Otter Conservation In Wyoming: Reaching A Turning Point

Table of Contents
The Historical Decline of Otter Populations in Wyoming
The decline of otter populations in Wyoming has a complex history, rooted in habitat destruction and unsustainable hunting practices.
Habitat Loss and Degradation
Historically, habitat loss significantly impacted Wyoming's otters. Damming rivers for hydroelectric power and irrigation drastically altered riverine ecosystems, reducing suitable habitat. Water pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial discharge further degraded water quality, affecting fish populations – the otters' primary food source. Development along riverbanks also fragmented habitat, isolating otter populations and hindering their ability to thrive.
- Specific rivers affected: The Snake River, Green River, and North Platte River all experienced significant habitat loss, impacting otter populations.
- Impact on prey availability: Reduced water quality and altered river flows led to decreased fish populations, directly impacting otter food security and survival rates.
- Population decline statistics: While precise historical data is limited, anecdotal evidence and early trapping records suggest a substantial decline in otter numbers throughout the 20th century.
Impact of Fur Trapping
For many decades, fur trapping played a significant role in the decline of Wyoming's otter populations. While trapping regulations have evolved over time, the historical impact remains undeniable.
- Timeline of trapping regulations: Early trapping practices were largely unregulated, leading to overexploitation. Modern regulations aim to ensure sustainable harvest levels, but their effectiveness is an ongoing area of study and debate regarding Wyoming otter conservation.
- Effectiveness of current regulations: Current regulations are stricter, but their long-term impact on otter populations requires continuous monitoring and assessment. Data on current trapping quotas and their impact on otter numbers is crucial for effective management.
- Historical data on trapping quotas: Analyzing historical trapping quotas alongside population estimates can help inform future management decisions and strategies for Wyoming otter conservation.
Current Conservation Strategies and Their Effectiveness
Recent decades have seen a concerted effort to reverse the decline of Wyoming's otters through various conservation strategies.
Habitat Restoration and Protection
Significant progress has been made in restoring and protecting otter habitats. Initiatives focus on improving water quality, restoring riparian areas, and creating new wetlands.
- Ongoing projects: River restoration projects aim to improve water flow and habitat complexity. Wetland creation initiatives provide crucial foraging and breeding grounds. Land acquisition by conservation organizations protects critical otter habitat from development.
- Organizations involved: The Wyoming Game and Fish Department, along with NGOs like the Wildlife Conservation Society and The Nature Conservancy, are actively involved in these efforts, focusing on vital Wyoming otter conservation.
Monitoring and Research
Ongoing research plays a vital role in understanding otter populations and their needs. Monitoring programs track population trends, habitat use, and the impact of various factors.
- Monitoring methods: Camera trapping, scat analysis, and radio telemetry are used to track otter movements, estimate population sizes, and assess habitat use.
- Key findings: Recent studies have provided valuable insights into otter distribution, habitat requirements, and the effectiveness of conservation measures. These findings inform adaptive management strategies for Wyoming otter conservation.
- Population estimates and trends: While precise numbers remain elusive, ongoing monitoring suggests a gradual increase in otter populations in certain areas, indicating the positive impact of conservation initiatives on Wyoming otter conservation efforts.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness is crucial for successful otter conservation. Educational programs and outreach initiatives aim to foster responsible recreation and stewardship of otter habitats.
- Educational programs: Schools, community groups, and conservation organizations conduct educational programs to inform the public about otters and the importance of their conservation.
- Outreach initiatives: Public awareness campaigns highlight the threats facing otters and promote responsible behavior near their habitats.
- Responsible recreation near otter habitats: Educating the public about responsible activities near otter habitats (e.g., minimizing disturbance, avoiding pollution) is critical for long-term conservation success.
Challenges and Future Outlook for Otter Conservation in Wyoming
Despite progress, significant challenges remain in ensuring the long-term survival of Wyoming's otters.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change poses a significant threat to otter habitats and populations. Changes in water availability, altered river flows, and shifts in prey distribution are potential consequences.
- Effects of drought: Droughts can severely reduce water levels, impacting food availability and habitat connectivity.
- Altered water flows: Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to increased flooding or reduced water flow, impacting habitat suitability.
- Changing prey availability: Climate change can affect fish populations, potentially reducing the availability of otter food sources.
Threats from Human Activity
Human activities continue to pose threats to otters. Pollution from various sources and habitat encroachment remain ongoing concerns.
- Pollution sources: Agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilizers, as well as industrial waste, can contaminate water sources and harm otter health.
- Methods to mitigate these threats: Implementing better farming practices, improving industrial waste management, and strengthening pollution regulations are crucial mitigation strategies for continued Wyoming otter conservation.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Successful otter conservation requires collaboration among government agencies, NGOs, and local communities. Continued partnerships are essential for effective management and long-term success.
- Successful collaborations: Examples of successful collaborations include joint research projects, coordinated habitat restoration efforts, and collaborative public awareness campaigns.
