Reasons For The Omission Of Excessive Heat Warnings In Weather Predictions
Table of Contents
Limitations of Forecasting Technology
Accurately predicting and issuing timely excessive heat warnings is hampered by several technological limitations. The challenge isn't simply predicting high temperatures, but anticipating the potentially life-threatening conditions resulting from a combination of heat and humidity.
Difficulty Predicting Localized Extreme Heat
Predicting extreme heat isn't just about broad regional forecasts; it's about pinpointing areas where heat intensifies significantly, often within small geographical areas. This localized extreme heat presents a significant challenge.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Cities often experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the abundance of concrete and asphalt, which absorb and radiate heat.
- Topography: Hills and valleys can trap heat, leading to localized temperature spikes. Areas with little wind circulation are particularly vulnerable.
- Vegetation Cover: Areas with sparse vegetation absorb more solar radiation, increasing local temperatures. Conversely, heavily vegetated areas tend to be cooler.
Current weather models, while constantly improving, still struggle to capture these small-scale variations with sufficient accuracy. The resolution of many models isn't fine enough to identify these microclimates where extreme heat can develop rapidly and unexpectedly. This leads to difficulties in issuing precise and targeted excessive heat warnings.
Uncertainty in Heat Index Forecasting
The heat index, a measure combining air temperature and relative humidity to reflect the perceived air temperature, is crucial for assessing the true danger of heat waves. However, accurately forecasting the heat index poses significant challenges.
- Complexity of Calculation: The heat index calculation is complex, incorporating multiple meteorological variables. Small errors in predicting any one variable (temperature, humidity, wind speed) can significantly affect the final heat index value.
- Margin of Error: There's an inherent margin of error in all weather predictions, and this error is magnified when dealing with the heat index, especially in predicting extreme values.
- Contributing Factors: Besides temperature and humidity, wind speed, sunshine, and even cloud cover can influence the perceived heat. Accurate forecasting requires considering all these factors.
The uncertainty in heat index forecasting directly impacts the reliability of excessive heat warnings. A slight miscalculation can lead to either underestimation (failing to issue a warning when needed) or overestimation (issuing unnecessary warnings, leading to "cry wolf" syndrome).
Data Availability and Infrastructure
The lack of comprehensive and accurate data is another major reason why excessive heat warnings might be omitted or delayed. This stems from deficiencies in monitoring networks and limitations in historical data.
Insufficient Monitoring Networks
A dense network of weather stations is essential for capturing precise temperature and humidity data across a region. However, many areas, particularly rural and less populated regions, suffer from a lack of sufficient monitoring infrastructure.
- Sparse Data Leads to Inaccuracies: Sparse data points make it difficult to detect localized heat spikes and create accurate heat maps. The resulting lack of granular data limits the ability to issue targeted excessive heat warnings.
- Cost and Logistical Challenges: Expanding weather monitoring networks requires significant investment in equipment, maintenance, and personnel. This presents a challenge, particularly in regions with limited resources.
This lack of data makes it difficult to generate accurate, localized heatwave forecasts and therefore to issue appropriate excessive heat warnings.
Historical Data Limitations
Historical climate data is crucial for understanding long-term trends and predicting future heat waves. However, limitations in the existing data present a significant challenge.
- Limited Data on Extreme Events: Historical records of extreme heat events may be limited in some regions, especially in less-developed countries. This makes it hard to establish reliable statistical models for predicting future events.
- Climate Change Impact: The accelerating pace of climate change means that past data may not accurately reflect future trends. The frequency and intensity of heatwaves are changing more rapidly than previously anticipated, rendering historical data less reliable for prediction.
This limited and potentially outdated historical data hinders the ability to accurately forecast future heat waves and issue appropriate excessive heat warnings.
Communication and Dissemination Challenges
Even with accurate forecasts, effectively disseminating excessive heat warnings to the public is crucial. Challenges exist in targeting specific vulnerable populations and setting appropriate warning thresholds.
Targeting Specific Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are disproportionately vulnerable to heat-related illnesses, including the elderly, low-income communities, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Effectively reaching these groups with timely warnings requires careful consideration.
- Targeted Communication Strategies: Multiple communication channels, including social media, community centers, local news outlets, and targeted mobile alerts are needed to reach these diverse communities effectively.
- Language Accessibility: Warnings need to be accessible in multiple languages and formats to cater to diverse linguistic backgrounds and literacy levels.
- Collaboration with Local Authorities: Close collaboration with local health authorities and community organizations is essential for tailoring communication strategies to the unique needs of vulnerable populations.
Effective communication is key to translating excessive heat warnings into action that saves lives.
Thresholds and Warning Criteria
Setting appropriate thresholds for issuing excessive heat warnings is critical. The criteria need to balance the need for timely warnings with the risk of issuing too many false alarms.
- Balancing Accuracy and Avoiding False Alarms: Setting thresholds too low may lead to frequent warnings, desensitizing the public. Setting them too high risks missing crucial warnings when they are most needed.
