Starship's Next Test: Addressing Previous Launch Failures
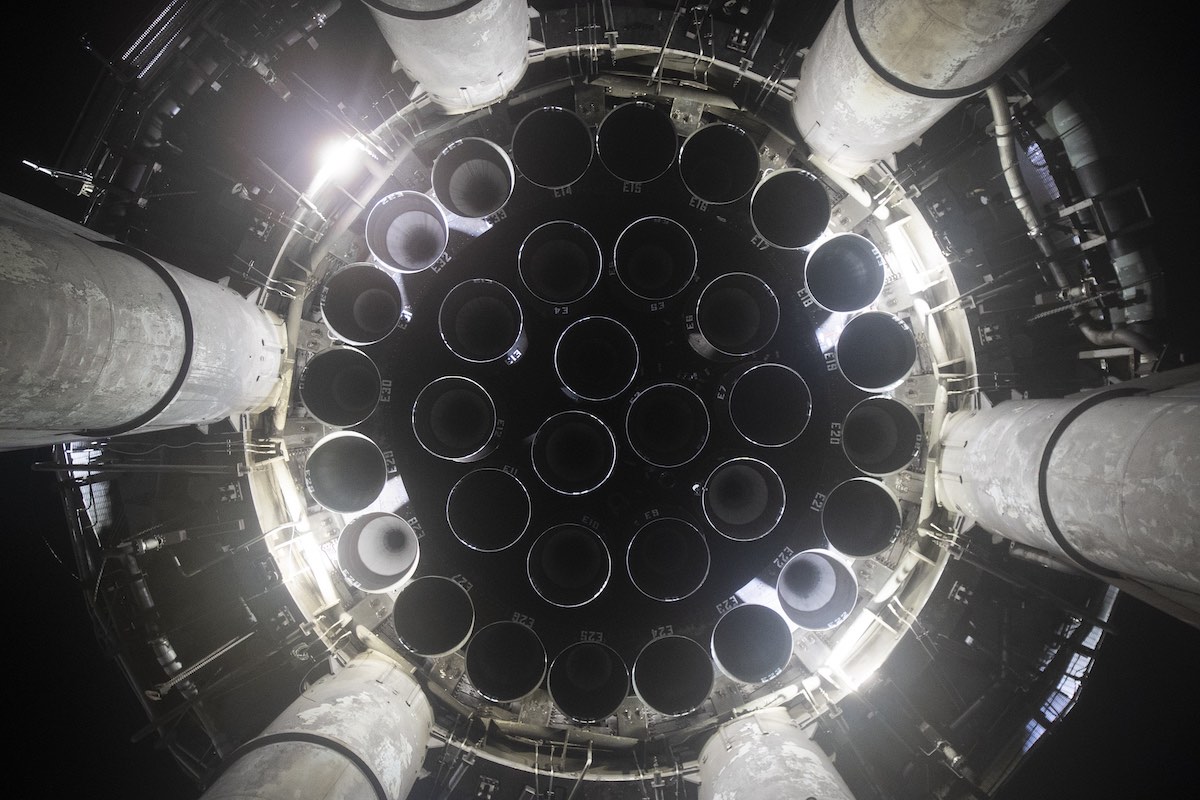
Table of Contents
Analyzing Past Starship Launch Failures
SpaceX's Starship development has involved a series of high-profile test flights, some of which ended in what SpaceX calls "rapid unscheduled disassembly" (RUD). Analyzing these failures is critical to understanding the iterative process of spacecraft development.
SN8, SN9, SN10 Explosions:
The early Starship prototypes, SN8, SN9, and SN10, provided invaluable data, though none achieved a successful landing. These tests, while ending in explosions, were crucial learning experiences.
- Starship SN8 failure analysis: SN8's failure was primarily attributed to insufficient propellant during the landing burn, leading to a hard impact. [Link to SpaceX SN8 video/report, if available].
- Starship SN10 RUD: SN10 experienced a RUD shortly after landing, likely due to a combination of factors, including potential structural damage during the landing and engine issues. [Link to SpaceX SN10 video/report, if available].
- Starship engine malfunction: Several engine malfunctions were observed across these tests, highlighting the need for improved Raptor engine reliability and redundancy. These issues involved both engine shutdown and inconsistent thrust performance. [Link to relevant SpaceX data, if available]
The Importance of Data Analysis:
SpaceX's approach relies heavily on iterative design and a relentless focus on data analysis. Each test flight generates a massive amount of data, used to refine the design and improve the chances of success.
- Starship data analysis: Telemetry from numerous sensors, high-speed camera footage, and post-flight physical inspections are meticulously analyzed.
