The High Cost Of Neglect: Investing In Childhood To Prevent Mental Health Issues
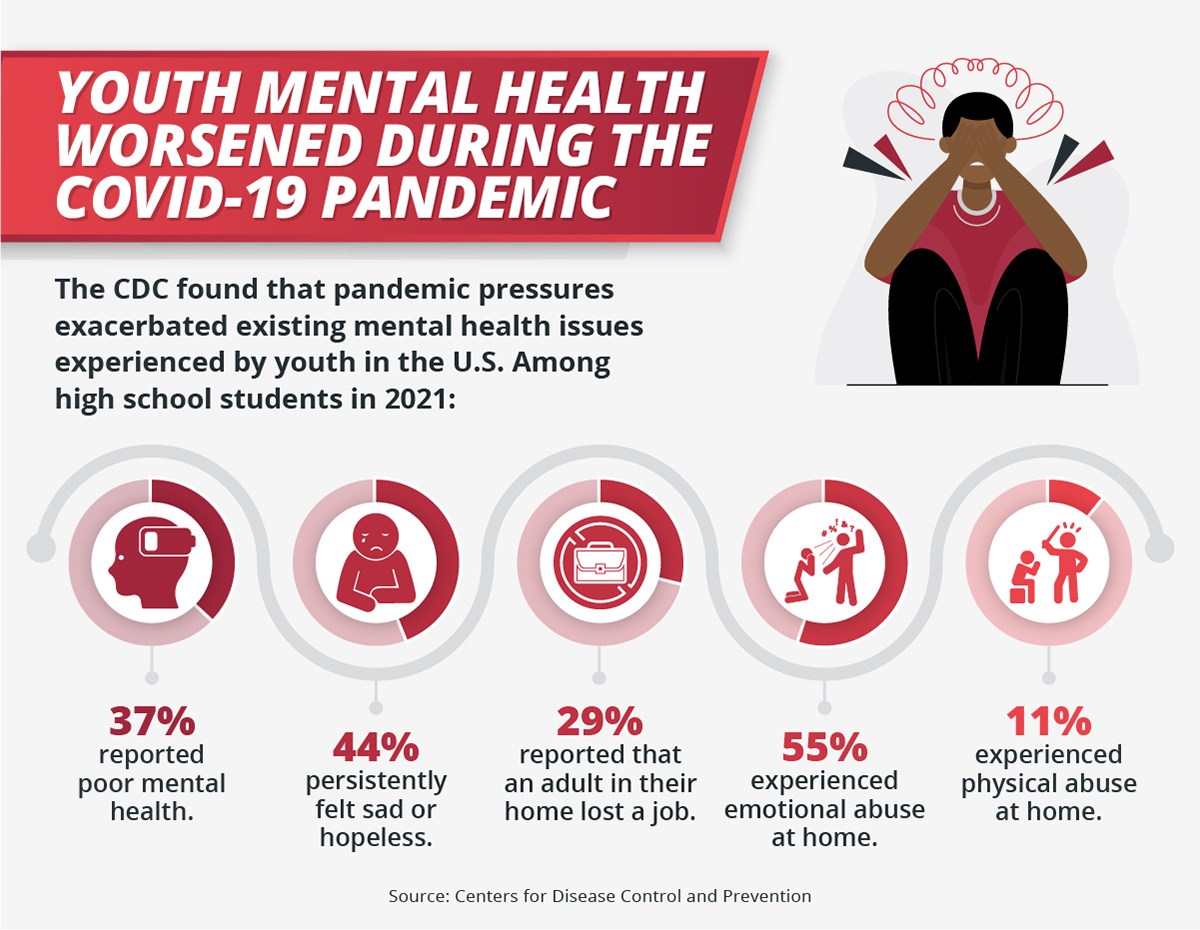
Table of Contents
The Economic Burden of Untreated Childhood Mental Health Issues
The financial consequences of untreated childhood mental health problems are profound and far-reaching, impacting individuals, families, and society as a whole.
Healthcare Costs
The escalating expenses associated with treating mental health disorders in adulthood are alarming. These costs encompass therapy, medication, hospitalization, and lost productivity, creating a significant drain on healthcare systems.
- Anxiety Disorders: Treatment for anxiety disorders, often stemming from childhood trauma or neglect, can involve ongoing therapy, medication, and potentially intensive inpatient care, costing thousands of dollars annually.
- Depression: Untreated childhood depression significantly increases the risk of severe depression and related health issues in adulthood, leading to substantial healthcare expenditures throughout life.
- Addiction: Substance abuse disorders, frequently linked to unresolved childhood trauma, necessitate expensive rehabilitation programs and ongoing support, resulting in immense lifetime costs.
- Lifetime Costs: Studies indicate that the lifetime cost of untreated mental illness is substantially higher than the cost of early intervention and prevention programs. The NIMH (National Institute of Mental Health) reports significant disparities in the cost of care depending on the severity and chronicity of the condition.
