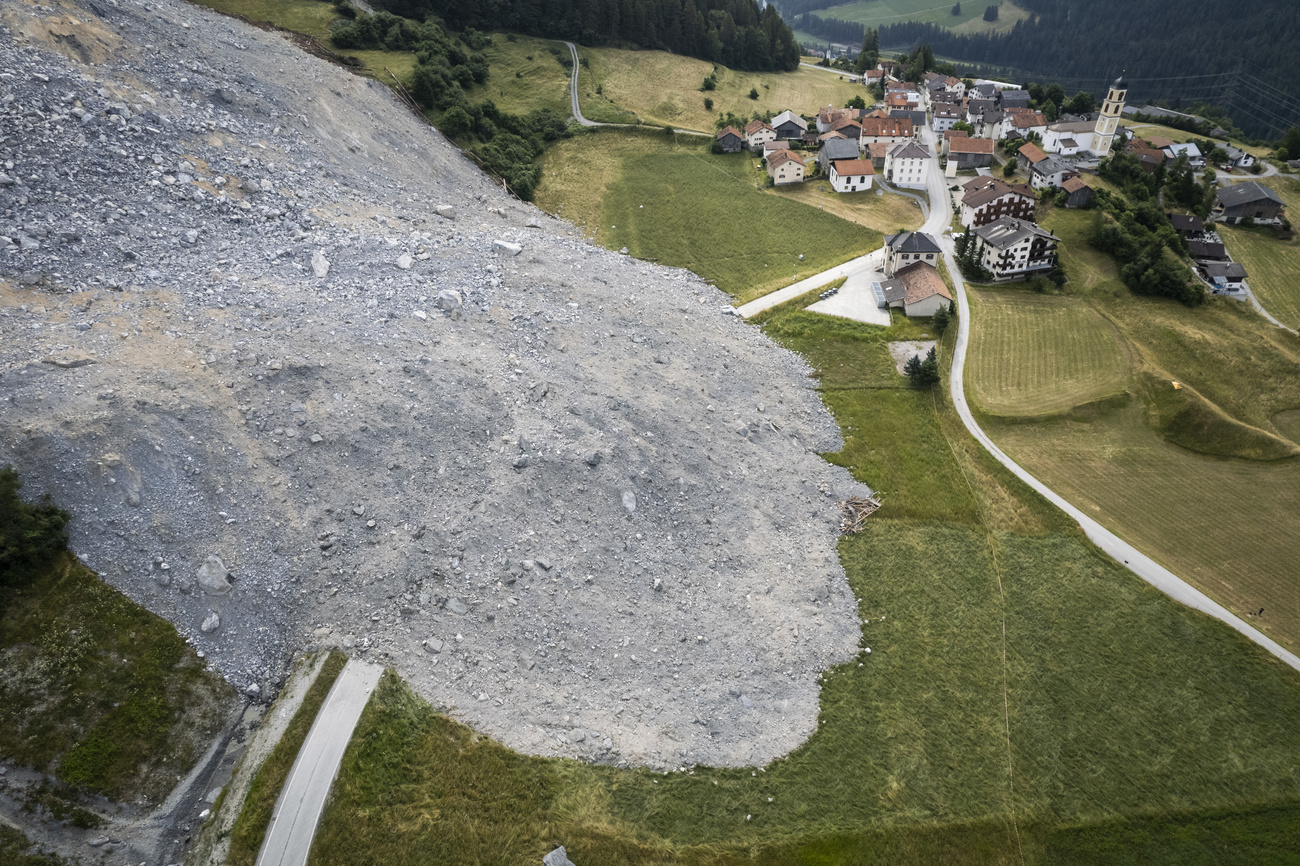

Table of Contents
The Imminent Landslide Threat
The imminent danger of a catastrophic landslide forced the swift evacuation of the Swiss village. This section delves into the geological instability and the early warning systems employed (or lacking) in this situation.
Geological Instability
The geological factors contributing to the landslide risk are complex and interconnected. The mountainside is composed of unstable shale and clay layers, prone to saturation and slippage, especially during periods of heavy rainfall. The steep slope angle further exacerbates the risk.
- Specific geological makeup: The mountainside consists primarily of highly weathered shale and clay, lacking sufficient cohesion to withstand the pressure of saturated soil.
- History of past landslides: Historical records indicate several smaller landslides in the area over the past century, hinting at the inherent instability of the terrain.
- Recent weather patterns: Unusually heavy rainfall in the weeks leading up to the evacuation significantly increased the water content of the soil, dramatically reducing its shear strength and increasing the likelihood of a major landslide. Rainfall totals exceeded [Insert Data if available, e.g., 200mm in a week]. The prolonged saturation weakened the already unstable slopes.
