The Fallout: Justice Department's School Desegregation Order And Its Consequences
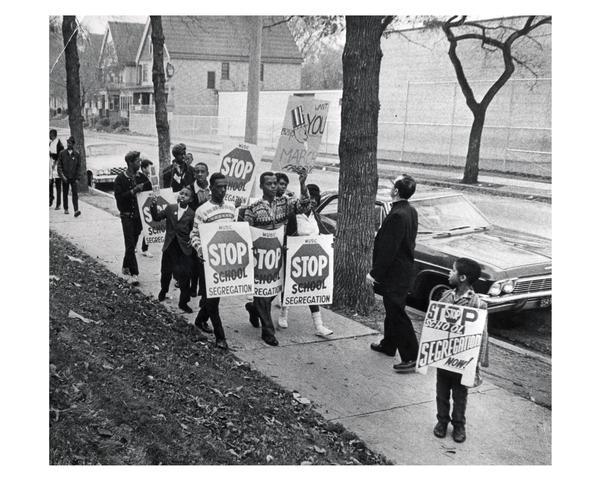

Table of Contents
The Initial Push for School Desegregation
The Role of the Justice Department
The Department of Justice played a crucial role in enforcing the Supreme Court's ruling, acting as a key driver of school desegregation. Their actions were vital in challenging deeply ingrained systems of racial segregation.
- Initiated numerous lawsuits across the Southern states: The DOJ filed lawsuits against countless school districts that refused to comply with the Brown decision, initiating a legal battle across the South.
- Utilized various legal strategies to overcome resistance: From injunctions to contempt citations, the DOJ employed a range of legal tactics to pressure resistant school boards and officials into compliance. These strategies often involved protracted legal battles.
- Collaborated with civil rights organizations to support desegregation efforts: The DOJ worked closely with organizations like the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund to coordinate legal strategies and provide support for desegregation efforts on the ground. This collaboration was essential for navigating the complex social and political landscape.
Early Resistance and its Manifestations
The South's resistance to school desegregation was fierce and multifaceted, employing various strategies to impede progress.
- Massive Resistance: This organized, widespread campaign of defiance actively worked to circumvent federal court orders mandating desegregation. It involved political maneuvering, legislative efforts, and public campaigns of misinformation.
- School closures: In some districts, schools were temporarily or permanently closed rather than integrate, depriving children of their education as a means of protest.
- White flight: Many white families moved to suburban areas to avoid integrated schools, creating further segregation and exacerbating resource disparities. This phenomenon contributed significantly to the creation of racially homogenous school districts.
- Violence and intimidation: Acts of violence, intimidation, and harassment were used against both Black students attempting to integrate and civil rights activists working to facilitate desegregation.
Strategies and Tactics Employed During Desegregation
Court-Ordered Busing
Busing students to achieve racial balance in schools became a highly controversial but frequently used strategy to overcome de facto segregation.
- Positive impact on academic opportunities for some students: For some students, busing provided access to better-resourced schools and improved educational opportunities.
- Negative consequences: Busing also increased racial tensions in many communities, fueled white flight to suburban schools, and presented significant logistical challenges. It remains a deeply divisive issue in many communities today.
Funding and Resource Allocation
The federal government attempted to provide funding to support desegregation, but the distribution was often uneven and insufficient to address existing disparities.
- Inequities in funding exacerbated existing disparities: Many previously underfunded, predominantly Black schools received inadequate resources even after desegregation efforts began, perpetuating educational inequities.
- Created challenges for achieving true equality in education: Unequal funding meant that integrated schools often lacked the resources necessary to provide all students with a quality education.
Community Involvement and Resistance to Desegregation
Community responses to desegregation were varied, ranging from active support to fierce resistance. Understanding these differing perspectives provides crucial context.
- The role of community leaders and activists: Local leaders, both Black and white, played critical roles in shaping community responses, either fostering cooperation or fueling resistance.
- The impact of media coverage and public opinion: Media portrayals of desegregation significantly influenced public opinion, often exacerbating tensions and shaping perceptions of the process.
Long-Term Consequences of School Desegregation
The Legacy of Achievement Gaps
Despite progress, significant achievement gaps persist between racial groups in education, a lingering consequence of historical and ongoing inequities.
- Socioeconomic factors affecting educational outcomes: Socioeconomic disparities continue to play a significant role in student achievement, compounding the challenges of achieving educational equity.
- The ongoing need for equitable educational opportunities: Addressing these achievement gaps requires ongoing commitment to equitable funding, resources, and policies.
