The Killer Seaweed Threatening Australia's Marine Life
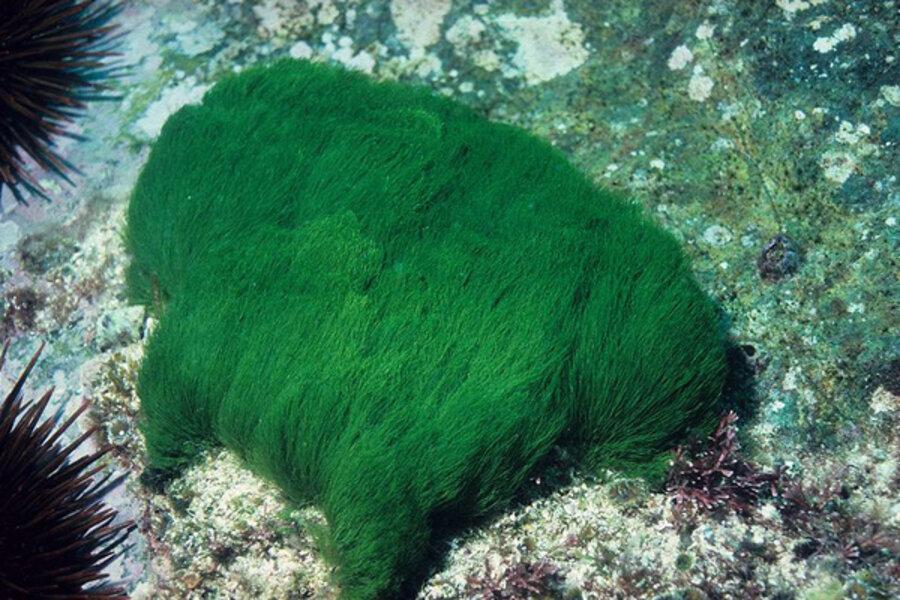

Table of Contents
2.1 The Invasive Seaweed Species: Identification and Characteristics
Caulerpa taxifolia, often dubbed the "killer seaweed," is a particularly aggressive invasive species. Its bright green, feathery fronds are easily recognizable, but its insidious nature lies in its rapid growth rate and efficient reproductive strategies. It reproduces both sexually and asexually, through fragmentation, meaning even small pieces can establish new colonies. (Include high-quality image of Caulerpa taxifolia here).
- Appearance: Dense, bright green, feathery fronds, reaching up to several centimeters in length.
- Growth Rate: Exceptionally fast, outcompeting native species for resources.
- Reproductive Strategies: Both sexual and asexual (fragmentation), allowing rapid colonization.
- Origin: The Mediterranean Sea.
- Introduction Pathways: Accidental introductions are suspected, possibly through ballast water from ships or the release of aquarium specimens.
2.2 Ecological Impacts: Disrupting Marine Habitats
The ecological consequences of Caulerpa taxifolia's invasion are profound. Its rapid growth smothers native seagrass beds, crucial habitats for countless marine species. This habitat destruction leads to a cascade effect, disrupting the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
- Seagrass Bed Degradation: Caulerpa taxifolia outcompetes seagrasses, resulting in their decline and loss of biodiversity.
- Resource Competition: It aggressively competes for sunlight, nutrients, and space, leaving native flora and fauna deprived.
- Biodiversity Loss: The displacement of native species leads to a decrease in overall biodiversity, threatening the survival of vulnerable species.
- Specific Examples: (Cite specific examples of affected species and population declines, linking to relevant scientific research.)
2.3 Economic Consequences: Impacts on Fisheries and Tourism
The economic impact of invasive seaweed like Caulerpa taxifolia is substantial. The degradation of marine habitats directly affects fisheries, impacting fish stocks and threatening the livelihoods of those dependent on the fishing industry. Furthermore, the decline in marine life and the degradation of coastal areas negatively impact the tourism sector, a crucial part of the Australian economy.
- Fisheries Decline: Reduced fish populations due to habitat loss translate to lower catches and reduced economic output.
- Tourism Impact: The unsightly appearance of invasive seaweed and the decline in marine life deter tourists, affecting revenue for coastal communities.
- Eradication Costs: The costs associated with monitoring, control, and eradication efforts are significant, demanding substantial government investment.
2.4 Current Control and Eradication Efforts
Controlling and eradicating invasive seaweed requires a multi-pronged approach. Several methods are employed, each with its own advantages and limitations.
- Physical Removal: Manually removing the seaweed, effective for small infestations, but labor-intensive and costly.
- Chemical Treatments: Using herbicides to kill the seaweed, but with potential negative impacts on other marine life.
- Biological Controls: Introducing natural predators or pathogens, a promising approach, but requiring extensive research and careful risk assessment.
2.5 Prevention and Future Strategies: Protecting Australia's Coastlines
Preventing the introduction and spread of invasive seaweed species is crucial for protecting Australia's coastlines. This requires a combination of measures:
- Stricter Ballast Water Management: Implementing stricter regulations on ballast water discharge from ships to prevent the introduction of invasive species.
- Biosecurity Measures: Strengthening biosecurity protocols to prevent the accidental introduction of invasive seaweed through the aquarium trade or other pathways.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the dangers of invasive species and the importance of reporting sightings.
- International Collaboration: Working with international partners to share information and coordinate efforts in managing invasive species.
