Measles Outbreak In The U.S.: A State-by-State Analysis
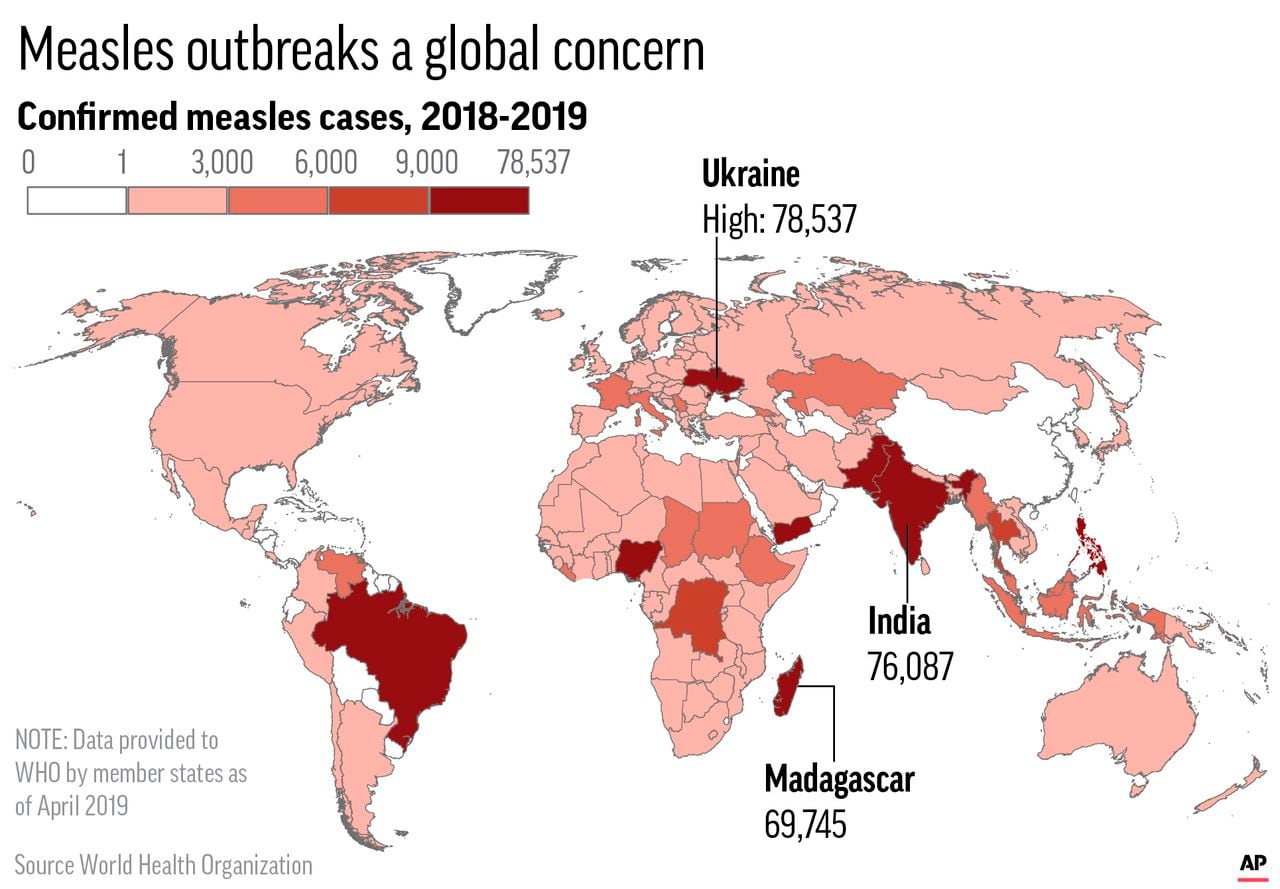
Table of Contents
States with the Highest Reported Measles Cases
Several states have reported significantly higher numbers of measles cases than others, creating measles hotspots requiring focused public health interventions. Understanding the geographical distribution of the US measles cases is crucial for effective resource allocation and targeted prevention strategies. The following data represents reported cases and may not reflect the full extent of the outbreak due to underreporting or delayed reporting.
(Insert a visually appealing map of the US here, color-coded by the number of measles cases reported in each state. Consider using interactive map tools for optimal user experience.)
-
State X (e.g., California): As of [Date], California reported [Number] measles cases. The majority of cases were concentrated in [Specific regions, e.g., Los Angeles County, Orange County], primarily affecting unvaccinated children and young adults. Many cases were linked to a specific event or location, highlighting the rapid transmission potential of measles.
-
State Y (e.g., New York): New York reported [Number] measles cases, with clusters identified in [Specific regions, e.g., Rockland County, Brooklyn]. Many of these outbreaks were associated with unvaccinated individuals within Orthodox Jewish communities. The situation underscores the need for targeted outreach and educational campaigns within specific demographic groups.
