New York City's 3°C Temperature Drop: Canadian Wildfire Smoke's Impact
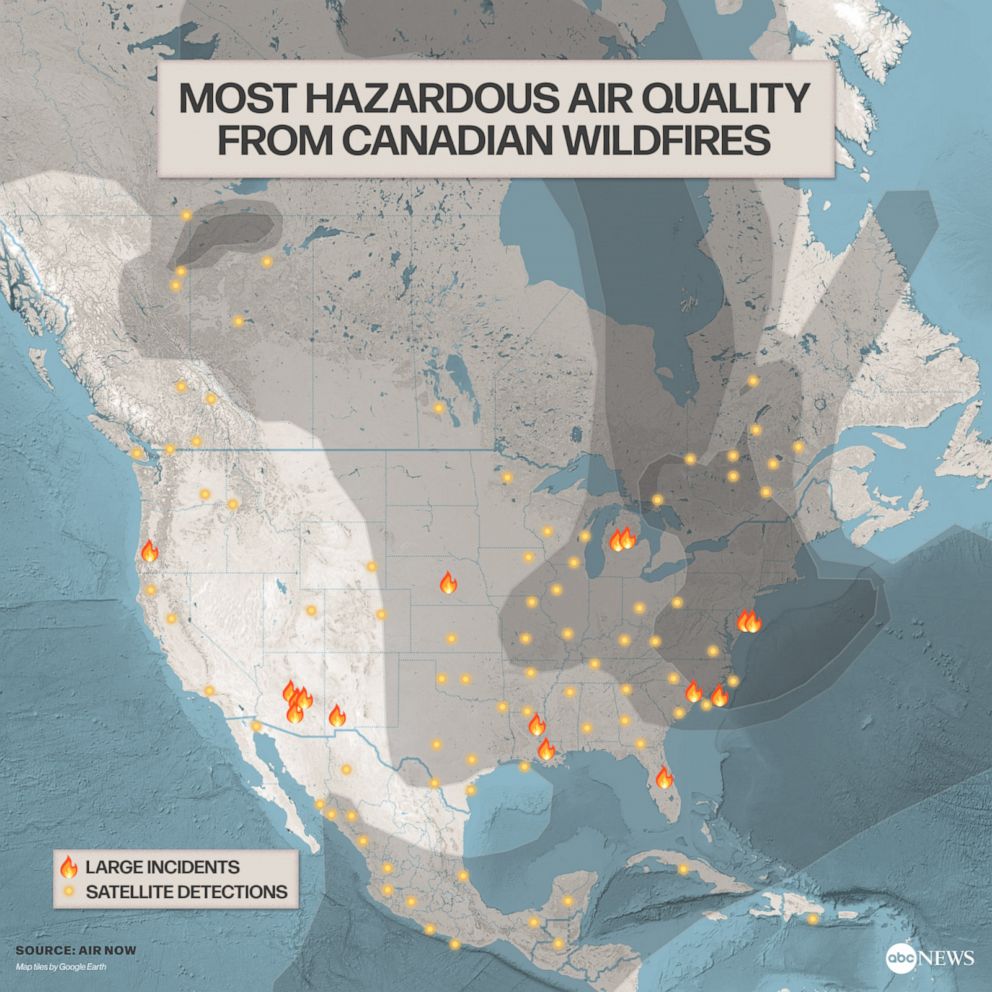
Table of Contents
The Meteorological Mechanism Behind the Temperature Drop
The unexpected temperature plunge in New York City wasn't a random weather fluctuation; it was a direct consequence of the massive plume of smoke from Canadian wildfires. Several meteorological factors contributed to this dramatic drop:
-
Temperature Inversion and Smoke Blanket: The dense smoke plume acted like a thick blanket, trapping heat near the ground and creating a temperature inversion. Normally, temperature decreases with altitude, but the smoke layer prevented warmer air from rising, resulting in cooler temperatures at the surface. This effect is similar to how clouds can trap heat at night.
-
Reduced Solar Radiation: The smoke particles effectively absorbed a significant amount of solar radiation, preventing sunlight from reaching the ground and warming the city. This reduction in incoming solar energy directly contributed to the lower temperatures experienced. Think of it like wearing a thick, dark coat on a sunny day – it keeps you cooler.
