The Fall Of School Desegregation Orders: Analyzing The Justice Department's Decision
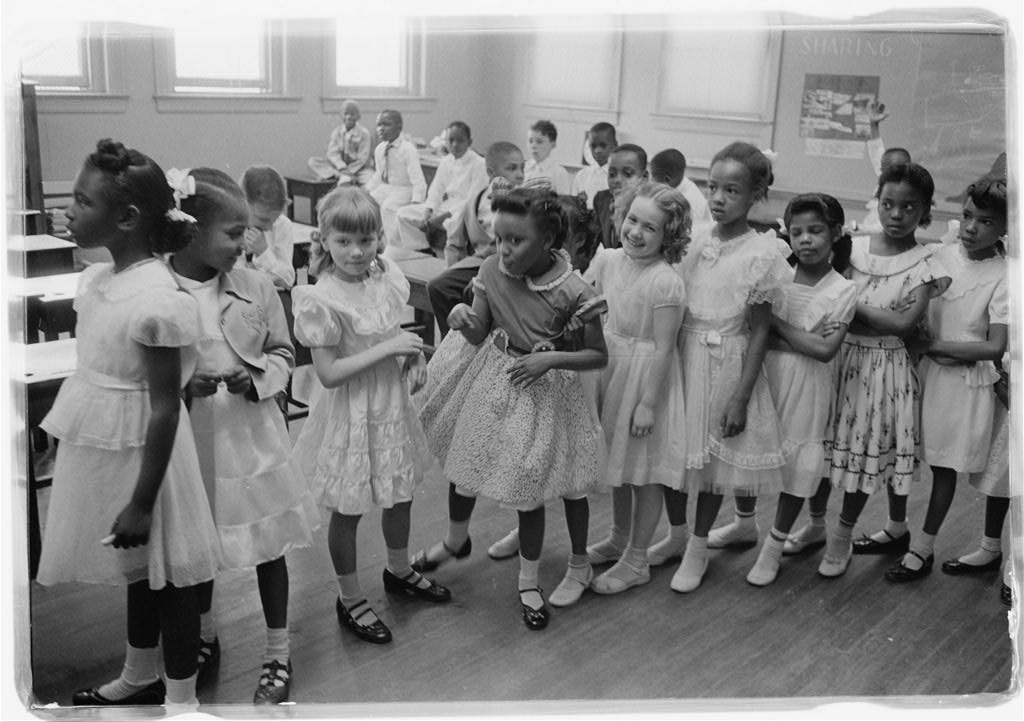

Table of Contents
The History of School Desegregation Orders and the Brown v. Board Decision
The landmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court case of 1954 declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. This ruling, a watershed moment in the Civil Rights Movement, aimed to dismantle the system of legally mandated segregation that had perpetuated educational inequality for generations. However, the implementation of Brown v. Board proved far more challenging than its declaration. Many Southern states actively resisted desegregation, employing tactics such as "massive resistance" to obstruct the court's mandate.
The federal government's role in enforcing desegregation evolved over time. While the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 provided legal frameworks to combat discrimination, the actual enforcement of desegregation often required protracted legal battles and court-ordered mandates. These school desegregation orders became crucial tools in achieving – albeit imperfectly – racial integration in many school districts.
- Key milestones in the desegregation movement: Brown v. Board of Education (1954), Civil Rights Act of 1964, Voting Rights Act of 1965, Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (1971).
- Examples of successful and unsuccessful desegregation efforts: Some districts successfully integrated schools through busing and other measures, while others faced persistent resistance and continued segregation.
- Challenges encountered during the desegregation process: Resistance from local communities, inadequate funding for desegregation efforts, and the persistent effects of historical segregation.
The Justice Department's Shift in Policy Regarding School Desegregation
Recently, the Justice Department has significantly altered its approach to school desegregation orders. This shift represents a departure from decades of federal intervention aimed at achieving racial balance in schools. The department has increasingly declined to intervene in cases involving alleged segregation, and in some instances, has actively sought to end or modify existing desegregation orders.
