NATO Defense Spending: Progress Towards Trump-Era Goal
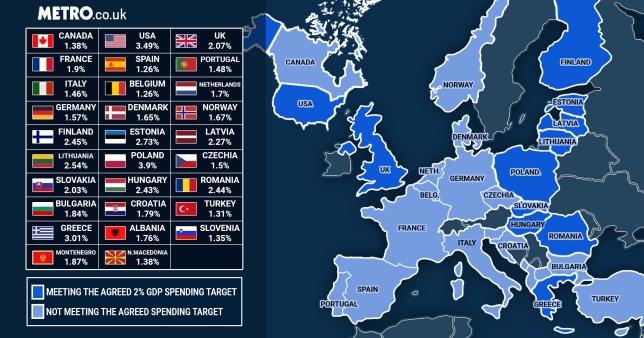
Table of Contents
H2: The Trump Administration's Call for Increased Defense Spending
The Trump administration's presidency was marked by a concerted effort to increase NATO defense spending, primarily focusing on the long-standing goal of achieving a 2% GDP target for defense expenditure.
H3: The 2% GDP Target
The 2% GDP target for defense spending, initially agreed upon by NATO members in 2006 at the Riga Summit, represents the commitment of each member nation to contribute a minimum of 2% of its gross domestic product to defense. The rationale behind the target was to ensure that each member contributes fairly to the alliance's collective security, thereby strengthening its overall defense capabilities. However, the target has faced considerable criticism. Some argue it’s an arbitrary number that doesn’t account for varying national security needs and economic capacities. Others critique the focus on a percentage of GDP rather than considering total spending or the effectiveness of the spending.
- Brief history of the 2% target's origin and evolution within NATO: The 2% target emerged from discussions surrounding burden-sharing within NATO, following criticism of some members' perceived underinvestment in defense.
- Specific examples of the Trump administration's pressure on member states to meet the target: President Trump frequently criticized European allies for their insufficient defense spending, publicly pressuring them to meet the 2% target. This pressure included bilateral discussions and public statements.
- Mention of the political and economic arguments supporting and opposing the 2% target: Proponents highlight its importance for collective security and deterring potential aggressors. Opponents raise concerns about the economic burden, particularly for countries with less robust economies, and the potential for reduced investment in other crucial areas like healthcare and education.
Supporting Details: Before Trump's presidency, many NATO members consistently fell short of the 2% mark. Following his calls for increased spending, there was a noticeable, albeit uneven, uptick in several member states' defense budgets. Data from the NATO website and reports from organizations like the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) provide valuable insights into this shift.
H2: Progress Towards the 2% Target: A Country-by-Country Analysis
Assessing progress towards the 2% target requires a nuanced, country-by-country analysis. While some nations have made substantial strides, others continue to lag.
H3: Top Performers
Countries like Greece and Poland have significantly increased their defense spending, surpassing or nearing the 2% GDP target. This surge is often linked to regional security concerns and a heightened perception of threats. Their increased spending demonstrates a commitment to strengthening their national defenses within the broader NATO framework. Specific data on their defense budgets and GDP growth will illustrate this point.
H3: Lagging Members
Several countries, however, remain significantly below the 2% mark. Economic constraints, differing threat perceptions, and domestic political priorities often contribute to lower defense spending. Analyzing these factors on a case-by-case basis, considering specific country contexts, is vital to understanding the varied approaches to NATO defense spending.
- Create a table or chart visually comparing the defense spending of different NATO members: This visual representation effectively compares spending levels and their progression toward the 2% target. Data should be sourced from reputable organizations like SIPRI and NATO.
- Use a variety of metrics beyond just the 2% GDP target (e.g., spending increases as a percentage, per capita spending): Utilizing multiple metrics provides a more comprehensive understanding of defense spending efforts.
- Include citations for all data presented: Transparency and accuracy are crucial.
Supporting Details: The reasons behind varying levels of defense spending are complex and multifaceted. A country's geographic location, proximity to conflict zones, and the perceived level of threat significantly influence its defense spending decisions.
H2: Factors Influencing NATO Defense Spending
Several key factors interact to shape NATO member states' decisions regarding defense spending.
H3: Geopolitical Factors
The ongoing war in Ukraine has profoundly impacted NATO defense spending. The conflict has highlighted the need for enhanced collective security and prompted many member states to reassess their defense capabilities and budgets accordingly. This includes increased investments in areas such as cyber defense and modernizing military equipment.
H3: Economic Considerations
A nation's economic strength profoundly impacts its capacity to invest in defense. Countries with strong, growing economies generally have more resources to allocate towards defense spending. Conversely, nations facing economic difficulties may prioritize other domestic needs over defense investment.
H3: Public Opinion and Domestic Politics
Public support for increased defense spending is crucial for governments to implement such policies. Public opinion polls, media coverage, and political debates significantly shape the public narrative around defense spending, influencing government decisions.
- Discuss the potential long-term implications of increased defense spending on national economies: Increased defense spending can stimulate economic growth through job creation and technological advancements, but it can also strain national budgets.
- Explain the role of public opinion polls and political debates in shaping defense spending policies: Public opinion can act as a constraint or a driver for increased defense spending, depending on the prevalent sentiment.
- Analyze the impact of changing alliances and geopolitical shifts on NATO defense spending priorities: Shifting geopolitical landscapes can prompt changes in defense spending priorities, leading to reallocation of resources.
Supporting Details: Expert opinions from security analysts, economists, and policymakers add valuable context to this complex interplay of factors.
3. Conclusion
Progress towards the Trump-era goal of increased NATO defense spending has been uneven. While several member states have significantly increased their defense budgets, others continue to lag, reflecting the diverse economic, political, and security contexts of each nation. The 2% GDP target, while a useful benchmark, does not fully capture the complexities of defense investment. The war in Ukraine has underscored the importance of robust defense spending, and it will be crucial to continue to monitor NATO defense spending and the ongoing debates surrounding its efficacy and equitability.
Key Takeaways: Reaching the 2% GDP target involves numerous challenges, from economic constraints to differing threat perceptions. Geopolitical events, public opinion, and domestic politics all play vital roles in shaping individual nations' defense spending decisions. A holistic approach, considering these various factors, is essential for understanding the dynamics of NATO defense spending.
Call to Action: Stay informed about NATO defense spending and the ongoing discussions about NATO's defense budget. Research the future of NATO defense spending and its implications for global security. Understanding the nuances of NATO's defense spending is vital for comprehending the dynamics of transatlantic security and the evolving global geopolitical landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Community Assists Bryan County Sheriffs Office In Search For Missing Teen
May 28, 2025
Community Assists Bryan County Sheriffs Office In Search For Missing Teen
May 28, 2025 -
 Could You Win The 202m Euromillions Jackpot Your Odds And Next Steps
May 28, 2025
Could You Win The 202m Euromillions Jackpot Your Odds And Next Steps
May 28, 2025 -
 Man Utd Transfer News Star Players Future Uncertain Amidst Ownership Dispute
May 28, 2025
Man Utd Transfer News Star Players Future Uncertain Amidst Ownership Dispute
May 28, 2025 -
 May 20 Mlb Player Prop Picks Kyle Stowers And Wilmer Flores
May 28, 2025
May 20 Mlb Player Prop Picks Kyle Stowers And Wilmer Flores
May 28, 2025 -
 Should You Consider Glp 1 Medications Weighing The Benefits And Risks
May 28, 2025
Should You Consider Glp 1 Medications Weighing The Benefits And Risks
May 28, 2025
