The Long-Term Consequences Of Trump's China Tariffs On US Economic Growth
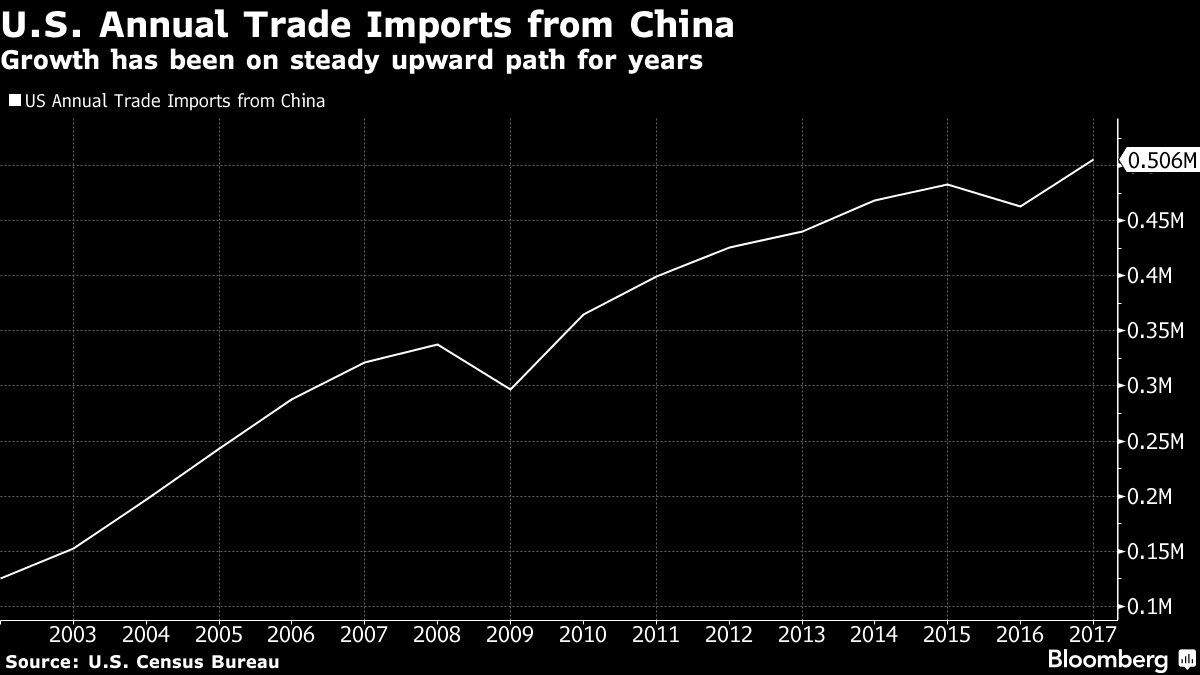
Table of Contents
Increased Prices for Consumers
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, directly increased the cost of numerous products for American consumers. This inflationary pressure had a significant impact on household budgets and overall economic activity.
-
Inflationary Pressure: The tariffs led to a noticeable increase in prices for a wide range of consumer goods. Examples include consumer electronics (like smartphones and laptops), clothing and apparel, furniture, and various household items. This price hike wasn't evenly distributed; lower-income households, which spend a larger proportion of their income on essential goods, were disproportionately affected. Studies from the Federal Reserve and other economic institutions have documented this inflationary effect, showing a clear correlation between tariff implementation and price increases.
-
Reduced Consumer Spending: Facing higher prices, consumers naturally reduced their spending. This decreased demand had a knock-on effect, slowing economic growth and impacting job creation in various sectors. The rise in inflation also eroded consumer confidence, creating a negative feedback loop: reduced spending leads to slower growth, which further diminishes confidence and spending. This dampening effect on consumer demand was a significant contributor to the overall negative economic consequences of the tariffs.
Negative Impact on US Businesses
The impact of Trump's China tariffs extended far beyond consumers, significantly impacting US businesses across various sectors.
-
Increased Input Costs: Many US businesses rely on imported raw materials and intermediate goods from China for their production processes. The tariffs increased the cost of these inputs, squeezing profit margins and hindering competitiveness. Industries particularly hard-hit included manufacturing (especially those relying on components from China) and agriculture (with increased costs for things like fertilizers and machinery). Businesses either absorbed these increased costs, leading to reduced profitability, or passed them onto consumers, contributing to inflation and reduced demand.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The tariffs disrupted global supply chains, creating significant challenges for US businesses. Many companies relied heavily on efficient and cost-effective supply chains involving Chinese manufacturers. Finding alternative sources proved costly and time-consuming, increasing the complexity and expense of managing their supply chains. The disruption to just-in-time manufacturing strategies, which rely on efficient and predictable supply chains, exacerbated the problem.
Retaliatory Tariffs and Reduced Exports
The imposition of tariffs by the US triggered retaliatory measures from China, further damaging the US economy.
-
China's Response: China responded by imposing its own tariffs on US goods, significantly impacting US exports. Industries like agriculture (soybeans, for example) and technology suffered considerable losses. Data from the US Census Bureau clearly demonstrates the reduction in US exports to China following the tariff increases, quantifying the negative impact.
-
Damage to Trade Relationships: The trade war inflicted long-term damage to US trade relationships with China and other countries. The adversarial environment created by the tariffs damaged trust and hindered future economic cooperation. This impacts the potential for future trade agreements and overall global economic stability. The disruption of established trade relationships has lasting consequences that extend beyond the immediate impact of the tariffs themselves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Trump's China tariffs have had significant negative long-term consequences on US economic growth. The increased prices for consumers, the negative impacts on businesses, the retaliatory tariffs from China, and the damage to trade relationships all contributed to a less robust and dynamic economy. Analyzing the effects of these tariffs on US economic growth highlights the complex interplay between trade policy and economic outcomes. Understanding the lasting impacts of Trump's China tariffs is crucial for informing future trade policies. Further research into the long-term economic effects of protectionist trade measures is needed to mitigate negative consequences and build a more sustainable and prosperous global economy. We need to learn from past mistakes and assess future trade policies with a keen eye towards promoting growth and stability.

Featured Posts
-
 Get Tickets To The Capital Summertime Ball 2025 The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Get Tickets To The Capital Summertime Ball 2025 The Ultimate Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Broadcoms V Mware Acquisition At And T Highlights Extreme Cost Increase
Apr 29, 2025
Broadcoms V Mware Acquisition At And T Highlights Extreme Cost Increase
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Beyond Quinoa Discovering The Health Benefits Of The New Supercrop
Apr 29, 2025
Beyond Quinoa Discovering The Health Benefits Of The New Supercrop
Apr 29, 2025 -
 New Report Details The Horrors Of The D C Blackhawk Passenger Jet Crash
Apr 29, 2025
New Report Details The Horrors Of The D C Blackhawk Passenger Jet Crash
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Report Black Hawk Helicopter And American Airlines Crash Reveals Fatal Errors
Apr 29, 2025
Report Black Hawk Helicopter And American Airlines Crash Reveals Fatal Errors
Apr 29, 2025
