New Research: Do COVID-19 Vaccines Lower Long COVID Risk?
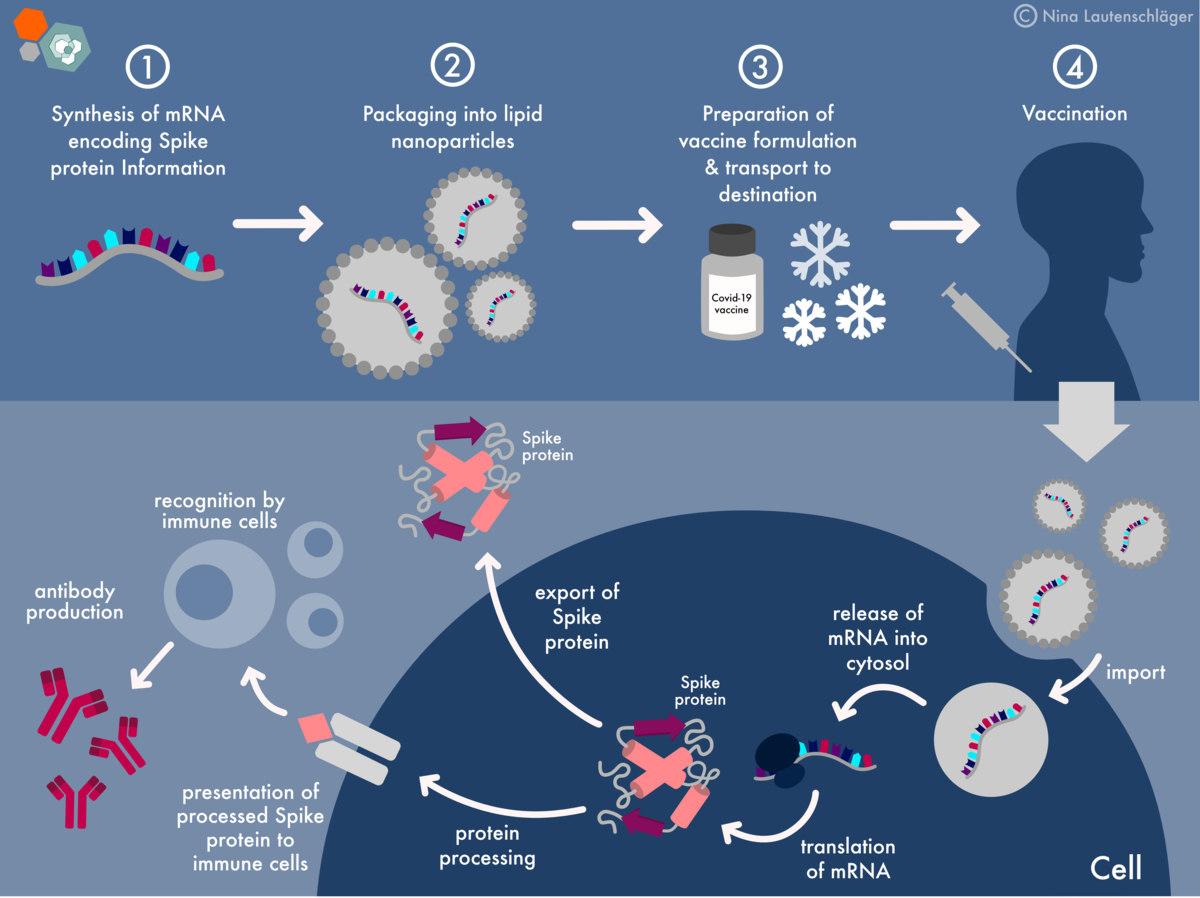
Table of Contents
The Science Behind Long COVID
Understanding the Mechanisms of Long COVID
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID-19 syndrome, chronic COVID, or long-haul COVID, is a complex condition affecting individuals weeks or months after an initial COVID-19 infection. It's characterized by a wide range of persistent symptoms, with fatigue, brain fog ("cognitive dysfunction"), and shortness of breath being among the most common. The exact mechanisms driving Long COVID remain unclear, but several potential contributors are under investigation:
- Immune dysregulation: An overactive or dysregulated immune response may contribute to ongoing inflammation and damage to various organs.
- Persistent viral presence: While rare, fragments of the SARS-CoV-2 virus may persist in some individuals, potentially triggering continued inflammation and symptoms.
- Autoimmune responses: The body's immune system may mistakenly attack its own tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms.
