Sustaining The Flow: European Shipyards In Russia's Arctic Gas Trade
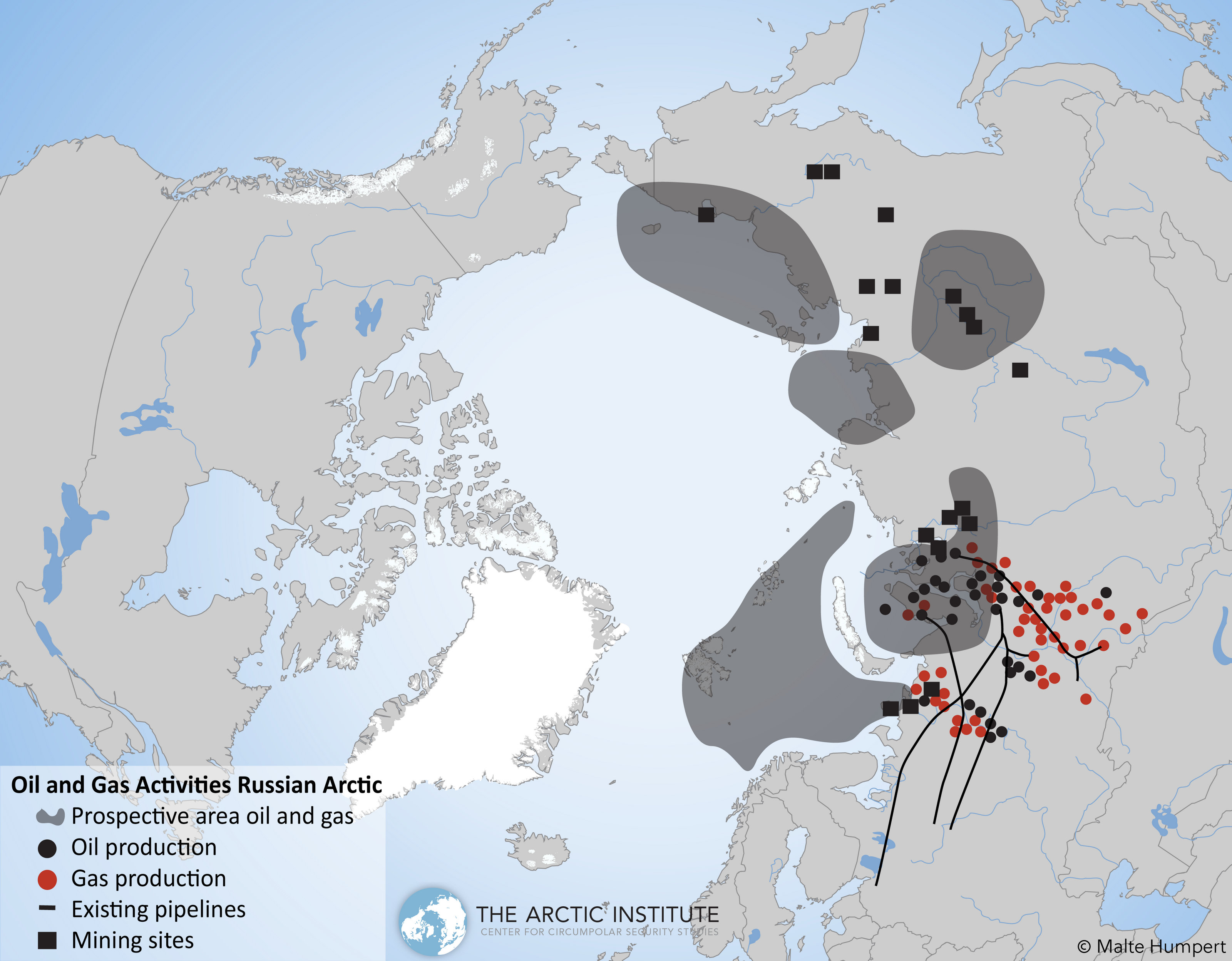
Table of Contents
The Demand for Ice-Class Vessels in the Arctic
The Arctic presents unique challenges for shipping, demanding specialized vessels and infrastructure. The harsh environment necessitates robust designs and advanced technology to ensure safe and efficient transport of LNG.
Navigating the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR), a shorter shipping route connecting Europe and Asia across the Arctic Ocean, offers significant potential for reduced transit times and cost savings. However, navigating this route presents formidable challenges:
- Extreme Ice Conditions: The NSR is characterized by varying ice conditions, requiring vessels with robust ice-breaking capabilities. Ice classes like Arc7 are essential for navigating the most challenging sections.
- Severe Temperatures: Sub-zero temperatures demand specialized materials and design considerations to prevent equipment failure and ensure the safety of crew.
- Limited Infrastructure: The relatively undeveloped infrastructure along the NSR necessitates self-sufficient vessels with advanced navigational systems and emergency preparedness.
- Long Distances: The vast distances involved in Arctic shipping require vessels with substantial fuel capacity and optimized hull designs for fuel efficiency.
Efficient Arctic shipping routes are crucial for the success of Arctic LNG projects. Icebreaker assistance often plays a vital role in opening safe passage through heavy ice concentrations, adding another layer of complexity and cost to Arctic shipping operations.
The Rise of Arctic LNG Projects
The significant growth of LNG production in the Russian Arctic, primarily driven by projects like Yamal LNG, is a key driver of the demand for ice-class vessels.