-
Atmospheric Pressure and Wind Patterns: Atmospheric pressure systems and prevailing wind patterns played a crucial role in concentrating the smoke over New York City. High-pressure systems can trap pollutants, preventing their dispersal, while specific wind patterns channeled the smoke plume directly into the city.
-
Data and Visuals: (Note: This section would ideally include graphs showing the temperature drop correlated with smoke density measurements, air quality index data, and possibly satellite imagery depicting the smoke plume over NYC. The inclusion of such visuals would significantly enhance the article's impact and SEO.)
Health Impacts of Wildfire Smoke on New York City Residents
The wildfire smoke wasn't just a meteorological phenomenon; it posed a serious threat to public health. High concentrations of particulate matter (PM2.5), a primary component of wildfire smoke, significantly impacted air quality, leading to various health problems:
-
Respiratory Problems: PM2.5 particles are small enough to penetrate deep into the lungs, causing irritation, inflammation, and exacerbating existing respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis. Many New Yorkers experienced coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
-
Cardiovascular Disease: Studies have linked exposure to wildfire smoke with increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. The tiny particles can trigger inflammation and blood clotting, increasing the strain on the cardiovascular system.
-
Eye Irritation: The smoke also caused widespread eye irritation, including burning, itching, and redness.
-
Vulnerable Populations: Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions were particularly vulnerable to the negative health impacts of the wildfire smoke. Hospitals reported a surge in emergency room visits and hospital admissions related to respiratory issues during this period.
-
Air Quality Advisories: Authorities issued air quality advisories urging residents to limit outdoor activities and take necessary precautions, such as wearing N95 masks. Public health recommendations included staying indoors, using air purifiers, and minimizing strenuous physical activity.
The Broader Implications of Climate Change and Wildfire Smoke
The New York City temperature drop is not an isolated incident; it underscores the increasingly significant link between climate change, wildfires, and air quality.
-
Climate Change and Wildfire Frequency: Climate change, driven by global warming and increased greenhouse gas emissions, is contributing to more frequent and intense wildfires. Higher temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
-
Deforestation and Human Activities: Deforestation, unsustainable land management practices, and human-caused ignitions all exacerbate the risk of wildfires. Reducing deforestation and implementing responsible land management strategies are crucial for mitigating wildfire risk.
-
Long-Term Environmental Consequences: Wildfire smoke has long-term environmental consequences, including damage to ecosystems, water pollution, and reduced air quality. The impact on air quality can be felt far beyond the immediate vicinity of the fires.
-
Economic Impacts: Wildfires have substantial economic impacts, including damage to property, infrastructure, and the economy. The costs associated with firefighting, evacuation, and recovery efforts are immense, highlighting the need for preventative measures and improved wildfire management.
Conclusion
The unexpected 3°C temperature drop in New York City, directly attributable to the Canadian wildfires and the resulting smoke, serves as a powerful illustration of the far-reaching consequences of climate change. The event highlighted the significant health risks associated with wildfire smoke, impacting vulnerable populations and straining healthcare systems. The long-term environmental and economic consequences of increasingly frequent and intense wildfires necessitate a proactive approach to climate change mitigation, responsible land management, and preparedness for future events. Understanding the impact of Canadian wildfires on New York City's weather and air quality is crucial. Stay informed about air quality alerts and take necessary precautions during periods of high wildfire smoke. Learn more about mitigating climate change and supporting efforts to reduce wildfire risk. Protect yourself and your community from the effects of future New York City temperature drops caused by wildfire smoke.

Featured Posts
-
 Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Bmw Open Zverev Rallies Into Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Official And Resale Glastonbury 2025 Coach Ticket Prices And Departure Points
May 31, 2025
Official And Resale Glastonbury 2025 Coach Ticket Prices And Departure Points
May 31, 2025 -
 First Northern Super League Debut Players And Coaches Reflect On A Unique Moment
May 31, 2025
First Northern Super League Debut Players And Coaches Reflect On A Unique Moment
May 31, 2025 -
 Fire Season Arrives Early Challenges For Canada And Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Fire Season Arrives Early Challenges For Canada And Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Addresses Failed Drug Test Maintains Innocence
May 31, 2025
Munguia Addresses Failed Drug Test Maintains Innocence
May 31, 2025