Conclusion: Combating the Killer Seaweed Threat
The threat posed by invasive seaweed like Caulerpa taxifolia to Australia's marine environment is undeniable. The ecological and economic consequences are far-reaching, demanding immediate and sustained action. Ongoing research, effective control measures, and preventative strategies are vital for protecting our marine ecosystems and preserving the biodiversity and economic value they represent. We must all play a role: Learn more about invasive seaweed, support conservation efforts, and report any sightings to the relevant authorities. Participate in citizen science initiatives to help track and monitor the spread of these invasive species. Let's work together to combat the killer seaweed threat and protect Australia's precious marine life.

Featured Posts
-
 Ticketmasters Oasis Tour Ticket Sales A Consumer Protection Law Audit
May 30, 2025
Ticketmasters Oasis Tour Ticket Sales A Consumer Protection Law Audit
May 30, 2025 -
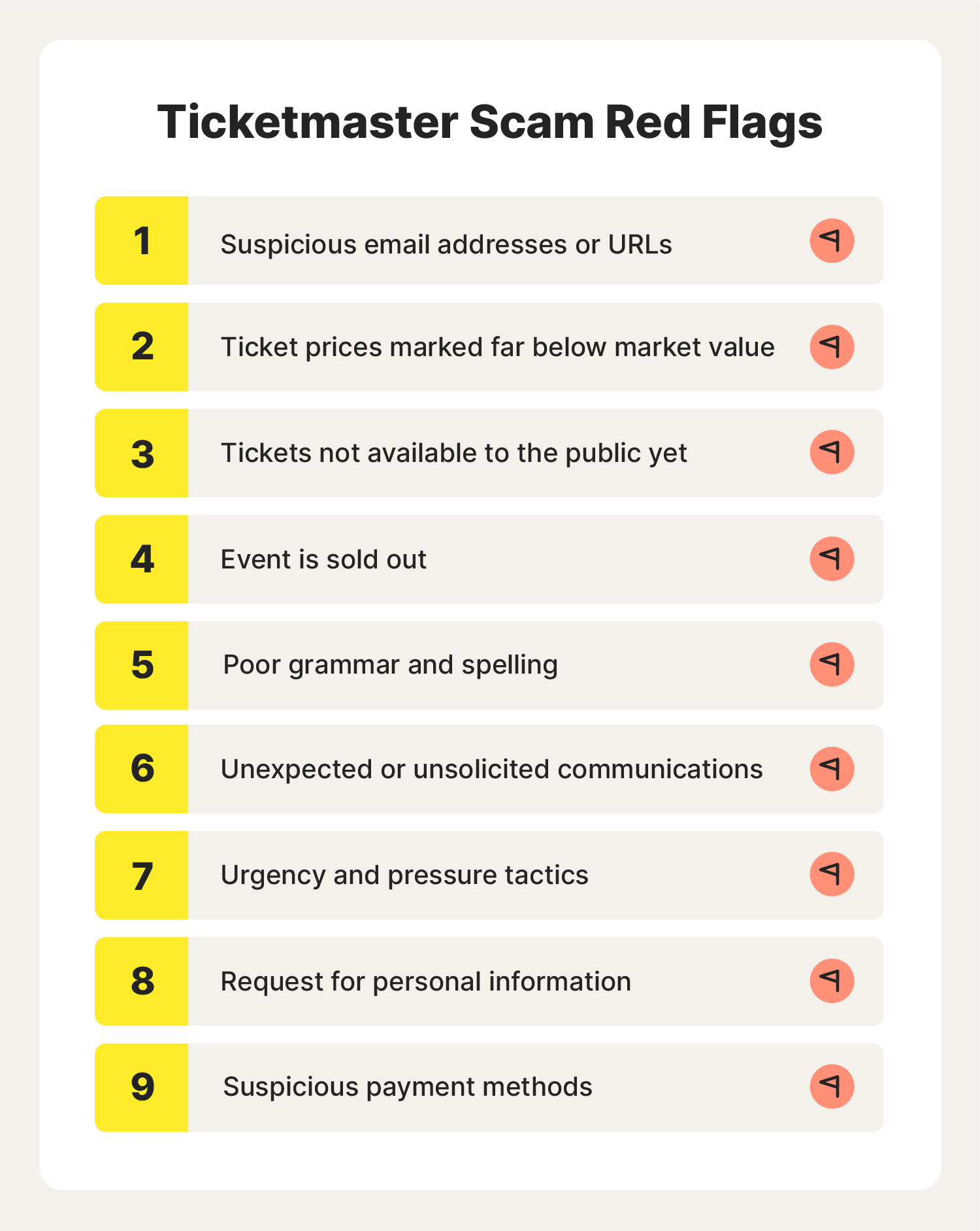 Ticketmaster Alert Protect Yourself From Fake Ticket Scams
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Alert Protect Yourself From Fake Ticket Scams
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Virtual Venue Redefine La Experiencia De Compra De Entradas
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Virtual Venue Redefine La Experiencia De Compra De Entradas
May 30, 2025 -
 Sosyal Medya Cilgina Doendue Pinar Deniz Ve Kaan Yildirim Ogullariyla Ilk Fotograflarini Paylasti
May 30, 2025
Sosyal Medya Cilgina Doendue Pinar Deniz Ve Kaan Yildirim Ogullariyla Ilk Fotograflarini Paylasti
May 30, 2025 -
 Odigos Tiletheasis Gia Tin Tetarti 23 Aprilioy
May 30, 2025
Odigos Tiletheasis Gia Tin Tetarti 23 Aprilioy
May 30, 2025
