Planning A Reactor Power Uprate? Navigating The NRC Process
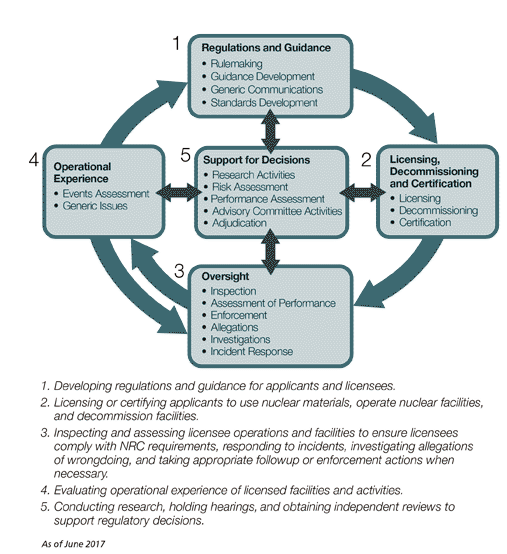
Table of Contents
Understanding the NRC's Regulatory Framework for Reactor Power Uprates
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) holds ultimate authority over all aspects of nuclear power plant operation in the United States, and reactor power uprates are no exception. Their role is to ensure the safety and security of the public and the environment. Understanding the NRC's regulatory framework is paramount for a successful power uprate project.
-
10 CFR Part 50 Requirements: This section of the Code of Federal Regulations details the licensing requirements for nuclear power plants, including those related to power uprates. A thorough understanding of these regulations is critical throughout the entire process. Specific attention must be paid to requirements related to safety analysis, technical specifications, and operational limits.
-
Licensing Process Overview: The NRC's licensing process for a reactor power uprate is multi-staged and rigorous. It generally involves:
- Pre-application meetings: Early engagement with the NRC is crucial to discuss project scope and approach, ensuring alignment with regulatory expectations.
- Submittals: A comprehensive application package must be submitted, meticulously addressing all NRC requirements.
- Reviews: The NRC's staff will conduct a thorough review of the submitted documentation, including safety analysis reports (SARs).
- Inspections: On-site inspections of the facility are standard procedure to verify the accuracy of the submitted information and the plant's condition.
- Licensing Approvals: Upon successful completion of the review and inspection process, the NRC will issue the necessary licenses and approvals.
-
Key Regulations Impacting Power Uprates: Specific regulations related to thermal limits, safety analyses (including probabilistic risk assessments or PRAs), and operational limits are crucial aspects of the power uprate process. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for licensing approval. Understanding these limits is fundamental to determining the feasibility of a power uprate.
-
Compliance: Maintaining strict compliance with all relevant NRC regulations and guidance is absolutely essential throughout the entire project lifecycle, from the initial feasibility study to post-approval implementation and ongoing operation.
Pre-Application Planning: Crucial Steps for Success
Thorough preparation before submitting a power uprate application to the NRC is vital for a smooth and efficient process. This pre-application phase sets the foundation for success.
-
Feasibility Study: Conducting a preliminary feasibility study is the first step. This assessment determines the technical and economic viability of the proposed power uprate, considering factors such as plant capacity, safety margins, and cost-benefit analysis. Power uprate feasibility assessments need to be comprehensive.
-
Expert Team: Assemble a highly qualified team of experts including nuclear engineers, thermal-hydraulic specialists, safety analysts, regulatory specialists, and legal counsel with extensive experience in nuclear power plant licensing and power uprate projects. Their expertise is critical for navigating the complex regulatory landscape and ensuring a successful outcome.
-
Challenge Identification and Mitigation: Proactively identify potential challenges, such as technical limitations, regulatory hurdles, or logistical constraints. Develop comprehensive mitigation strategies to address these potential issues before they impact the project timeline or budget. Effective risk management is key.
-
Project Schedule and Budget: Develop a realistic and detailed project schedule and budget, encompassing all phases of the power uprate project, from planning and application submission to implementation and post-approval monitoring.
-
Early NRC Engagement: Initiate early engagement with the NRC through pre-application meetings. These meetings allow for open communication, address potential concerns, and ensure a collaborative approach to the licensing process. This proactive engagement can significantly streamline the approval process.
Technical Evaluations and Analyses for Reactor Power Uprates
The technical aspects of a power uprate project are critical. Meticulous evaluations and analyses are necessary to ensure the safe operation of the reactor at the increased power levels.
