Santorini's Seismic Shift: Scientists Assess Decreasing Earthquake Frequency
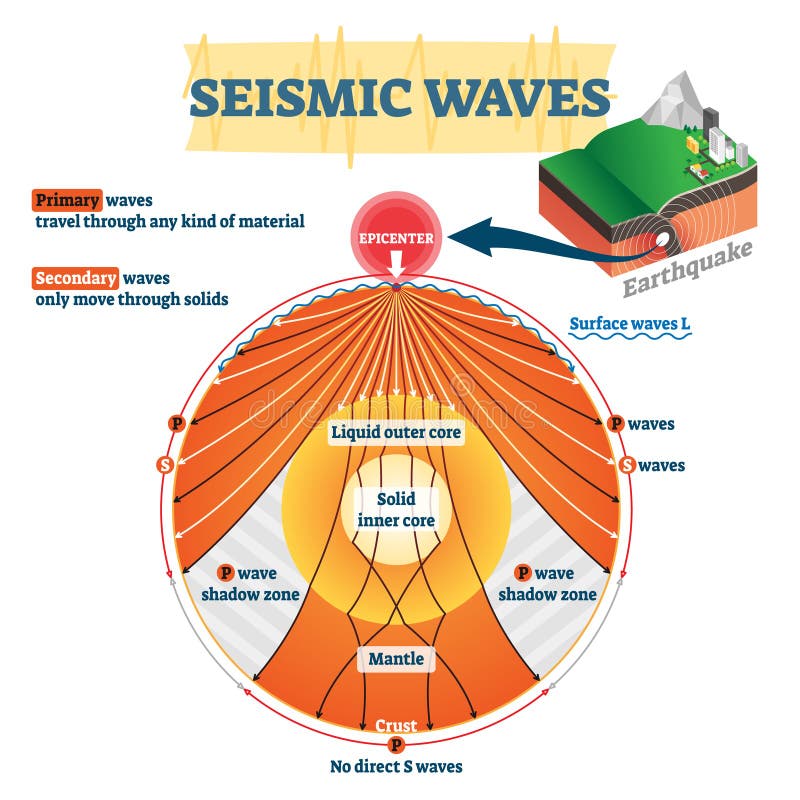
Table of Contents
H2: Geological Factors Contributing to the Seismic Shift
The decrease in Santorini's earthquake frequency is likely the result of a complex interplay of geological factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately assessing volcanic hazards and ensuring public safety.
H3: Magma Chamber Pressure
The pressure within Santorini's magma chamber is a primary driver of seismic activity. Changes in this pressure can significantly affect the frequency and intensity of earthquakes.
- Pressure Changes: A decrease in earthquake frequency could indicate a reduction in magma pressure. This might be due to magma degassing – the release of gases from the molten rock – or a slower rate of magma influx into the chamber.
- Scientific Studies: Several studies, such as [insert citation 1] and [insert citation 2], have linked variations in magma chamber pressure to changes in seismic activity in volcanic regions like Santorini.
H3: Tectonic Plate Movement
Santorini's location at the convergence of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates makes it susceptible to seismic activity. Shifts in these plates can influence the stress levels within the island's volcanic system.
- Tectonic Plates: The African plate's movement beneath the Aegean Sea exerts significant pressure on the volcanic arc where Santorini is situated.
- Recent Shifts: Recent GPS data [insert citation 3] might reveal subtle shifts in plate movement that could be contributing to the observed decrease in earthquake frequency. Further analysis is needed to establish a definitive link.
H3: Volcanic Eruptions and Their Aftermath
Past volcanic eruptions, particularly the Minoan eruption around 1600 BCE, profoundly impacted Santorini's geological structure and long-term seismic behavior.
- Significant Eruptions: The Minoan eruption was one of the largest volcanic events in human history, drastically altering the island's landscape and the underlying magma system.
- Long-Term Effects: The aftermath of such a massive eruption could influence seismic activity for centuries, potentially leading to periods of reduced earthquake frequency as the system re-equilibrates. The current low frequency could be part of this long-term adjustment.