- Microclotting: Small blood clots throughout the body could restrict blood flow and contribute to various Long COVID symptoms.
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective treatments and preventative strategies, including the role of COVID-19 vaccination.
COVID-19 Vaccination and its Impact on Long COVID Risk
Studies Investigating Vaccine Efficacy Against Long COVID
Several studies have investigated the association between COVID-19 vaccination and the reduced risk of developing Long COVID. While research is ongoing, several studies suggest a correlation between vaccination and a lower incidence of Long COVID.
- Study 1 (Example): A large-scale study published in the Lancet (replace with actual study) found a significant reduction in the risk of Long COVID among vaccinated individuals compared to unvaccinated individuals. This study employed a cohort design, following a large group of individuals over time.
- Study 2 (Example): Another study conducted by the CDC (replace with actual study) demonstrated a similar trend, observing a lower prevalence of persistent symptoms among those who received a complete COVID-19 vaccine series. This study used a case-control methodology.
It is important to note that limitations exist in many studies, such as variations in sample size, study design, and differing definitions of Long COVID. Further research is needed to solidify these findings and address these limitations. Despite these limitations, the emerging data consistently suggest that COVID-19 vaccination offers a measure of protection against Long COVID.
Types of COVID-19 Vaccines and Their Effectiveness Against Long COVID
Comparing mRNA and other vaccine types
Currently, research is still exploring whether different types of COVID-19 vaccines (mRNA, viral vector, etc.) exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness in preventing Long COVID. While some preliminary studies suggest that mRNA vaccines might offer slightly better protection, more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
- Ongoing Research: Many studies are actively comparing the long-term efficacy of different vaccine types against Long COVID, focusing on both the incidence and severity of persistent symptoms. These ongoing studies are crucial in providing a more comprehensive understanding of the differences, if any, between vaccine types in preventing Long COVID.
- Data Limitations: Currently, data comparing the efficacy of various COVID-19 vaccine types against Long COVID are still limited, requiring further investigation and larger-scale studies to confirm any potential differences.
Boosters and Long COVID Risk Reduction
The Role of Booster Shots
Emerging evidence suggests that booster shots may further reduce the risk of developing Long COVID. While the exact mechanisms aren't fully understood, booster shots help maintain higher levels of antibodies and strengthen the immune response against SARS-CoV-2, potentially mitigating the risk of prolonged illness.
- Supporting Evidence: Studies (replace with actual studies) are showing that individuals who received booster doses experienced a lower likelihood of developing persistent symptoms compared to those only receiving the initial vaccine series.
- Ongoing Debate: The extent to which boosters reduce Long COVID risk is still under investigation and further research is needed to solidify these findings and determine optimal booster schedules.
- Health Organization Recommendations: Many health organizations recommend staying up-to-date with COVID-19 vaccinations, including booster doses, to maximize protection against both initial infection and the potential for developing Long COVID.
Conclusion
In summary, while the mechanisms of Long COVID remain complex, research indicates a significant association between COVID-19 vaccination and a reduced risk of developing this debilitating condition. Studies suggest that vaccination, particularly with a complete primary series and booster shots, offers substantial protection. Although more research is needed to fully understand the nuances of vaccine type efficacy and the optimal booster schedule, the current evidence strongly supports the importance of COVID-19 vaccination in mitigating the risk of Long COVID. Stay protected against the debilitating effects of Long COVID. Talk to your doctor about getting vaccinated and boosted today. Learn more about the latest research on COVID-19 vaccines and Long COVID prevention to make informed decisions about your health.

Featured Posts
-
 Malcolm In The Middle Revival What We Know So Far
May 29, 2025
Malcolm In The Middle Revival What We Know So Far
May 29, 2025 -
 Cota Moto Gp Johann Zarcos Dramatic Performance Upgrade
May 29, 2025
Cota Moto Gp Johann Zarcos Dramatic Performance Upgrade
May 29, 2025 -
 Zoellner Family Honors Outstanding Paraeducator
May 29, 2025
Zoellner Family Honors Outstanding Paraeducator
May 29, 2025 -
 New Information On Malcolm In The Middle Revival From Bryan Cranston
May 29, 2025
New Information On Malcolm In The Middle Revival From Bryan Cranston
May 29, 2025 -
 New Arcane Ep Fuels Speculation Vi And Caitlyn Spinoff
May 29, 2025
New Arcane Ep Fuels Speculation Vi And Caitlyn Spinoff
May 29, 2025