-
Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis: Performing detailed thermal-hydraulic analysis is crucial. This analysis verifies that the reactor core and other plant systems can safely withstand the increased thermal loads associated with higher power output.
-
Safety System Impact: Assess the impact of the power uprate on all safety systems and components. This assessment ensures that these vital systems maintain their effectiveness and reliability at the higher power levels.
-
Fuel Performance and Aging Management: Evaluate the effects of the increased power output on fuel performance and plant aging management programs. This is critical to ensure the continued safe and reliable operation of the reactor.
-
Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA): Conduct a thorough PRA to identify and quantify potential risks associated with the power uprate. This quantitative assessment helps to prioritize mitigation strategies and improve overall plant safety.
-
Environmental Impact: Address potential environmental impacts, if any, associated with the power uprate. This may involve conducting an environmental impact statement (EIS) as required by environmental regulations.
Navigating the NRC Application and Review Process
The NRC application and review process is a significant undertaking. Careful preparation and effective communication are crucial for a successful outcome.
-
Application Package: Prepare and submit a comprehensive application package that meticulously addresses all NRC requirements. The application should clearly and concisely articulate the technical basis for the power uprate, addressing all safety and regulatory concerns.
-
RAI Responses: Be prepared to respond promptly and thoroughly to any Requests for Additional Information (RAI) from the NRC. These requests are common and indicate areas needing further clarification or substantiation. Timely and accurate responses are essential for maintaining project momentum.
-
Meetings and Inspections: Actively participate in meetings and inspections conducted by the NRC. Open communication and collaboration during these interactions are crucial for resolving issues and ensuring a positive outcome.
-
Addressing Concerns: Address any concerns or issues raised by the NRC proactively and effectively. Collaborate with the NRC to develop solutions that satisfy regulatory requirements and maintain the safety and reliability of the reactor.
-
Licensing Approval: The ultimate goal is to obtain final NRC approval for the power uprate. This approval signifies the successful completion of the rigorous regulatory review process.
Post-Approval Implementation and Ongoing Compliance
Once NRC approval is secured, the implementation phase begins, followed by ongoing compliance monitoring.
-
Implementation: Implement the power uprate by modifying equipment, upgrading systems, and training personnel on new operational procedures. This stage requires precise execution to ensure the successful transition to the higher power level.
-
Performance and Safety Monitoring: Monitor plant performance and safety closely to ensure continued compliance with NRC regulations and to identify any potential issues early. This ongoing monitoring is critical for maintaining safe and reliable operation.
-
Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of all aspects of the power uprate project, including design changes, modifications, and operational data. This rigorous documentation is vital for auditing, regulatory compliance, and future reference.
-
Communication with NRC: Maintain regular communication with the NRC, reporting any significant events or findings. This open communication fosters a positive and collaborative relationship with the regulator.
Conclusion
Successfully completing a reactor power uprate requires careful planning, a thorough understanding of NRC regulations, and a robust technical and regulatory strategy. This involves thorough pre-application planning, meticulous technical evaluations, effective communication with the NRC, and ongoing compliance post-approval. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can navigate the NRC process efficiently and achieve a successful reactor power uprate, maximizing energy production and optimizing your facility's performance. Contact our experts today to learn more about planning your own reactor power uprate.

Featured Posts
-
 Spoedprocedure Kampen Aansluiting Op Stroomnet Van Enexis Betwist
May 01, 2025
Spoedprocedure Kampen Aansluiting Op Stroomnet Van Enexis Betwist
May 01, 2025 -
 Indigenous Arts Festival Faces Funding Crisis Amid Economic Downturn
May 01, 2025
Indigenous Arts Festival Faces Funding Crisis Amid Economic Downturn
May 01, 2025 -
 Ia Da Meta App Proprio Chega Para Competir Com O Chat Gpt
May 01, 2025
Ia Da Meta App Proprio Chega Para Competir Com O Chat Gpt
May 01, 2025 -
 Mercedes Mone Pleads With Momo Watanabe For Tbs Championship Return
May 01, 2025
Mercedes Mone Pleads With Momo Watanabe For Tbs Championship Return
May 01, 2025 -
 Feltri Un Opinione Sul Venerdi Santo
May 01, 2025
Feltri Un Opinione Sul Venerdi Santo
May 01, 2025