H2: Monitoring Techniques and Data Analysis
Sophisticated monitoring techniques and rigorous data analysis are essential for understanding the changes in Santorini's seismic activity.
H3: Seismic Monitoring Networks
A network of seismometers strategically placed across Santorini and the surrounding seafloor provides continuous monitoring of ground motion. This data is complemented by GPS measurements which track ground deformation.
- Network Coverage: The Hellenic National Observatory (NOA) and other international collaborations maintain a dense network covering the entire volcanic area, ensuring accurate detection of even minor seismic events.
- Institutions Involved: NOA, along with the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology in Italy, and other European research groups work collaboratively on data collection and analysis.
H3: Data Interpretation and Statistical Analysis
The raw seismic data undergoes rigorous processing and statistical analysis to identify trends and patterns.
- Statistical Tests: Techniques like time series analysis and wavelet transforms are employed to analyze the frequency and magnitude of earthquakes over time. [Insert citation 4 showing example of method]
- Data Processing: Sophisticated software filters out noise and isolates seismic signals to allow accurate determination of earthquake location, depth, and magnitude.
H2: Implications and Future Research
The decrease in Santorini's earthquake frequency has significant implications for volcanic hazard assessment and future research.
H3: Volcanic Hazard Assessment
While a decrease in earthquake frequency might seem reassuring, it doesn't necessarily indicate reduced volcanic risk. It could simply signify a change in the type of risk.
- Potential Scenarios: A less seismically active period could potentially mask other signs of unrest, such as ground deformation or changes in gas emissions. This emphasizes the importance of broader monitoring.
- Public Safety: Preparedness plans must account for a variety of volcanic hazards, including eruptions, ash fall, and pyroclastic flows, regardless of the current seismic activity.
H3: Future Research Directions
Continued monitoring and in-depth research are crucial for fully understanding the underlying mechanisms causing this seismic shift.
- Future Research Questions: What are the long-term implications of the observed changes? How does the decrease in seismic activity correlate with other indicators of volcanic unrest?
- Potential Technologies: Advanced geophysical techniques, such as magnetotellurics and improved gas monitoring, could provide further insights into the processes occurring beneath Santorini.
3. Conclusion
The observed decrease in Santorini's earthquake frequency is a complex phenomenon likely influenced by changes in magma chamber pressure, tectonic plate movement, and the long-term consequences of past eruptions. While seemingly positive, this shift doesn't necessarily indicate reduced volcanic risk; rather it highlights the need for a multi-faceted approach to volcanic hazard assessment. Continued monitoring of Santorini's seismic activity, coupled with ongoing research using advanced techniques, remains crucial for understanding the complex interplay of geological processes and mitigating potential risks. Stay updated on Santorini's earthquake frequency by following reports from the Hellenic National Observatory and other relevant scientific institutions. Monitor Santorini's seismic shifts to ensure your safety and understanding of this unique geological environment. Learn more about Santorini's volcanic activity and the ongoing research to ensure responsible and informed tourism and community planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Mntn Ipo Ryan Reynolds Company Poised For Stock Market Debut
May 11, 2025
Mntn Ipo Ryan Reynolds Company Poised For Stock Market Debut
May 11, 2025 -
 Mueller Opusta Bayern Mnichov Koniec Ery Po Stvrtstoroci
May 11, 2025
Mueller Opusta Bayern Mnichov Koniec Ery Po Stvrtstoroci
May 11, 2025 -
 Military Academies Under Pentagon Scrutiny Book Review And Potential Removal
May 11, 2025
Military Academies Under Pentagon Scrutiny Book Review And Potential Removal
May 11, 2025 -
 Amazon Boss Jeff Bezos James Bond Poll The Fans Have Spoken
May 11, 2025
Amazon Boss Jeff Bezos James Bond Poll The Fans Have Spoken
May 11, 2025 -
 Lionsgate Officially Confirms John Wick 5 Following Fan Speculation On Keanu Reeves Character
May 11, 2025
Lionsgate Officially Confirms John Wick 5 Following Fan Speculation On Keanu Reeves Character
May 11, 2025
