Student Loan Privatization: Understanding Trump's Potential Approach
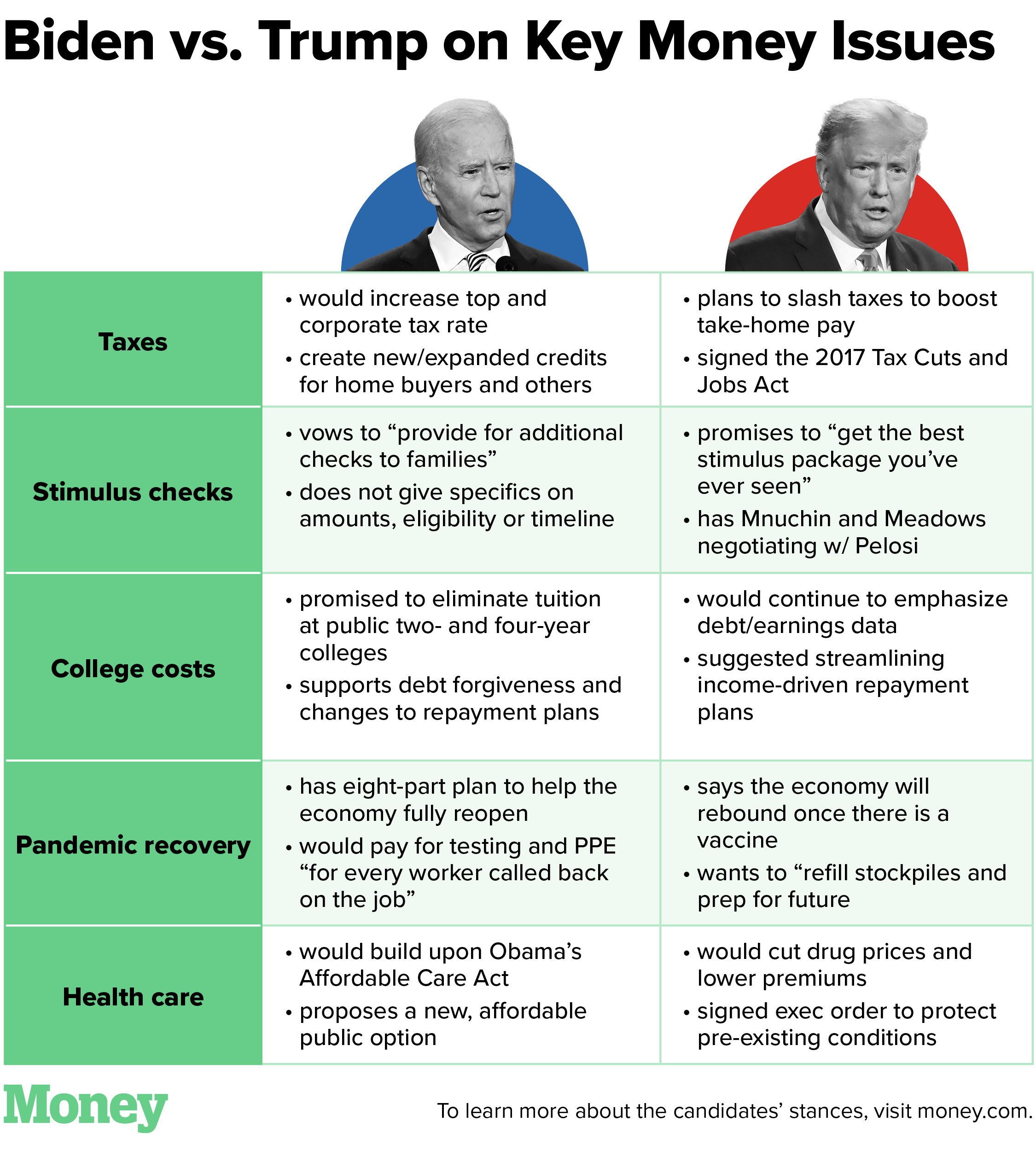
Table of Contents
Potential Benefits of Student Loan Privatization
Proponents of student loan privatization argue it could bring several advantages to the student loan market and higher education system.
Increased Efficiency and Innovation
Private student loan lenders, it's argued, might operate more efficiently and be more innovative than government agencies. This could translate into several key improvements:
- Streamlined application processes: Private lenders could potentially offer faster and simpler application procedures, reducing the bureaucratic hurdles faced by students seeking financial aid. This could involve leveraging technology for faster processing times and more user-friendly online portals.
- More flexible repayment options: Private lenders might offer a broader range of repayment options tailored to individual borrower circumstances. This could include options beyond the standard federal repayment plans, potentially providing more flexibility for students facing financial difficulties. This flexibility could significantly reduce the student loan default rate.
