The Impact Of Wildfires: Driving Record-High Global Forest Loss
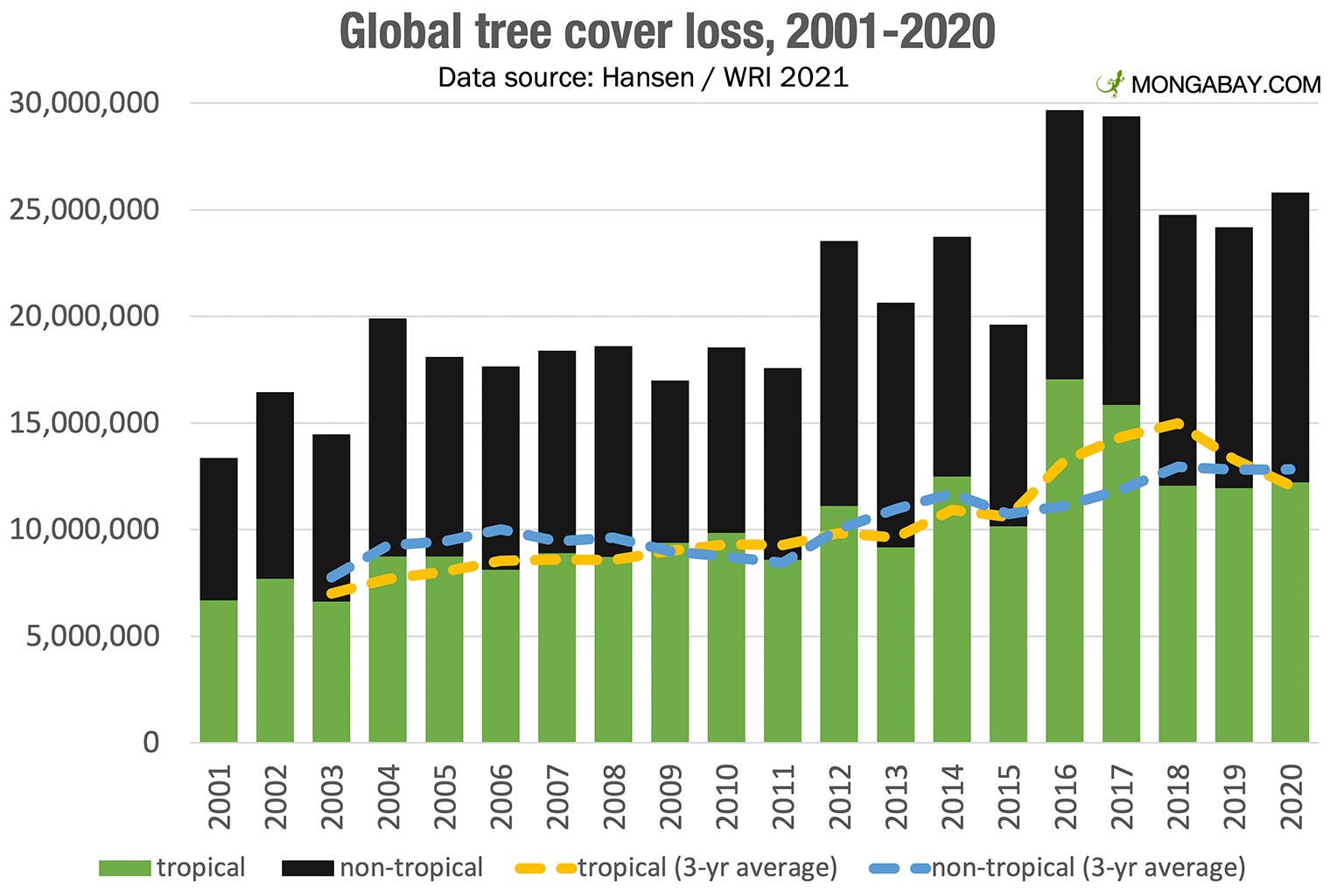
Table of Contents
The Rising Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
The sheer scale of global forest loss is alarming, and wildfires are a major contributor to this crisis. Understanding the reasons behind the rising frequency and intensity of these devastating events is crucial to addressing the problem.
Climate Change as a Key Driver
Climate change is undeniably exacerbating wildfire risk. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered weather patterns create ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread.
- Increased fuel dryness: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, turning forests into tinderboxes.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer springs and autumns extend the periods when wildfires are most likely to occur.
- Stronger winds: Climate change can influence wind patterns, leading to faster and more unpredictable wildfire spread.
Data from the Global Forest Watch indicates a significant upward trend in the area burned by wildfires globally, with certain regions experiencing particularly dramatic increases. The effects of wildfires are becoming increasingly severe and widespread.
Human Activities and Wildfire Risk
While climate change plays a significant role, human activities also contribute significantly to wildfire risk.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture, logging, and urban development removes natural barriers and creates more fuel for wildfires.
- Inadequate fire prevention measures: Insufficient forest management, including the lack of controlled burns and firebreaks, increases the risk of uncontrolled wildfires.
