Tariff Hikes And The Subsequent Bond Market Volatility
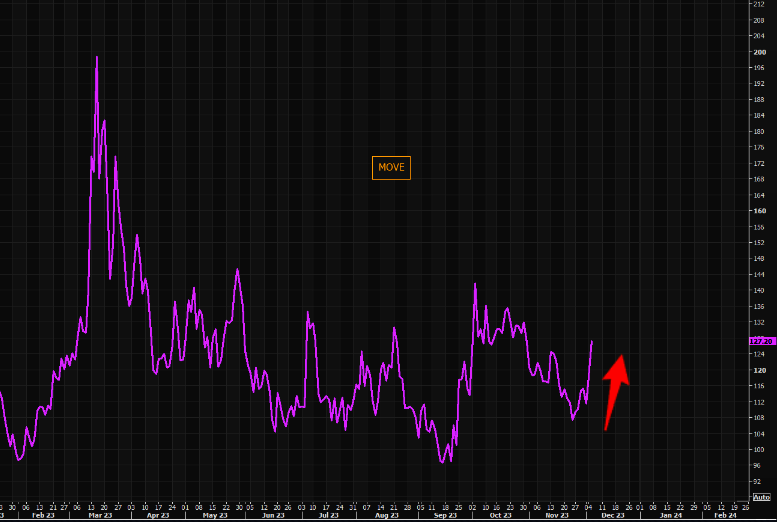
Table of Contents
Understanding the Mechanism: How Tariff Hikes Impact Bond Markets
The global economy is a complex web of interconnected trade relationships. Tariff hikes disrupt this delicate balance, creating uncertainty and impacting investor confidence. Increased tariffs lead to higher import costs, directly impacting inflation. This, in turn, influences central bank policies and overall economic growth projections. The increased uncertainty discourages investment and can trigger a "flight to safety," where investors initially move towards government bonds perceived as less risky. However, this can quickly shift depending on the severity and duration of the tariff impacts.
- Increased inflation due to higher import costs: Tariffs increase the price of imported goods, leading to higher consumer prices and potentially fueling inflationary pressures.
- Reduced economic growth expectations: Uncertainty caused by tariffs discourages businesses from investing and expanding, leading to slower economic growth. This dampens demand for corporate bonds.
- Flight to safety (initially): Investors often seek refuge in government bonds perceived as safer assets during times of heightened uncertainty. However, prolonged uncertainty can even impact these "safe havens."
- Potential for decreased corporate bond ratings: Companies facing higher input costs due to tariffs may experience reduced profitability, potentially leading to downgrades in their credit ratings and impacting their bond yields.
Analyzing the Volatility: Specific Indicators and Trends
Analyzing the volatility requires examining key indicators. The yield curve, a graphical representation of bond yields across different maturities, is a crucial tool. A flattening or inversion of the yield curve (where short-term yields exceed long-term yields) can signal an impending recession, often exacerbated by tariff-induced uncertainty. Changes in bond prices, particularly the divergence between corporate and government bond prices, reflect shifts in investor sentiment and risk appetite. Widening credit spreads, the difference between yields on corporate bonds and government bonds, indicate increased risk aversion in the market.
- Case studies: Examining historical instances of significant tariff increases (e.g., the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act) reveals the significant negative consequences on bond markets and economic growth.
- Charts and graphs: Visual representations of yield curve movements, bond price fluctuations, and credit spread widening provide compelling evidence of the impact of tariff hikes on bond market volatility. Analyzing the US Treasury bond index, for instance, is crucial in this context.
- Specific bond indexes affected: The impact varies across different bond markets. Indexes tracking corporate bonds, emerging market bonds, and municipal bonds will all show varied reactions depending on the sector's sensitivity to tariff changes.
The Role of Central Banks in Managing Volatility
Central banks play a critical role in attempting to mitigate the impact of tariff hikes on bond markets. They can employ various tools, including interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing (QE), to influence bond yields and overall market liquidity. However, their ability to effectively manage the situation is constrained by several factors. The effectiveness of these tools depends heavily on the severity and duration of tariff-induced economic shocks.
- Examples of past central bank interventions: Analyzing historical responses to economic crises and trade wars reveals the varying effectiveness of different monetary policy tools in stabilizing bond markets.
- Discussion of the effectiveness of different policy tools: QE, while effective in injecting liquidity, can also lead to unintended consequences like inflation. Interest rate cuts might stimulate growth but also risk increasing inflation and weakening the currency.
- Analysis of the trade-offs involved: Central banks often face difficult trade-offs between stimulating growth, controlling inflation, and maintaining financial stability in the face of tariff-induced volatility.
Predicting Future Trends: The Outlook for Bond Markets and Tariffs
Predicting future trends requires considering various scenarios based on potential tariff policies. Economic models and expert opinions can help forecast the likely impact on bond markets. Investors need to develop robust risk assessment and mitigation strategies. The long-term implications of prolonged tariff disputes on global trade and economic growth remain significant unknowns that can impact the bond market significantly.
- Predictions based on economic models and expert opinions: Analyzing economic forecasts and expert commentary can provide insights into potential future scenarios and their impact on bond market volatility.
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies for investors: Investors need to diversify their portfolios, hedge against inflation, and carefully consider the risk tolerance relevant to their investment strategy.
- Discussion of potential long-term implications: Prolonged trade tensions can lead to structural changes in global supply chains and investment patterns, significantly impacting the long-term performance of bond markets.
Conclusion
Tariff hikes have a demonstrable and significant impact on bond market volatility. Increased uncertainty, inflation, and changes in investor sentiment all contribute to fluctuations in bond prices and yields. Central banks play a crucial role in managing this volatility, but their actions are subject to various limitations and trade-offs. Understanding the complex interplay between tariff hikes and bond market volatility is paramount for making informed investment decisions.
To navigate this challenging environment, stay informed about global trade developments and their impact on the bond market. Conduct thorough research into "Tariff Hikes and Bond Market Volatility," utilizing resources like financial news outlets, economic research papers, and central bank publications to track bond market trends and tariff policies. Understanding this dynamic relationship is vital for effective financial planning and successful investment in the current climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Chicago O Hare Why United And American Airlines Are Locked In A Head To Head Battle
May 12, 2025
Chicago O Hare Why United And American Airlines Are Locked In A Head To Head Battle
May 12, 2025 -
 The Unexpected Box Office Failure Of Guy Ritchies And Henry Cavills 2024 War Movie
May 12, 2025
The Unexpected Box Office Failure Of Guy Ritchies And Henry Cavills 2024 War Movie
May 12, 2025 -
 Takuma Sato Secures 34th Indy 500 Entry Bump Day Looms
May 12, 2025
Takuma Sato Secures 34th Indy 500 Entry Bump Day Looms
May 12, 2025 -
 Billeteras Virtuales Uruguayas Cuentas Gratuitas Para Argentinos
May 12, 2025
Billeteras Virtuales Uruguayas Cuentas Gratuitas Para Argentinos
May 12, 2025 -
 Experiences That Keep On Giving Meeting Shane Lowry
May 12, 2025
Experiences That Keep On Giving Meeting Shane Lowry
May 12, 2025