- Regional Variations: Warning criteria may vary across different regions based on factors such as climate, population density, and societal vulnerabilities.
- Criteria Considerations: Thresholds need to consider not only temperature and heat index but also the duration of the heatwave and the associated public health risks.
Careful consideration of these factors is required to create an effective early warning system for excessive heat.
Conclusion
The omission of excessive heat warnings is a multifaceted issue stemming from limitations in forecasting technology, inadequate data availability, and communication challenges. Improving the accuracy and timeliness of these warnings requires significant investment in modernizing weather monitoring infrastructure, advancing forecasting models, and implementing more targeted and accessible communication strategies. By addressing these challenges, we can substantially improve public safety and reduce the devastating impacts of extreme heat. Understanding the reasons behind the omission of excessive heat warnings allows us to advocate for better preparedness and ultimately, save lives during future heat waves. Let's work together to ensure reliable and comprehensive heatwave warnings are readily available for everyone.

Featured Posts
-
 Real Madrid To Launch 90m Pursuit Of Manchester United Player
May 30, 2025
Real Madrid To Launch 90m Pursuit Of Manchester United Player
May 30, 2025 -
 Us Measles Count Updated 1 046 Cases Indiana Outbreak Resolved
May 30, 2025
Us Measles Count Updated 1 046 Cases Indiana Outbreak Resolved
May 30, 2025 -
 The Enduring Appeal Of Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason
May 30, 2025
The Enduring Appeal Of Dara O Briains Voice Of Reason
May 30, 2025 -
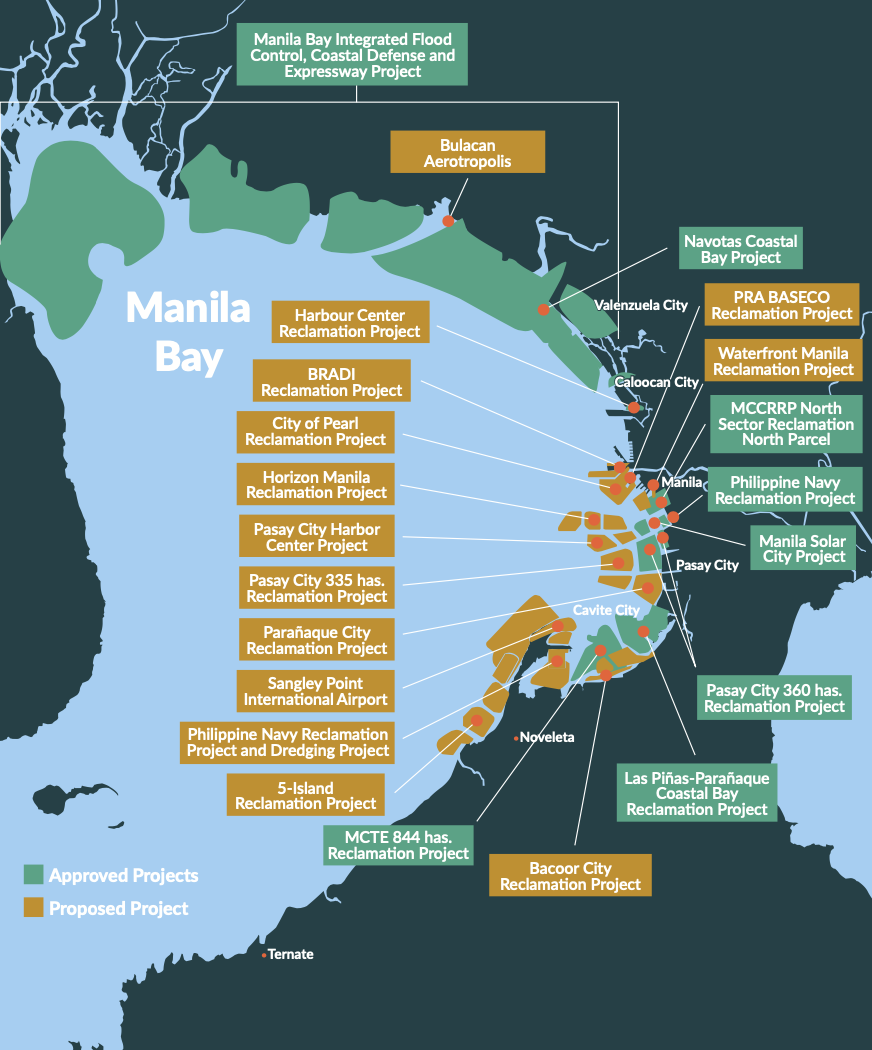 How Long Can Manila Bay Remain Vibrant
May 30, 2025
How Long Can Manila Bay Remain Vibrant
May 30, 2025 -
 Get To Know Jacob Alon One To Watch In Industry
May 30, 2025
Get To Know Jacob Alon One To Watch In Industry
May 30, 2025