-
State Z (e.g., Washington): Washington State experienced [Number] measles cases, with the outbreak initially linked to international travel and subsequently spreading within unvaccinated communities. The state implemented robust contact tracing and quarantine measures to control the spread effectively. This emphasizes the importance of swift public health responses.
Factors Contributing to the Measles Outbreak
The resurgence of measles in the US is multifactorial, with vaccine hesitancy playing a significant role. Low vaccination rates, fueled by misinformation and anti-vaccine movements, have created pockets of vulnerability where the virus can easily spread.
-
Declining vaccination rates due to misinformation: The spread of misinformation about vaccine safety via social media and unreliable sources significantly impacts vaccination rates. This leads to decreased community immunity and increased susceptibility to outbreaks.
-
The influence of anti-vaccine movements and social media: Anti-vaccine groups actively disseminate misinformation, exploiting anxieties and fears related to vaccine safety. Social media platforms, despite efforts to combat misinformation, continue to facilitate the spread of these harmful narratives.
-
Gaps in access to healthcare and vaccination services in underserved communities: Limited access to healthcare and vaccination services disproportionately affects underserved communities, creating disparities in vaccination rates and increased vulnerability to outbreaks.
-
International travel and importation of the virus: International travel plays a role in introducing measles into the US, particularly from countries with lower vaccination rates or ongoing outbreaks. This highlights the interconnected nature of global health security.
Public Health Responses and Prevention Strategies
Effective public health responses are crucial in controlling and preventing measles outbreaks. Strategies include vaccination campaigns, contact tracing, quarantine measures, and improved access to healthcare.
-
Vaccination campaigns targeting specific communities: Targeted vaccination campaigns are implemented in communities with low vaccination rates or identified outbreaks to rapidly increase herd immunity. These campaigns often incorporate community engagement and outreach to address concerns and misconceptions.
-
Public health communication strategies to address misinformation: Clear, evidence-based communication is vital in countering misinformation about vaccines. Public health officials work to disseminate accurate information and address specific concerns and anxieties related to vaccines.
-
Contact tracing and quarantine protocols to contain the spread: Identifying and isolating individuals exposed to measles is essential in controlling the spread. Contact tracing and quarantine are crucial tools to break the chain of transmission.
-
Efforts to improve vaccine access and affordability: Improving access to affordable vaccines and healthcare services, especially in underserved communities, is crucial to ensuring equitable protection against measles.
The Importance of Measles Vaccination
Measles vaccination, specifically the MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) vaccine, remains the most effective strategy for preventing measles outbreaks. The vaccine's high effectiveness, coupled with the serious potential complications of measles, makes vaccination a crucial public health measure.
-
MMR vaccine effectiveness in preventing measles: The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles, with a typical effectiveness rate of over 97%. This significantly reduces the risk of infection and severe complications.
-
Importance of achieving herd immunity to protect vulnerable populations: High vaccination rates create herd immunity, which protects individuals who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. This shields vulnerable populations from the risk of infection.
-
Addressing common myths and concerns surrounding the measles vaccine: Addressing common myths and misconceptions about the measles vaccine through factual information is vital in building trust and increasing vaccination rates.
-
Resources for parents and individuals seeking accurate information about vaccines: Reliable sources of information about vaccines, such as the CDC website and other reputable health organizations, are crucial in empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
Conclusion
The resurgence of measles in the U.S. highlights the urgent need for increased vaccination rates and targeted public health interventions. This state-by-state analysis reveals the geographical distribution of outbreaks and the contributing factors, underscoring the importance of addressing vaccine hesitancy and improving access to healthcare. The data emphasizes that measles is a preventable disease and achieving high vaccination rates is essential in protecting communities.
Call to Action: Protect yourself and your community from the preventable disease of measles. Learn more about the MMR vaccine, find vaccination resources near you through your local health department or healthcare provider, and help combat misinformation by sharing accurate information about measles prevention. Staying informed about the measles outbreak in your state is crucial for protecting your health and the health of those around you. Don't delay; get vaccinated today and contribute to herd immunity.

Featured Posts
-
 Pete Muntean On Cnn What Happens When Air Traffic Control Fails
May 30, 2025
Pete Muntean On Cnn What Happens When Air Traffic Control Fails
May 30, 2025 -
 Marine Le Pen Et La Justice Jacobelli Defend Une Application Equitable De La Loi
May 30, 2025
Marine Le Pen Et La Justice Jacobelli Defend Une Application Equitable De La Loi
May 30, 2025 -
 Sinner And Djokovic Analyzing Their French Open Prospects
May 30, 2025
Sinner And Djokovic Analyzing Their French Open Prospects
May 30, 2025 -
 Brooke Shields No Children With Andre Agassi A Decision She Doesnt Regret
May 30, 2025
Brooke Shields No Children With Andre Agassi A Decision She Doesnt Regret
May 30, 2025 -
 Eight Ways Trumps Trade War Is Harming Canadas Economy
May 30, 2025
Eight Ways Trumps Trade War Is Harming Canadas Economy
May 30, 2025
