Measles Cases In The US: A Slowdown Explained
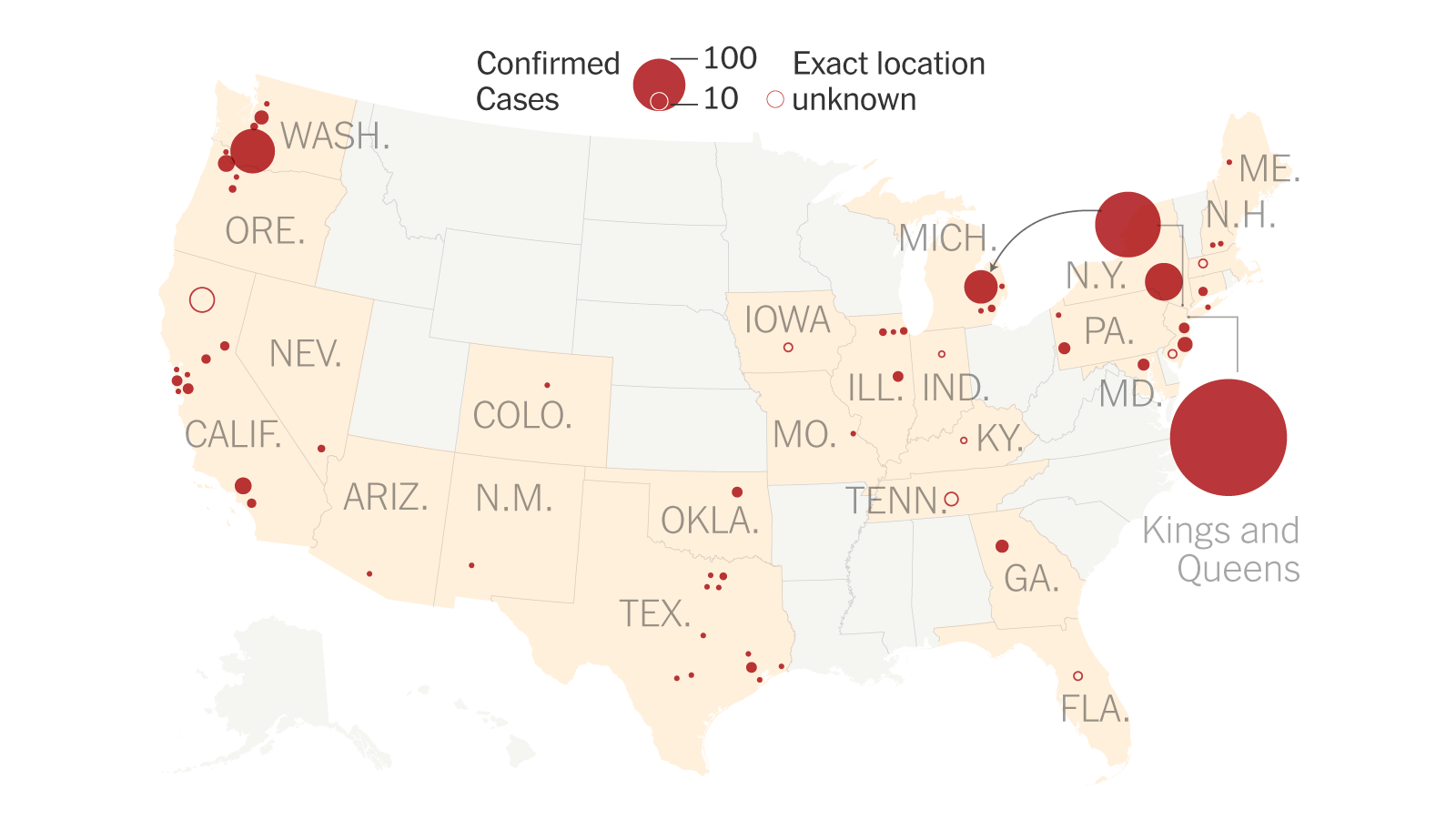
Table of Contents
Increased Vaccination Rates: A Crucial Factor
A strong correlation exists between higher MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccination rates and the decline in measles cases. Increased vaccination coverage is undeniably a cornerstone of this positive shift in Measles Cases in the US. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported a noticeable uptick in MMR vaccination rates across various age groups.
