The Auto Industry's Ongoing Battle Against EV Mandates
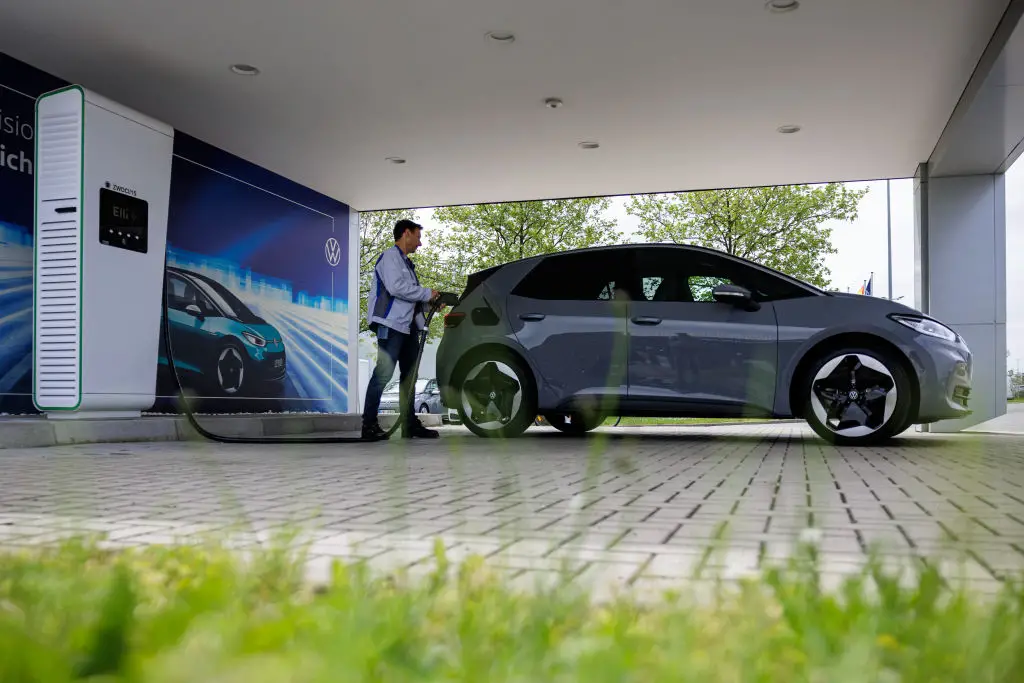

Table of Contents
H2: The Economic Challenges of Rapid EV Adoption
The rapid adoption of EVs, as mandated by many governments, presents significant economic hurdles for the auto industry. These challenges go beyond simply producing electric cars; they encompass the entire manufacturing and sales ecosystem.
H3: High Upfront Costs of EV Production:
Producing EVs is currently more expensive than manufacturing ICE vehicles. This is largely due to the high cost of battery technology, a critical component impacting both vehicle price and profitability.
- Battery technology remains expensive: The cost of lithium-ion batteries, the dominant technology in current EVs, remains a major barrier to entry for mass-market adoption. Research into cheaper and more efficient battery technologies like solid-state batteries is ongoing, but hasn't yet reached widespread commercial viability.
- Investment in new manufacturing facilities and infrastructure is substantial: Automakers require significant investment to retool existing factories and build new ones specifically designed for EV production. This includes specialized equipment for battery assembly and other EV-specific components.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities for critical EV components (batteries, rare earth minerals): The supply chains for crucial EV components are often geographically concentrated and vulnerable to disruptions, leading to price volatility and potential production delays. Securing reliable and diverse supply chains is a critical concern for automakers.
- Need for government subsidies and incentives to bridge the economic gap: Many governments are providing subsidies and tax incentives to stimulate EV adoption and support the industry's transition. These are crucial in making EVs more price-competitive with ICE vehicles in the short term.
H3: Consumer Demand and Market Readiness:
Even with government incentives, consumer acceptance of EVs is not yet widespread. Several factors hinder mass adoption.
- Range anxiety and charging infrastructure limitations remain concerns for consumers: The limited range of some EVs and the uneven distribution of charging stations create anxiety among potential buyers. Expanding the charging network and improving battery technology are key to overcoming this obstacle.
- The higher initial cost of EVs compared to ICE vehicles presents a barrier to entry for many: Despite government subsidies, the upfront cost of an EV often remains higher than a comparable ICE vehicle. This is a significant barrier for many consumers, particularly those on lower incomes.
- Consumer education and awareness of EV benefits are crucial for wider adoption: Many consumers remain unaware of the long-term cost savings, environmental benefits, and performance advantages of EVs. Targeted education campaigns are crucial to increasing acceptance.
- Addressing consumer concerns through improved technology and infrastructure development is vital: Only through continuous innovation in battery technology, expansion of charging infrastructure, and increased consumer education can the automotive industry overcome these hurdles and boost market demand.
H2: The Technological Hurdles in Meeting EV Mandate Targets
Meeting the ambitious targets set by EV mandates requires significant technological advancements. Current technology presents several bottlenecks.
H3: Battery Technology Limitations:
Battery technology is the most critical limiting factor in widespread EV adoption. While advancements have been made, significant challenges persist.