- SpaceX iterative design: This data is fed into simulations and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling to identify weak points and predict potential failures. This iterative process is at the heart of SpaceX's rapid development cycle.
- Starship failure investigation: A dedicated team rigorously investigates each failure, examining every aspect of the design, manufacturing, and operation to pinpoint the root cause.
SpaceX's Solutions and Improvements
SpaceX has responded to the Starship launch failures with significant upgrades and improvements across multiple systems.
Engine Upgrades and Testing:
The Raptor engine, the heart of Starship, has undergone considerable refinement.
- Raptor 2 engine improvements: Raptor 2 engines boast increased thrust, improved combustion efficiency, and enhanced thermal management.
- Starship engine reliability: Rigorous testing procedures, including numerous static fire tests, are implemented to validate engine performance and reliability before flight.
- Raptor engine testing: These tests subject the engines to extreme conditions, ensuring they can withstand the stresses of launch and landing.
Structural Enhancements and Material Selection:
Improvements to the Starship's structure address the structural weaknesses identified in previous tests.
- Starship structural integrity: Advanced welding techniques and stronger alloys are used to enhance the overall structural integrity of the vehicle.
- Starship material science: The selection of materials considers factors like thermal resistance, strength-to-weight ratio, and resistance to extreme temperature changes.
- Starship design improvements: Modifications to the landing legs, heat shielding, and overall aerodynamic profile aim to improve stability and survivability during landing.
Software and Flight Control System Updates:
Significant upgrades have been made to the software and flight control systems.
- Starship flight control system: Enhanced guidance, navigation, and control (GNC) algorithms provide improved stability and control during flight.
- Starship autonomous landing: The autonomous landing system has been refined, incorporating improved sensor fusion and fail-safe mechanisms.
- Starship software upgrades: Redundancy in software systems and improved error handling enhance robustness and resilience to unexpected events.
The Significance of Future Starship Tests
The upcoming tests are crucial for validating the improvements and achieving the ultimate goal of a fully operational Starship.
Orbital Flight Tests:
Successful orbital tests are the next major milestone.
- Starship orbital flight test: These tests will assess the performance of the entire vehicle, including the Super Heavy booster and Starship upper stage, during ascent, orbit, and re-entry.
- Starship Super Heavy: The Super Heavy booster’s performance is critical for achieving orbit. Its successful operation will be a key indicator of overall mission success.
- Starship full stack launch: A successful full-stack launch and landing will demonstrate the capabilities needed for interplanetary missions.
Path to Mars and Beyond:
The ultimate aim of the Starship program is ambitious: to make human spaceflight more affordable and accessible.
- Starship Mars mission: A successful Starship is a crucial step towards establishing a permanent human presence on Mars.
- Starship interplanetary travel: Beyond Mars, Starship could pave the way for missions to other planets and moons in our solar system.
- SpaceX colonization: SpaceX's vision extends to facilitating the colonization of other celestial bodies, making humanity a multi-planetary species.
Conclusion:
SpaceX's Starship program is facing significant challenges, but the company's commitment to rigorous testing and data-driven improvements offers hope for future success. Understanding the past Starship launch failures and the implemented solutions is critical in appreciating the progress being made. By analyzing data from past tests and continuously improving the design, SpaceX is striving to make Starship a fully functional and reliable vehicle for space exploration. Stay tuned for updates on future Starship tests and the continued evolution of this ambitious project. Follow the latest news on the next steps to overcome Starship launch failures and witness the future of space travel unfold.

Featured Posts
-
 Smith Rejects Claims Of Joshlin Sale Points Finger At Lombaard And Boyfriend
May 29, 2025
Smith Rejects Claims Of Joshlin Sale Points Finger At Lombaard And Boyfriend
May 29, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Reports 1050 Price Increase From Broadcom
May 29, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket At And T Reports 1050 Price Increase From Broadcom
May 29, 2025 -
 Update Cuaca Semarang Prediksi Hujan Sore Dan Malam 26 Maret 2024 Di Jawa Tengah
May 29, 2025
Update Cuaca Semarang Prediksi Hujan Sore Dan Malam 26 Maret 2024 Di Jawa Tengah
May 29, 2025 -
 Bryan Cranstons Net Worth 2025 Projections And Financial Success
May 29, 2025
Bryan Cranstons Net Worth 2025 Projections And Financial Success
May 29, 2025 -
 Arcane Coldplay Stromae Et Pomme Reinterpretent Ma Meilleure Ennemie
May 29, 2025
Arcane Coldplay Stromae Et Pomme Reinterpretent Ma Meilleure Ennemie
May 29, 2025