- Accidental ignitions: Human negligence, such as discarded cigarettes, unattended campfires, and power line malfunctions, are frequent causes of wildfires.
- Urban sprawl: The expansion of urban areas into forested regions increases the interface between human activity and wildfire-prone landscapes, leading to higher risks.
Devastating Consequences of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The consequences of wildfire-driven forest loss are far-reaching and devastating, impacting various aspects of our planet's health and human well-being.
Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption
Wildfires decimate plant and animal populations, destroying habitats and disrupting delicate ecological balances.
- Habitat destruction: Wildfires eliminate crucial habitats, forcing species to relocate or face extinction.
- Loss of keystone species: The disappearance of keystone species can trigger cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
- Disruption of food webs: Wildfires disrupt the intricate relationships between plants and animals, impacting entire food chains.
For instance, the Australian bushfires of 2019-2020 led to the significant loss of koalas and other unique wildlife, demonstrating the devastating impact of wildfires on biodiversity.
Climate Change Amplification
Wildfires release massive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and creating a dangerous feedback loop.
- Carbon release from burning biomass: Burning trees and other vegetation releases vast quantities of stored carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Reduced carbon sequestration capacity: Damaged forests have a diminished ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Studies have shown that wildfires contribute significantly to annual global greenhouse gas emissions, further accelerating the climate crisis and increasing the frequency and intensity of future wildfire events. The effects of wildfires on climate change are undeniable.
Economic and Social Impacts
The economic and social costs associated with wildfires are substantial.
- Costs of firefighting efforts: Suppressing large-scale wildfires requires immense resources and financial investments.
- Economic losses from damaged timber and tourism: Wildfires can decimate timber industries and damage tourism infrastructure, leading to significant economic losses.
- Health impacts from smoke inhalation: The smoke from wildfires poses severe health risks, leading to respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Social displacement of communities: Wildfires can force people to evacuate their homes, leading to displacement and disruptions to daily life.
The economic impact of wildfires extends far beyond immediate damage, affecting local economies dependent on forest resources and impacting insurance markets.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies to Combat Wildfire Impact
Addressing the impact of wildfires requires a multifaceted approach encompassing mitigation, adaptation, and proactive strategies.
Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial in mitigating wildfire risk.
- Fuel reduction strategies: Controlled burns and the thinning of forests can reduce the amount of flammable material available for wildfires.
- Creating firebreaks: Strategic clearing of vegetation can create barriers that slow or stop the spread of wildfires.
- Community-based forest management: Engaging local communities in forest management promotes sustainable practices and increases awareness of wildfire risks.
Implementing these practices requires collaboration between government agencies, forestry professionals, and local communities.
Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is paramount in reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
- Transition to renewable energy: Shifting away from fossil fuels reduces greenhouse gas emissions, curbing climate change.
- Carbon capture technologies: Developing and implementing technologies that capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere can help mitigate climate change.
- International cooperation on climate action: Global cooperation is essential to achieving significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Combating climate change is a collective responsibility requiring global efforts and coordinated policies.
Early Warning Systems and Fire Suppression Techniques
Advancements in technology play a vital role in improving wildfire response.
- Satellite monitoring: Sophisticated satellite systems allow for early detection of wildfires, providing crucial time for intervention.
- Improved communication systems: Effective communication networks are essential for coordinating firefighting efforts and evacuations.
- Development of more effective firefighting equipment: Ongoing research and development are crucial for improving firefighting techniques and equipment.
Conclusion
The impact of wildfires on record-high global forest loss is undeniable. We've seen how increased frequency and intensity, fueled by climate change and human activities, lead to devastating consequences for biodiversity, climate, and human societies. The economic and social costs are significant, emphasizing the urgent need for proactive mitigation and adaptation strategies. Understanding the devastating impact of wildfires is the first step towards effective action. We must collectively work towards mitigating climate change, improving forest management, and supporting policies that prioritize wildfire prevention and preparedness. Let's protect our forests and secure a sustainable future by addressing the effects of wildfires and working towards a more resilient world. The future of our forests depends on our collective commitment to tackling the wildfire impact.

Featured Posts
-
 Jenson Button Back In The 2009 Brawn A Look Back
May 25, 2025
Jenson Button Back In The 2009 Brawn A Look Back
May 25, 2025 -
 Proposed Changes To Juvenile Sentencing In France
May 25, 2025
Proposed Changes To Juvenile Sentencing In France
May 25, 2025 -
 Florentino Perez Y El Futuro Del Real Madrid
May 25, 2025
Florentino Perez Y El Futuro Del Real Madrid
May 25, 2025 -
 Veterans Memorial Elementary Welcomes Lego Master Manny Garcia A Photo Recap
May 25, 2025
Veterans Memorial Elementary Welcomes Lego Master Manny Garcia A Photo Recap
May 25, 2025 -
 Surviving A Flash Flood Emergency Essential Tips And Advice
May 25, 2025
Surviving A Flash Flood Emergency Essential Tips And Advice
May 25, 2025
