Rising Measles Cases In Kansas: Understanding The Resurgence
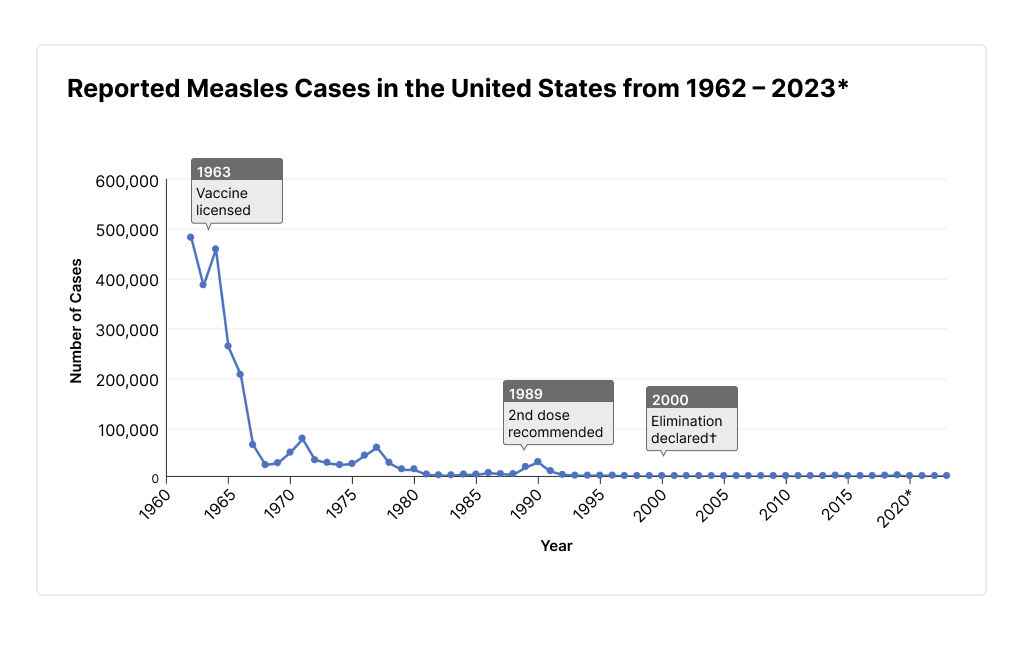
Table of Contents
Understanding the Measles Virus and its Transmission
What is Measles?
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious viral infection. It's spread through the air via tiny droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can remain suspended in the air for several hours, making it easy for others to inhale and contract the virus.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include a high fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic red, blotchy rash that spreads across the body. Other symptoms can include conjunctivitis (pink eye) and Koplik's spots (small white spots inside the mouth).
- Incubation Period: The incubation period (time between infection and symptom onset) is typically 7-14 days.
- Contagious Period: Measles is highly contagious from about four days before the rash appears until four days after the rash erupts.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are particularly vulnerable to severe complications from measles:
- Infants: Their immune systems are still developing, making them less able to fight off the infection.
- Pregnant Women: Measles infection during pregnancy poses risks to both the mother and the developing fetus.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: People with weakened immune systems (due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer treatments) are at higher risk of severe illness and complications.
Potential complications from measles can include pneumonia, encephalitis (brain inflammation), and even death. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in minimizing these risks.
Factors Contributing to the Resurgence of Measles in Kansas
Decreased Vaccination Rates
A primary driver of the resurgence is the decline in MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccination rates in Kansas. Vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation and distrust in vaccines has contributed significantly to this decline. The lack of widespread vaccination weakens herd immunity, making the entire community more susceptible to outbreaks.
- Herd Immunity: Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of the population is vaccinated, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated (e.g., infants) from infection.
- Misconceptions: Common misconceptions about the MMR vaccine, such as its link to autism (which has been thoroughly debunked by numerous scientific studies), contribute to vaccine hesitancy.
International Travel and Importation of Cases
International travel plays a substantial role in the spread of infectious diseases like measles. Individuals traveling from countries with low vaccination rates and ongoing measles outbreaks can unintentionally introduce the virus into Kansas communities.
- Travel Routes: International airports in Kansas serve as potential entry points for the virus. Travelers from regions with active measles transmission pose a considerable risk.
- Quarantine Measures: Early detection and implementation of appropriate quarantine measures are essential to prevent the spread of imported cases.
Community Clusters and Outbreaks
Low vaccination rates within specific communities create environments where measles can rapidly spread, forming clusters and outbreaks. These outbreaks can overwhelm local healthcare systems and pose a significant public health challenge.
- Rapid Response: Prompt identification of cases, contact tracing, and isolation of infected individuals are critical in containing outbreaks.
- Community Engagement: Public health initiatives focused on educating and engaging communities are vital to increase vaccination rates and prevent future outbreaks.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
The Role of Public Health Agencies
The Kansas Department of Health and Environment (KDHE) and other public health agencies play a critical role in controlling the measles outbreak.
- Contact Tracing: KDHE actively investigates cases, identifies contacts of infected individuals, and monitors for further spread.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Targeted vaccination campaigns are implemented in areas affected by outbreaks to increase community immunity.
- Public Awareness Initiatives: Public health messages aim to educate the public about measles, its prevention, and the importance of vaccination.
Importance of MMR Vaccination
The MMR vaccine is safe and highly effective in preventing measles. It significantly reduces the risk of contracting the virus and protects against severe complications.
- Vaccine Effectiveness: The MMR vaccine is over 97% effective in preventing measles after two doses.
- Addressing Concerns: Addressing public concerns about vaccine safety through accurate information and open dialogue is crucial.
Promoting Vaccination Awareness
Combating misinformation and promoting vaccine uptake requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Healthcare Provider Role: Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating patients about the importance of vaccination and answering their questions.
- Community Leaders: Trusted community leaders can influence vaccination decisions by publicly supporting vaccination and promoting health literacy.
- Public Health Campaigns: Targeted public health campaigns using various media channels can effectively communicate the benefits of vaccination and dispel common myths.
Conclusion:
The rising measles cases in Kansas are a serious public health concern driven by decreased vaccination rates, international travel, and community spread. The MMR vaccine remains the most effective way to prevent measles, and increased vaccination rates are crucial for achieving herd immunity and protecting vulnerable populations. We urge everyone to get vaccinated, talk to their healthcare provider about the MMR vaccine, and actively share accurate information about measles prevention with their communities. Visit the KDHE website for up-to-date information and resources to combat the rising measles cases in Kansas and protect your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Telechargement De L Emission Integrale Europe 1 Soir 19 03 2025
May 30, 2025
Telechargement De L Emission Integrale Europe 1 Soir 19 03 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Conciertos Bad Bunny Madrid And Barcelona Preventa De Entradas Ticketmaster Y Live Nation
May 30, 2025
Conciertos Bad Bunny Madrid And Barcelona Preventa De Entradas Ticketmaster Y Live Nation
May 30, 2025 -
 Investigating The Resurgence Of Measles Cases In Kansas
May 30, 2025
Investigating The Resurgence Of Measles Cases In Kansas
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillaz 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And London Shows
May 30, 2025
Gorillaz 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And London Shows
May 30, 2025 -
 Honda St 125 Dax Vs Kawasaki W175 Gaya Klasik Vs Modern Mana Pilihan Anda
May 30, 2025
Honda St 125 Dax Vs Kawasaki W175 Gaya Klasik Vs Modern Mana Pilihan Anda
May 30, 2025