- The need for continued partnerships: Strengthening partnerships and communication among all stakeholders is essential for addressing the multifaceted challenges facing otter conservation in Wyoming.
Conclusion
Otter conservation in Wyoming has reached a critical turning point. While significant progress has been made through habitat restoration, monitoring, and public education, challenges remain, particularly related to climate change and human activity. Continued collaboration and commitment are essential to ensure the long-term survival of otter populations in the state. The success of Wyoming otter conservation hinges on a continued, collective effort.
Call to Action: Learn more about how you can contribute to Otter Conservation in Wyoming. Support organizations working to protect these vital animals and their habitats. Get involved in local conservation initiatives and help spread awareness about the importance of preserving Wyoming's natural heritage. The future of otter conservation in Wyoming depends on collective action.

Featured Posts
-
 Trans Australia Run A Historic Record Under Threat
May 22, 2025
Trans Australia Run A Historic Record Under Threat
May 22, 2025 -
 Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Player Tier List And Best Cards
May 22, 2025
Ea Fc 24 Fut Birthday Ultimate Player Tier List And Best Cards
May 22, 2025 -
 A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
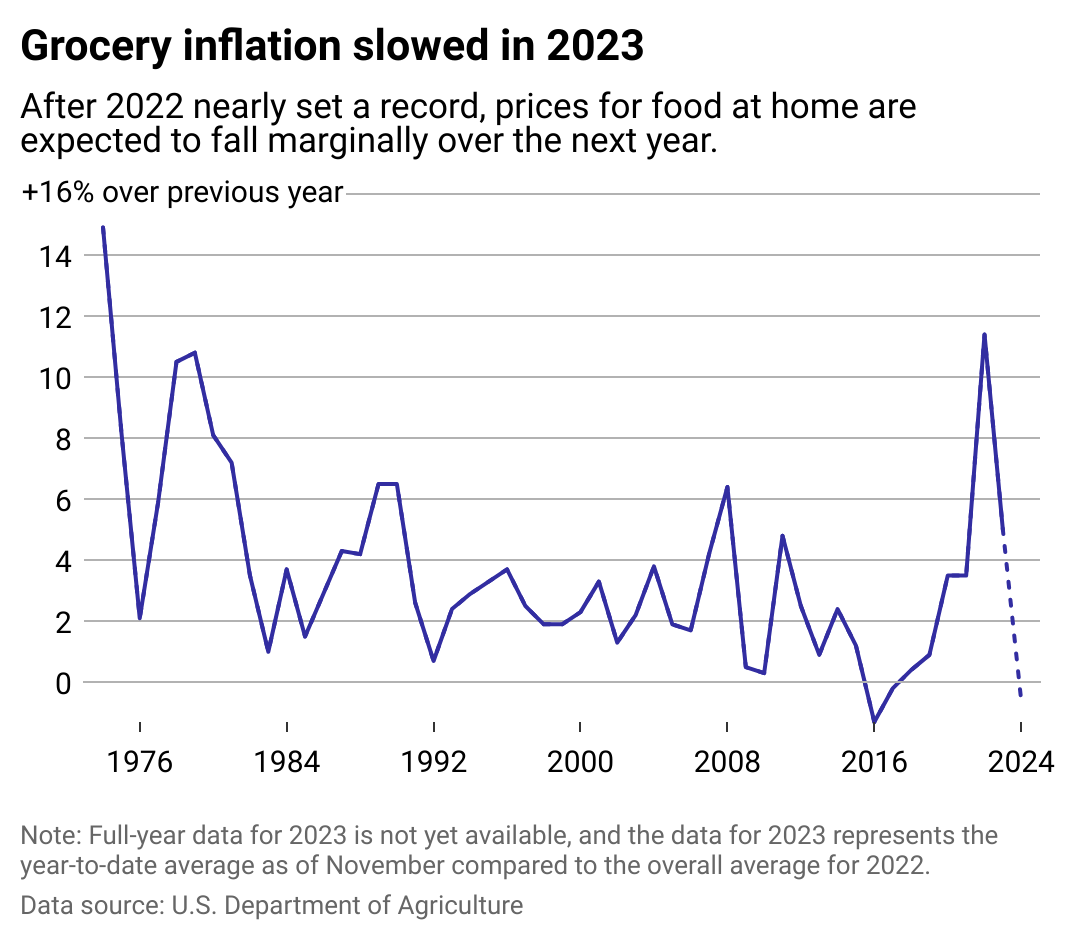 Grocery Inflation Soars Prices Continue To Rise Faster Than Overall Inflation
May 22, 2025
Grocery Inflation Soars Prices Continue To Rise Faster Than Overall Inflation
May 22, 2025 -
 Kenny Picketts Pittsburgh Homecoming Overcoming The Odds
May 22, 2025
Kenny Picketts Pittsburgh Homecoming Overcoming The Odds
May 22, 2025