Early Warning Systems and Monitoring
While the village did not possess a sophisticated, real-time landslide monitoring system, geological surveys and historical data informed the risk assessment. However, the effectiveness of these methods in predicting the precise timing of a landslide is limited.
- Monitoring techniques: The primary monitoring involved visual inspections by geologists and analysis of historical rainfall data. Ground-penetrating radar may have been used in previous studies of the area but was not continuously monitored.
- Effectiveness of early warning: The existing system proved effective in identifying a high risk but lacked the precision to provide sufficient warning for a timely evacuation, highlighting the need for advanced monitoring technology. The system relied heavily on visual inspection and historical data, lacking a real-time, automated alert system.
Evacuation Procedures and Support for Affected Residents
The evacuation was a carefully orchestrated operation involving local authorities, emergency services, and volunteer organizations. This section details the process and the support offered to displaced residents.
Evacuation Process
The evacuation order was issued with less than [Insert timeframe if available, e.g., 24 hours] notice, prompting a rapid response from residents. Authorities utilized a combination of sirens and direct phone calls to alert residents, emphasizing the urgency of the situation.
- Timeline of the evacuation: The evacuation began at [Insert time if available] and was largely completed within [Insert timeframe if available].
- Methods of communication: Sirens were used to alert residents, supplemented by phone calls and announcements via local media.
- Transport methods: Local buses and private vehicles were used to transport residents to designated evacuation centers.
Support and Resources
Evacuees were provided with temporary housing in nearby towns and villages, along with food, clothing, and essential supplies. Psychological support was also offered to address the trauma and stress associated with the evacuation.
- Organizations involved: The Red Cross, local government agencies, and volunteer groups provided aid and support to the evacuees.
- Type of support offered: Support included temporary accommodation in hotels and community centers, food provisions, clothing, financial assistance, and psychological counseling.
Long-Term Solutions and Risk Mitigation
Addressing the long-term landslide risk requires a multi-pronged approach that combines engineering solutions, effective land-use planning, and public awareness initiatives.
Engineering Solutions
Several engineering solutions can be implemented to stabilize the mountainside and mitigate the risk of future landslides.
- Possible solutions: These may include constructing retaining walls, installing drainage systems to divert surface water, terracing the slope to reduce its angle, and bioengineering techniques to improve soil stability.
- Feasibility and cost: The feasibility and cost-effectiveness of these solutions need to be carefully evaluated, taking into account the geological conditions and the environmental impact.
Land-Use Planning and Zoning
Effective land-use planning and zoning regulations are crucial in minimizing the risk of landslides.
- Recommendations for future development: Future development in high-risk areas should be strictly regulated or prohibited altogether.
- Importance of building codes: Strict building codes and regulations are essential to ensure that structures are built to withstand potential ground movement.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about landslide risks and promoting community preparedness is paramount in reducing casualties and damage.
- Importance of education: Educating residents about landslide hazards, warning signs, and evacuation procedures is crucial.
- Community preparedness plans: Establishing community preparedness plans that include evacuation routes, assembly points, and communication strategies is essential.
Conclusion
The landslide threat in the Swiss village serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of natural disasters and the critical need for proactive risk management. The successful evacuation demonstrates the importance of early warning systems and community preparedness, while the ongoing efforts to find long-term solutions highlight the commitment to safety and resilience. Understanding and mitigating landslide risks is crucial for the safety and well-being of communities worldwide. Learn more about landslide prevention and preparedness in your area. Stay informed about potential landslide threats and be prepared to act swiftly in case of an emergency. Further research into landslide mitigation techniques and early warning systems is vital to prevent future tragedies like the Swiss village evacuation.

Featured Posts
-
 Trinidads Defence Minister To Decide On Restrictions For Kartel Concert
May 23, 2025
Trinidads Defence Minister To Decide On Restrictions For Kartel Concert
May 23, 2025 -
 Interpreting Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 And Laser 101 7 Results
May 23, 2025
Interpreting Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 And Laser 101 7 Results
May 23, 2025 -
 Jonathan Groffs Just In Time Opening A Star Studded Affair
May 23, 2025
Jonathan Groffs Just In Time Opening A Star Studded Affair
May 23, 2025 -
 Sexist Chants Aimed At Female Referee Spark Investigation
May 23, 2025
Sexist Chants Aimed At Female Referee Spark Investigation
May 23, 2025 -
 Bahrain Gp Qualifying Piastri Takes Pole
May 23, 2025
Bahrain Gp Qualifying Piastri Takes Pole
May 23, 2025