- Data from CDC on MMR vaccination coverage: The CDC's data shows a significant increase in MMR vaccination coverage among children aged 1-5, reaching over 90% in many states. This improved coverage significantly reduces the risk of measles outbreaks.
- State-level initiatives: Several states implemented targeted vaccination campaigns, including mobile vaccination clinics and outreach programs in underserved communities. These initiatives played a crucial role in boosting vaccination rates, particularly in areas with previously low coverage.
- Increased parental awareness campaigns: Public health efforts focusing on educating parents about the safety and effectiveness of the MMR vaccine have significantly increased parental confidence in immunization. Addressing vaccine hesitancy through factual information and open dialogue has been pivotal in raising vaccination rates.
Effective Public Health Interventions
Beyond vaccination, effective public health interventions have been instrumental in controlling measles outbreaks and contributing to the reduced number of Measles Cases in the US. Swift and decisive action during outbreaks has prevented widespread transmission.
- Successful public health campaigns: Targeted campaigns emphasizing the importance of vaccination, early detection, and isolation of infected individuals successfully influenced public behavior. Clear messaging, utilizing various media channels, reached a broader audience.
- Contact tracing effectiveness: Rigorous contact tracing enabled public health officials to quickly identify and isolate individuals who came into contact with infected persons. This strategy prevented further spread of the virus within the community.
- Role of quick response teams: Rapid response teams were deployed to affected areas to implement control measures, including vaccination campaigns in high-risk populations and isolation procedures. These teams played a vital role in minimizing the impact of outbreaks.
The Role of Herd Immunity in Preventing Outbreaks
Herd immunity is a crucial concept in understanding the decline in Measles Cases in the US. It refers to the indirect protection of unvaccinated individuals when a significant percentage of the population is vaccinated. This protection is achieved through the reduction of the virus's ability to spread.
- Herd immunity defined: Herd immunity occurs when a large enough portion of the population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread. This indirectly protects those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants or individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Protection of unvaccinated individuals: High vaccination rates establish a protective shield around those who cannot be vaccinated, minimizing their risk of exposure. This is especially critical for vulnerable populations.
- Percentage needed for herd immunity: For measles, a vaccination rate of around 95% is generally considered necessary to achieve herd immunity.
Challenges and Ongoing Concerns
While the slowdown in Measles Cases in the US is encouraging, it's vital to acknowledge that measles remains a significant threat. Challenges persist, requiring continued vigilance.
- Vaccine hesitancy and its causes: Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and unfounded concerns about vaccine safety, remains a significant obstacle to achieving and maintaining high vaccination rates. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication and education is crucial.
- Dangers of misinformation: The spread of misinformation regarding vaccine safety poses a serious risk to public health. Combating this requires a multi-pronged approach involving fact-checking, media literacy education, and promoting reliable sources of health information.
- Importance of continued vigilance: Maintaining high vaccination rates, strengthening public health infrastructure, and continuing robust surveillance efforts are crucial to prevent future outbreaks of measles. complacency is dangerous.
Conclusion: Understanding the Slowdown in Measles Cases in the US
The recent decrease in Measles Cases in the US is a result of a multifaceted approach: increased vaccination rates, effective public health interventions, and the establishment of herd immunity. Maintaining high vaccination coverage is paramount in preventing future outbreaks. Continued efforts are needed to address vaccine hesitancy and combat misinformation. Understanding US Measles trends and actively participating in measles prevention in the US are key. Learn more about measles, get vaccinated if you haven't already, and support public health initiatives to protect yourself and your community. Let's work together to ensure measles remains a rare disease in the US.

Featured Posts
-
 Bruno Fernandes Close To Joining Tottenham Hotspur
May 30, 2025
Bruno Fernandes Close To Joining Tottenham Hotspur
May 30, 2025 -
 Cool Wet And Windy Weather Impacts San Diego County
May 30, 2025
Cool Wet And Windy Weather Impacts San Diego County
May 30, 2025 -
 E Thessalia Gr Pasxalines Ekpompes And Metadoseis
May 30, 2025
E Thessalia Gr Pasxalines Ekpompes And Metadoseis
May 30, 2025 -
 Is A New Electric Nissan Primera On The Horizon
May 30, 2025
Is A New Electric Nissan Primera On The Horizon
May 30, 2025 -
 Andrej Kramarics Penalty Saves Hoffenheim From Augsburg Defeat
May 30, 2025
Andrej Kramarics Penalty Saves Hoffenheim From Augsburg Defeat
May 30, 2025