- Battery lifespan, charging times, and range limitations continue to hinder widespread EV adoption: Improving battery lifespan, reducing charging times, and increasing range are all critical areas for ongoing research and development.
- Development of more efficient and sustainable battery technologies is crucial: Research into solid-state batteries, lithium-sulfur batteries, and other alternative technologies is vital for increasing energy density, reducing costs, and improving sustainability.
- Recycling and disposal of EV batteries pose environmental challenges: The responsible recycling and disposal of EV batteries is essential to mitigate environmental impacts. Developing efficient and sustainable recycling processes is critical.
- Research and innovation in battery technology are paramount for achieving mandate targets: Continued investment in research and development is crucial to overcome the limitations of current battery technology and meet the stringent demands of EV mandates.
H3: The Electric Grid Infrastructure Challenge:
Widespread EV adoption will place immense strain on existing electricity grids. This necessitates substantial infrastructure upgrades.
- The increased electricity demand from widespread EV adoption requires significant grid upgrades: Power grids must be significantly upgraded to handle the increased demand from charging millions of EVs.
- Investment in renewable energy sources is crucial to power EVs sustainably: To ensure EVs are truly environmentally friendly, a transition to renewable energy sources for electricity generation is essential.
- Smart grid technologies can help manage the increased electricity demand efficiently: Smart grid technologies, such as demand-side management and energy storage solutions, can help optimize electricity distribution and mitigate peak demand.
- A holistic approach addressing both electricity generation and grid infrastructure is necessary: A coordinated strategy that addresses both the generation and distribution of electricity is vital for successfully integrating EVs into the energy system.
H2: The Auto Industry's Response to EV Mandates
The auto industry's response to EV mandates has been multifaceted, encompassing both opposition and adaptation.
H3: Lobbying Efforts and Regulatory Challenges:
Automakers have engaged in significant lobbying efforts to influence the stringency and timelines of EV mandates.
- Automakers engage in extensive lobbying to influence the stringency and timelines of EV mandates: The industry has lobbied for more gradual transitions, arguing that rapid change is economically unsustainable and technologically infeasible.
- Arguments often center on economic viability, technological feasibility, and consumer readiness: Automakers emphasize the economic challenges of rapid EV adoption, the limitations of current battery technology, and the need for increased consumer acceptance.
- Concerns about job losses in traditional automotive manufacturing are raised: The transition to EVs could lead to job losses in traditional automotive manufacturing, creating concerns about economic disruption and worker displacement.
- Finding a balance between regulatory goals and industry realities is crucial: Governments must find a balance between ambitious environmental goals and the need for a pragmatic approach that considers the economic and technological realities faced by the auto industry.
H3: Strategic Investments and Innovation:
Despite the challenges, major automakers are investing heavily in the future of electric mobility.
- Major automakers are investing heavily in EV research, development, and production: Significant investments are being made in battery technology, electric motor design, charging infrastructure, and autonomous driving technologies.
- Collaborations and partnerships are forming to accelerate technological advancements: Automakers are increasingly collaborating with technology companies, battery manufacturers, and research institutions to accelerate innovation.
- Diversification of production lines and exploration of alternative powertrains (hybrids, hydrogen): Many automakers are diversifying their production lines to include hybrid vehicles and exploring alternative powertrains, such as hydrogen fuel cells, as part of their long-term strategy.
- A strategic approach combining adaptation and innovation is essential for survival: The auto industry must adopt a strategic approach that combines adaptation to evolving regulations with continuous innovation to remain competitive in the rapidly changing automotive landscape.
3. Conclusion:
The auto industry's relationship with EV mandates is a complex and evolving story. The transition to electric vehicles is undeniably crucial for environmental reasons, but a balanced approach is needed to ensure a sustainable and successful transformation. Addressing the economic challenges, technological hurdles, and consumer concerns requires collaboration between governments, automakers, and consumers. Only through open dialogue and strategic partnerships can we navigate the complexities of EV mandates and shape a future of transportation that is both sustainable and economically viable. To stay informed on the latest developments concerning electric vehicle mandates and the ongoing industry response, continue your research into government regulations and the wider transition to electric vehicles. Understanding the nuances of EV mandates is crucial for shaping a responsible and efficient future for the automotive industry.

Featured Posts
-
 Raznitsa V Otsenkakh Tramp Vs Dzhonson O Reytinge Prezidenta Ukrainy
May 12, 2025
Raznitsa V Otsenkakh Tramp Vs Dzhonson O Reytinge Prezidenta Ukrainy
May 12, 2025 -
 U S China Trade Negotiations Bessent Announces Progress But No Deal
May 12, 2025
U S China Trade Negotiations Bessent Announces Progress But No Deal
May 12, 2025 -
 The Streaming Rise Of Henry Cavills Action Thriller Night Hunter
May 12, 2025
The Streaming Rise Of Henry Cavills Action Thriller Night Hunter
May 12, 2025 -
 Former Bellator Champ Freire Targets Jose Aldo Fight
May 12, 2025
Former Bellator Champ Freire Targets Jose Aldo Fight
May 12, 2025 -
 16 Million Penalty For T Mobile A Three Year Data Breach Timeline
May 12, 2025
16 Million Penalty For T Mobile A Three Year Data Breach Timeline
May 12, 2025