Societal Costs
The economic impact extends far beyond healthcare, encompassing a broader range of societal costs.
- Decreased Workforce Participation: Individuals struggling with untreated mental health issues often experience reduced work productivity, absenteeism, and even unemployment, leading to a loss of tax revenue and economic output.
- Increased Crime Rates: Research suggests a strong correlation between childhood trauma and increased crime rates in adulthood. The costs associated with law enforcement, incarceration, and the criminal justice system are substantial.
- Strain on Social Services: Untreated mental health issues often lead to reliance on social welfare programs, placing a strain on government resources and budgets. Studies consistently demonstrate a connection between childhood adversity and later reliance on social support systems.
Lost Productivity and Earning Potential
Untreated mental health problems significantly impact an individual's future earning capacity, perpetuating economic inequality.
- Career Limitations: Mental health challenges can hinder career advancement, leading to lower-paying jobs and reduced lifetime earnings.
- Decreased Lifetime Earnings: Individuals with untreated mental health issues often earn considerably less throughout their working lives compared to their mentally healthy peers. This impacts not only their personal finances but also contributes to the overall economic burden on society.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Preventative Measures
Addressing mental health challenges in childhood is crucial for mitigating the long-term economic and social consequences.
Identifying Risk Factors
Recognizing potential risk factors is the first step in effective prevention.
- Poverty: Children living in poverty are significantly more likely to experience mental health issues due to stress, lack of resources, and inadequate healthcare access.
- Neglect: Neglect and abuse can have devastating and long-lasting effects on a child's mental well-being.
- Trauma: Exposure to traumatic events, such as violence or natural disasters, can increase the risk of developing mental health problems.
- Genetics: While not deterministic, genetic predisposition plays a role in mental health, making early identification and monitoring crucial.
Effective Early Intervention Strategies
Implementing early intervention strategies is vital to prevent the escalation of childhood mental health issues.
- Parental Support Programs: Programs providing parents with education, resources, and support can significantly improve child outcomes.
- Access to Mental Healthcare: Ensuring children have access to age-appropriate mental health services is crucial for early detection and treatment.
- Early Childhood Education: High-quality early childhood education programs foster resilience and provide a supportive environment for development.
- Therapeutic Approaches: Evidence-based therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and play therapy, can effectively address childhood mental health challenges.
The Role of Parental Support and Education
Parental involvement is critical in reducing the risk of mental health issues.
- Supportive Parenting: A warm, nurturing, and consistent parenting style fosters emotional well-being.
- Positive Family Environments: A positive family environment promotes resilience and reduces stress.
- Parental Education: Educating parents about child mental health allows for early identification of potential problems and prompt intervention.
Investing in Prevention: A Societal Investment
Investing in preventative measures is a far more cost-effective strategy than dealing with the consequences of untreated mental health problems in adulthood.
Cost-Effectiveness of Prevention
Prevention programs yield a substantial return on investment (ROI).
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Early intervention significantly reduces the need for expensive long-term treatment.
- Improved Workforce Participation: Preventing mental health issues contributes to a healthier, more productive workforce.
- Lower Crime Rates: Addressing childhood trauma can contribute to lower crime rates and reduced costs associated with the justice system.
Policy Recommendations
Policy changes are necessary to enhance access to mental healthcare for children and families.
- Increased Funding for Mental Health Services: Greater investment in early intervention programs is vital.
- Improved Access to Early Childhood Education: Expanding access to high-quality early childhood education programs is crucial.
- Comprehensive Mental Health Training for Educators: Equipping educators with the skills to recognize and address mental health concerns in children.
Conclusion
Neglecting children's mental health needs carries immense financial and societal costs. Investing in childhood to prevent mental health issues is not merely an act of compassion; it's a crucial investment in a healthier, more productive, and economically stable future. We must prioritize early intervention and preventative measures through increased funding, improved access to care, and strengthened support systems for families. Contact your elected officials, support organizations dedicated to children's mental health, and raise awareness within your communities. Let's collectively champion the cause of "Investing in Childhood to Prevent Mental Health Issues" and create a brighter future for generations to come. Learn more and get involved by visiting [link to a relevant organization].

Featured Posts
-
 Understanding This Country People Places And Politics
May 03, 2025
Understanding This Country People Places And Politics
May 03, 2025 -
 Drone Attack On Gaza Freedom Flotilla Ship Sos Signal Issued Near Malta
May 03, 2025
Drone Attack On Gaza Freedom Flotilla Ship Sos Signal Issued Near Malta
May 03, 2025 -
 Bbc Two Hd Programming Newsround
May 03, 2025
Bbc Two Hd Programming Newsround
May 03, 2025 -
 Reform Uks Agricultural Plan A Farmers Perspective
May 03, 2025
Reform Uks Agricultural Plan A Farmers Perspective
May 03, 2025 -
 Understanding The Recent Decline In Riot Platforms Riot Stock Price
May 03, 2025
Understanding The Recent Decline In Riot Platforms Riot Stock Price
May 03, 2025