This change in policy has been met with criticism from civil rights advocates who argue it will lead to increased segregation and exacerbate existing inequalities. The Justice Department, however, contends that these orders are no longer necessary and that other means of addressing racial disparities should be pursued.
- Specific examples of cases impacted by the policy shift: Mention specific court cases where the Justice Department has intervened to end or modify desegregation orders. Include links to relevant court documents.
- Key figures and their roles in shaping the policy change: Identify key individuals within the Justice Department and their roles in the policy shift.
- Statements from the Justice Department justifying the decisions: Quote relevant statements from the Justice Department explaining their rationale for the changes.
The Impact of the Policy Shift on Affected School Districts and Students
The consequences of ending or modifying school desegregation orders are far-reaching and potentially devastating for affected school districts and students. The most immediate concern is the risk of re-segregation, potentially leading to a return to the racially stratified educational system that Brown v. Board sought to dismantle.
This re-segregation could have a profound impact on student achievement, particularly for minority students who may lack access to the same resources and opportunities as their white counterparts. The loss of diverse learning environments could also negatively impact social and emotional development.
- Potential negative effects on minority student achievement: Discuss the documented correlation between school segregation and lower academic achievement for minority students.
- Re-segregation trends in impacted school districts: Provide data or examples illustrating a rise in school segregation in districts where desegregation orders have been lifted.
- Opinions of various stakeholders regarding the Justice Department’s decisions: Include perspectives from students, parents, teachers, administrators, and community members.
Legal and Ethical Considerations Surrounding the End of School Desegregation Orders
The Justice Department's decisions regarding school desegregation orders raise significant legal and ethical questions. Opponents argue that these actions violate the principles of equality and social justice established by Brown v. Board and subsequent legislation. The legal arguments surrounding the issue involve interpretations of existing laws and precedents, and the potential for future legal challenges remains.
From an ethical standpoint, ending court-ordered desegregation raises concerns about fairness, equity, and the government's responsibility to address historical injustices. Critics argue that the policy shift disproportionately harms vulnerable populations and undermines efforts to create a more equitable educational system.
- Legal precedents relevant to the current situation: Discuss relevant Supreme Court cases and legal interpretations that bear on the issue of school desegregation.
- Ethical arguments for maintaining desegregation orders: Explain the ethical principles that support the continued enforcement of desegregation orders.
- Potential legal avenues for challenging the Justice Department: Discuss the potential for legal challenges to the Justice Department's actions, such as lawsuits and appeals.
Conclusion: The Future of School Desegregation and the Justice Department's Role
The Justice Department's decision to curtail school desegregation orders marks a significant shift in policy with potentially far-reaching consequences. The risk of re-segregation and its negative impact on student achievement and racial equality are substantial. The long-term implications for educational equity in the United States remain uncertain, but the current trajectory suggests a worrying retreat from the ideals of Brown v. Board. This underscores the ongoing struggle for educational equity and the crucial need for continued vigilance and advocacy. To ensure progress toward a truly integrated and equitable educational system, we must stay informed about school desegregation efforts, support organizations fighting for school desegregation, and learn more about the ongoing debate surrounding school desegregation orders.

Featured Posts
-
 Reform Uk Investigation Into Rupert Lowe Following Bullying Complaints
May 02, 2025
Reform Uk Investigation Into Rupert Lowe Following Bullying Complaints
May 02, 2025 -
 Nebraska Voter Id Initiative Receives National Recognition
May 02, 2025
Nebraska Voter Id Initiative Receives National Recognition
May 02, 2025 -
 Reform Uk To Investigate Serious Bullying Claims Against Rupert Lowe
May 02, 2025
Reform Uk To Investigate Serious Bullying Claims Against Rupert Lowe
May 02, 2025 -
 Fortnite Community Outraged Over Backward Music Update
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Community Outraged Over Backward Music Update
May 02, 2025 -
 Justice Departments Decision The Fallout From Ending School Desegregation
May 02, 2025
Justice Departments Decision The Fallout From Ending School Desegregation
May 02, 2025