The Sociopolitical Impact of School Desegregation
School desegregation had a profound and lasting impact on American society, shaping political discourse and social relations for decades to come.
- The impact on racial attitudes and social cohesion: While desegregation fostered progress, its impact on racial attitudes and social cohesion has been complex and uneven across communities.
- The enduring legacy of the Civil Rights Movement: School desegregation was a pivotal component of the broader Civil Rights Movement, shaping its trajectory and leaving a lasting legacy on the fight for racial justice.
Contemporary Relevance of School Desegregation
The fight for equitable education continues today, with ongoing debates on critical issues directly related to school desegregation.
- The relevance of school desegregation in the 21st century: The legacy of segregation continues to impact school systems today, requiring ongoing efforts to address persistent inequities.
- Ongoing debates on school choice, funding, and racial equity: Current debates over school choice, funding mechanisms, and approaches to achieving racial equity directly reflect the ongoing struggle for educational justice rooted in the legacy of school desegregation.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's efforts to enforce school desegregation represent a critical chapter in American history. While the struggle for racial equality in education continues, the legacy of the school desegregation era remains profoundly impactful. Understanding the successes, challenges, and lasting consequences of these efforts is crucial to informing current educational policies and practices. By acknowledging the complexities and ongoing challenges associated with school desegregation, we can strive towards a more equitable future for all students. Learn more about the ongoing fight for school desegregation and how to support these efforts today.

Featured Posts
-
 Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results Check The Latest Draw Numbers
May 03, 2025
Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results Check The Latest Draw Numbers
May 03, 2025 -
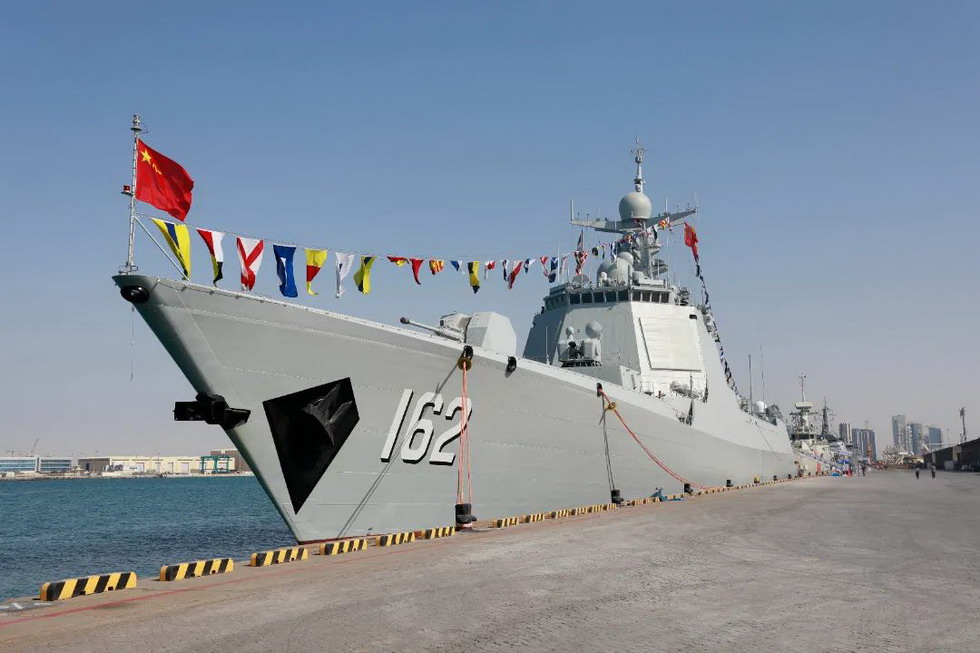 Chinese Navy Ships Spotted Near Sydney Implications For Australias Security
May 03, 2025
Chinese Navy Ships Spotted Near Sydney Implications For Australias Security
May 03, 2025 -
 The History Of Pancake Day From Shrove Tuesday To Modern Celebrations
May 03, 2025
The History Of Pancake Day From Shrove Tuesday To Modern Celebrations
May 03, 2025 -
 Sulm Me Arme Te Bardhe Ne Ceki Bilanc Tragjik Me Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025
Sulm Me Arme Te Bardhe Ne Ceki Bilanc Tragjik Me Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025 -
 Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Ne Ceki Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025
Sulm Me Thike Ne Qender Tregtare Ne Ceki Dy Te Vdekur
May 03, 2025