- Potential for technological advancements in loan management: The private sector often leads in technological innovation. This could lead to the development of more sophisticated tools for managing student loans, potentially improving the borrower experience and reducing administrative costs. This could include AI-driven tools for personalized repayment advice and proactive risk management.
Reduced Government Burden
A major argument for privatization is that it could lessen the financial and administrative strain on the government. This could manifest in:
- Less government spending on loan programs: Transferring the responsibility of loan origination and servicing to private entities could decrease government expenditure on student aid programs.
- Reduced reliance on taxpayer funding for student aid: Privatization could reduce the direct reliance on taxpayer dollars to fund student loans.
- Decreased administrative costs for the government: The government could potentially reduce its administrative overhead by delegating significant aspects of student loan management.
Potential Drawbacks of Student Loan Privatization
Despite the potential advantages, student loan privatization also raises significant concerns.
Increased Costs for Borrowers
One of the most substantial criticisms is the potential for higher costs for students.
- Higher interest rates compared to federal loans: Private lenders, driven by profit motives, may charge significantly higher interest rates than those offered through federal loan programs, increasing the overall cost of education.
- Additional fees and charges: Private loans often come with additional fees and charges that are not always present in federal loan programs, further increasing the total borrowing cost.
- Potential for predatory lending practices: There's a risk of predatory lending practices targeting vulnerable students, particularly those lacking financial literacy, leading to exploitative loan terms.
Reduced Access to Loans
Privatization could create inequities in access to higher education funding.
- Stricter lending criteria from private lenders: Private lenders may employ stricter lending criteria than federal programs, potentially excluding students from lower-income backgrounds or those attending less prestigious institutions.
- Limited availability of loans in certain areas: Private lenders may be less willing to lend in certain geographic areas, potentially creating disparities in access to higher education based on location.
- Increased inequality in access to higher education: This could exacerbate existing inequalities in higher education access, disproportionately affecting students from marginalized communities.
Lack of Borrower Protections
Federal student loans generally offer robust borrower protections not always found in private loans.
- Limited options for income-driven repayment plans: Private loans may lack the flexible income-driven repayment plans offered by federal programs, leaving borrowers vulnerable to financial hardship if their income decreases.
- Fewer protections against default: Private loans might offer fewer protections against default, potentially leading to more severe financial consequences for borrowers.
- Potential for aggressive debt collection practices: Borrowers with private student loans may face more aggressive and less regulated debt collection practices compared to federal loan borrowers.
Alternative Approaches to Student Loan Reform
Instead of complete privatization, alternative strategies could be pursued to tackle the student debt crisis. These include:
- Increased funding for Pell Grants: Expanding Pell Grant funding could make college more affordable for low-income students, reducing their reliance on loans.
- Expansion of income-driven repayment plans: Expanding access to and improving existing income-driven repayment plans could make federal loans more manageable for borrowers struggling with repayment.
- Debt forgiveness programs for specific demographics or situations: Targeted debt forgiveness programs could address the needs of specific groups disproportionately burdened by student loan debt.
Conclusion
Student loan privatization presents a multifaceted issue with potential advantages such as increased efficiency and reduced government burden, but also significant disadvantages including elevated costs for borrowers, diminished access, and a lack of borrower safeguards. A thorough evaluation of these aspects is crucial. Exploring alternative approaches centered on affordability improvements and enhanced borrower protections is essential to guarantee equitable access to higher education. Understanding the intricacies of student loan privatization is paramount. Continue researching diverse approaches to student loan reform and participate in informed discussions about the future of student loan policy and its impact on access to higher education.

Featured Posts
-
 Andor Season 2 Trailer Release Date Updates And Confirmed Information
May 17, 2025
Andor Season 2 Trailer Release Date Updates And Confirmed Information
May 17, 2025 -
 Comparatif Des Trottinettes Xiaomi 5 5 Pro Et 5 Max
May 17, 2025
Comparatif Des Trottinettes Xiaomi 5 5 Pro Et 5 Max
May 17, 2025 -
 Japans Economy Contracts In Q1 Pre Tariff Impact Analyzed
May 17, 2025
Japans Economy Contracts In Q1 Pre Tariff Impact Analyzed
May 17, 2025 -
 Josh Harts Status Will He Play Against The Celtics On February 23rd
May 17, 2025
Josh Harts Status Will He Play Against The Celtics On February 23rd
May 17, 2025 -
 Rs 1 45 Lakh Ultraviolette Tesseract Electric Scooter Launch And Specifications
May 17, 2025
Rs 1 45 Lakh Ultraviolette Tesseract Electric Scooter Launch And Specifications
May 17, 2025