- Yamal LNG: This massive project on the Yamal Peninsula is a cornerstone of Russia's Arctic LNG strategy, exporting significant volumes of LNG to global markets.
- Increased Export Volumes: The success of Yamal LNG and other planned Arctic LNG projects will lead to a substantial increase in the volume of LNG transported via the NSR, further boosting the demand for specialized ice-class vessels.
- Global Energy Market Impact: Arctic LNG production is reshaping global energy supply chains, making the region a major player in the international energy market. The infrastructure required for the export of this LNG necessitates the continued and expanding use of robust, ice-capable vessels.
European Shipyards: Key Players in Arctic Shipping
European shipyards possess the specialized expertise and technology to construct the ice-class vessels critical for Arctic LNG transportation. This collaboration carries significant economic and geopolitical weight.
Specialization and Expertise
European shipyards have invested heavily in developing the specialized skills and technologies required for building ice-class vessels, establishing themselves as leaders in this niche market.
- Key Shipyards: Several European shipyards, including those in Finland, South Korea and China, are prominent players in the construction of Arc7 and other ice-class vessels for Arctic operations. (Note: Including links to relevant shipyards would enhance this section).
- Technological Advancements: These shipyards continuously refine their designs and incorporate cutting-edge technologies, improving the ice-breaking capabilities, fuel efficiency, and overall performance of the vessels. This ongoing innovation reflects the dynamic nature of the Arctic shipping industry.
- Contributions to Arctic LNG Shipping: European shipyards are not just building the ships; they're contributing significantly to the engineering, design and implementation of crucial technology that is integral to the transportation of LNG in the Arctic region.
Economic and Geopolitical Implications
The construction of ice-class vessels for the Russian Arctic gas trade presents both economic benefits and geopolitical complexities for European shipyards.
- Economic Benefits: These projects generate significant revenue and employment opportunities for European shipyards and their supply chains. The specialized nature of the work often commands premium pricing.
- Technological Leadership: This collaboration solidifies Europe's position as a leader in the development and application of advanced shipbuilding technologies for extreme environments.
- Geopolitical Risks: The geopolitical landscape involving Russia and the Arctic carries inherent risks, including the potential impact of sanctions and international relations. Navigating these complex political realities is crucial for long-term success. The European Union's energy policy and its ongoing discussions concerning energy independence will also impact the future of this collaboration.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the significant progress, challenges remain regarding environmental concerns and the need for continued technological advancements in Arctic shipping.
Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of Arctic shipping is a growing concern, requiring careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: LNG transportation, while cleaner than some other fossil fuels, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing these emissions is crucial for environmental sustainability.
- Potential for Environmental Damage: Accidents involving LNG carriers could have devastating consequences for the fragile Arctic ecosystem. Stricter regulations and preventative measures are needed.
- Mitigation Strategies: The industry is exploring various mitigation strategies, including the adoption of cleaner fuels, improved vessel designs, and stricter environmental regulations to minimize the environmental footprint of Arctic shipping. Sustainable Arctic shipping practices are vital for long-term environmental protection.
Technological Advancements
Future advancements in ice-class vessel design and Arctic shipping technology will further enhance efficiency and safety.
- Autonomous Shipping: The development of autonomous vessels could revolutionize Arctic shipping, improving safety and efficiency by reducing human error.
- Improved Ice-Breaking Capabilities: Continuous research and development are leading to more efficient and powerful ice-breaking technologies.
- Advancements in Fuel Efficiency: Innovations in propulsion systems and hull design are crucial for reducing fuel consumption and minimizing environmental impact. The future of Arctic LNG transport relies heavily on breakthroughs in this area.
Conclusion
European shipyards play a pivotal role in facilitating Russia's Arctic gas trade, a venture with profound economic and geopolitical ramifications. The demand for specialized ice-class vessels capable of navigating the challenging conditions of the Northern Sea Route is driving innovation and shaping the future of Arctic LNG transportation. While challenges regarding environmental impact and geopolitical stability remain, technological advancements promise to enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability in this rapidly developing sector.
Learn more about the future of European shipyards and their involvement in Russia's Arctic gas trade. Continue to explore how advancements in ice-class vessel technology are shaping the future of Arctic LNG transportation and the impact on global energy markets. Stay informed on the latest developments in the European shipyards and Russia's Arctic gas trade to understand the changing dynamics of this critical sector.

Featured Posts
-
 Ai Driven Podcast Creation Transforming Repetitive Documents Into Engaging Content
Apr 26, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Creation Transforming Repetitive Documents Into Engaging Content
Apr 26, 2025 -
 A Conservative Harvard Professors Prescription For Harvards Future
Apr 26, 2025
A Conservative Harvard Professors Prescription For Harvards Future
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Exposition Photographique Galerie Le Labo Du 8 Pierre Terrasson
Apr 26, 2025
Exposition Photographique Galerie Le Labo Du 8 Pierre Terrasson
Apr 26, 2025 -
 The Nepo Baby Controversy Amanda Seyfrieds F Bomb Reaction
Apr 26, 2025
The Nepo Baby Controversy Amanda Seyfrieds F Bomb Reaction
Apr 26, 2025 -
 California Governor Newsom Addresses Internal Democratic Conflict
Apr 26, 2025
California Governor Newsom Addresses Internal Democratic Conflict
Apr 26, 2025
