The Decrease In US Measles Cases: Factors Contributing To The Decline
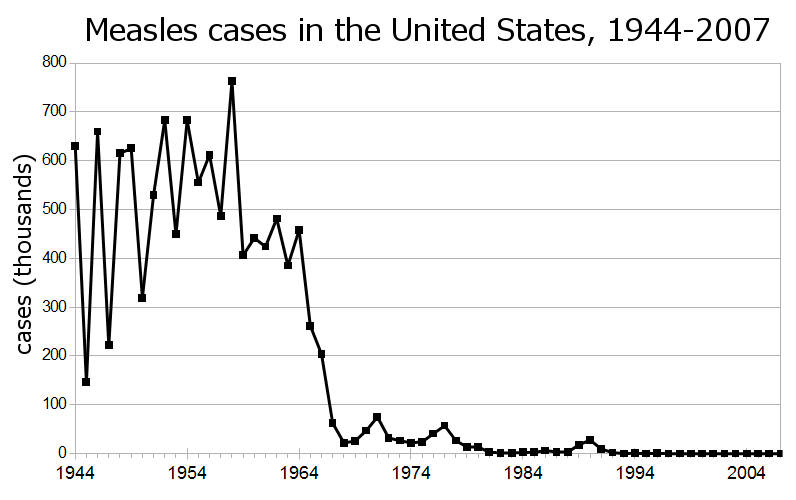
Table of Contents
The Impact of the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The MMR vaccine is undoubtedly the cornerstone of measles prevention. Its high efficacy in preventing measles infection is widely documented. The vaccine significantly reduces the risk of contracting the disease, and subsequent complications like pneumonia and encephalitis. Increased vaccination rates among children in the US have played a pivotal role in reducing measles transmission. This success is a direct result of sustained public health campaigns promoting MMR vaccination from infancy.
- Statistical data: The CDC reports a dramatic increase in MMR vaccination coverage from the 1960s to the present day, reaching over 90% for the first dose in many states. This significant increase in vaccination rates directly correlates with the sharp decline in measles cases.
- Successful public health initiatives: Government-led campaigns, educational programs in schools, and community outreach initiatives have successfully raised awareness about the importance of MMR vaccination. These efforts have effectively addressed parental concerns and misconceptions about vaccine safety.
- Challenges: Despite the considerable progress, challenges remain. Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and distrust of scientific evidence, continues to pose a threat to maintaining high vaccination rates. Addressing these concerns through evidence-based communication remains a crucial priority.
Improved Surveillance and Public Health Response
Enhanced surveillance systems are vital in detecting and controlling measles outbreaks swiftly. Modern public health infrastructure enables rapid identification of cases, allowing for prompt interventions to prevent further spread. Rapid response teams, composed of epidemiologists, healthcare professionals, and public health officials, play a critical role in containing outbreaks. These teams swiftly investigate cases, identify contacts, and implement control measures such as quarantine and targeted vaccination campaigns.
- Effective surveillance programs: The CDC’s National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) plays a crucial role in tracking measles cases and identifying trends. This enables real-time monitoring and rapid response to potential outbreaks.
- Rapid response teams: These teams are expertly trained to manage outbreaks effectively, minimizing transmission and preventing widespread infection. Their swift actions are paramount in reducing the impact of outbreaks.
- Successful outbreak control: Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of rapid response strategies in controlling measles outbreaks. Quick identification of cases and swift implementation of control measures significantly reduced the spread of the virus.
The Role of Herd Immunity in Reducing Measles Transmission
Herd immunity is a critical concept in understanding the decline in measles cases. It refers to the indirect protection of individuals who are not immune to a disease, achieved by immunizing a large proportion of the population. High vaccination rates are crucial for achieving herd immunity, which significantly reduces the risk of measles transmission within the community. When a large percentage of the population is immune, the virus finds it difficult to spread, thus protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated.
- Scientific explanation: Herd immunity works by interrupting the chain of transmission. When a sufficient proportion of the population is vaccinated, the virus is less likely to find susceptible individuals, thereby preventing outbreaks.
- Vaccination rates and herd immunity: Studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between high MMR vaccination rates and the establishment of herd immunity, leading to a significant reduction in measles incidence.
- Communities achieving herd immunity: Many communities across the US have achieved high vaccination rates, leading to the eradication of measles within those specific areas. This showcases the power of herd immunity in protecting entire populations.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Vaccine hesitancy, driven by misinformation and distrust, poses a significant challenge to maintaining the decline in measles cases. Combating this requires strategic communication and addressing public concerns with evidence-based information. This includes debunking myths and providing accurate information about vaccine safety and efficacy.
- Effective strategies: Targeted public health campaigns using trusted sources of information, such as doctors and public health organizations, can help counter vaccine hesitancy. These campaigns can focus on factual information and answering commonly asked questions.
- Trusted sources of information: Providing accessible and reliable information from credible sources like the CDC and WHO is essential. This helps build trust and counter misinformation that is prevalent online.
- Impact of social media: Social media platforms, while having potential for positive impact, also play a significant role in spreading misinformation regarding vaccines. Combating this requires proactive strategies to counter false narratives.
Maintaining the Decline in US Measles Cases: A Call to Action
The significant decrease in US measles cases is a result of several interconnected factors: the high efficacy of the MMR vaccine, improved surveillance and public health response systems, the establishment of herd immunity through high vaccination rates, and the ongoing effort to counter vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. Maintaining this progress requires sustained high vaccination rates to prevent future outbreaks. Preventing measles is a collective responsibility.
We urge everyone to get vaccinated against measles, advocate for vaccination within their communities, and actively promote accurate information about measles and the MMR vaccine. By working together to ensure high vaccination rates and combating misinformation, we can continue to reduce measles cases and protect public health. Continued vigilance and unwavering dedication to vaccination efforts are critical in maintaining the hard-won progress in preventing measles and ensuring a healthier future for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025
Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Dana Whites Update Fuels Debate Did Jon Jones Mentally Exhaust Tom Aspinall
May 30, 2025
Dana Whites Update Fuels Debate Did Jon Jones Mentally Exhaust Tom Aspinall
May 30, 2025 -
 Djokovic And Sinners French Open Showdown A Step By Step Analysis
May 30, 2025
Djokovic And Sinners French Open Showdown A Step By Step Analysis
May 30, 2025 -
 Glastonbury Tickets Official Resale Sells Out In 30 Minutes
May 30, 2025
Glastonbury Tickets Official Resale Sells Out In 30 Minutes
May 30, 2025 -
 The Musk Gates Debate Examining The Claims Of Child Mortality And Corporate Responsibility
May 30, 2025
The Musk Gates Debate Examining The Claims Of Child Mortality And Corporate Responsibility
May 30, 2025
