The Los Angeles Wildfires: A Reflection Of Societal Shifts And The Rise Of Disaster Betting
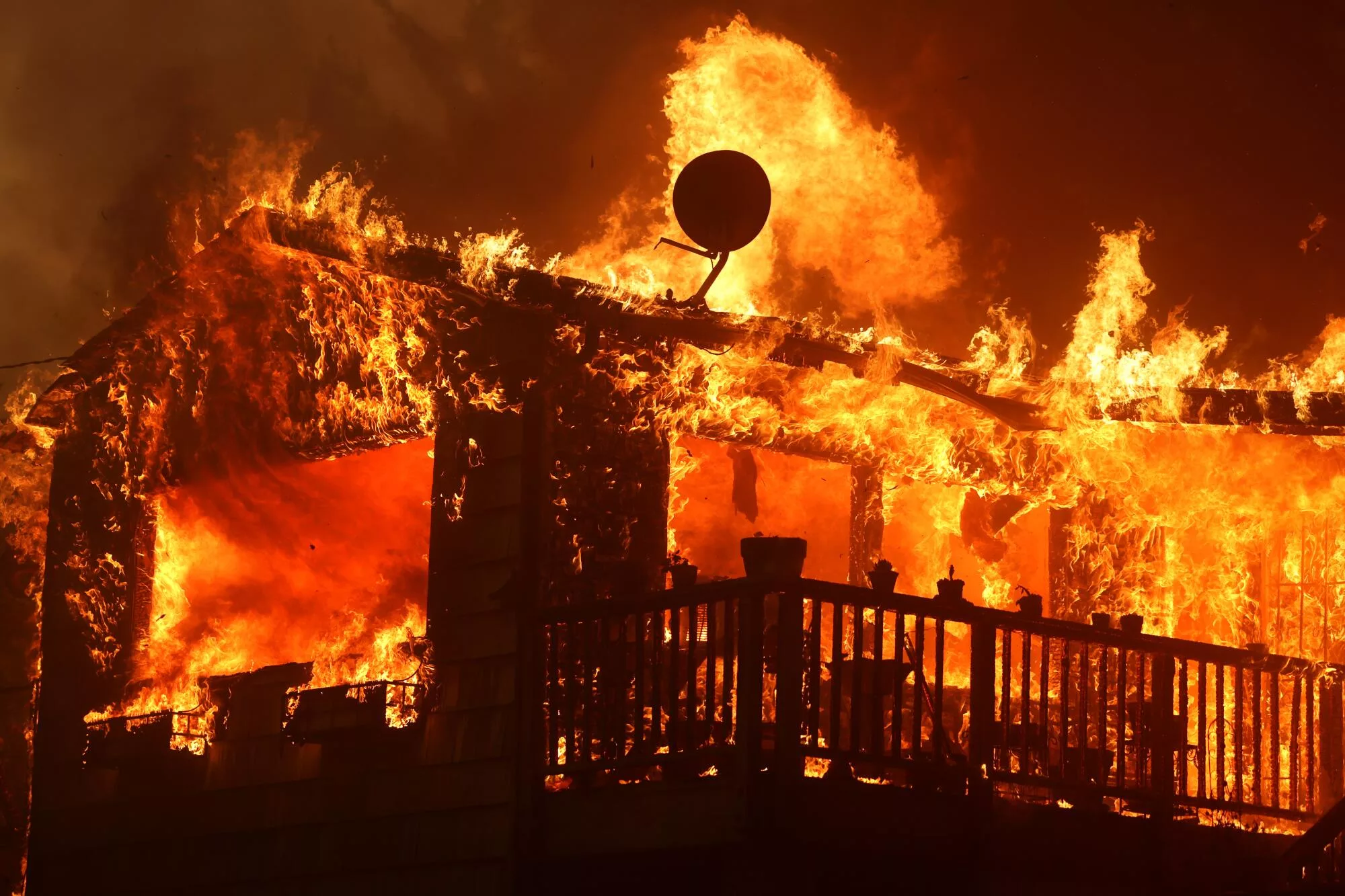

Table of Contents
The Environmental Factors Fueling the Los Angeles Wildfires
The frequency and intensity of Los Angeles wildfires are inextricably linked to environmental factors, many exacerbated by human activity.
Climate Change and its Impact
Climate change is significantly altering the wildfire landscape in Los Angeles. Increased temperatures and prolonged drought conditions create a tinderbox environment, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and difficult to control.
- Rising Temperatures: Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows a clear upward trend in average temperatures in the Los Angeles area, contributing to drier vegetation and increased flammability.
- Decreased Rainfall: Reduced rainfall leads to prolonged periods of drought, stressing vegetation and making it highly susceptible to ignition. This trend is evident in long-term rainfall data for the region.
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is also increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and Santa Ana winds, which act as powerful wildfire accelerants.
Urban Sprawl and Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI)
The expansion of housing into areas prone to wildfires, known as the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI), significantly increases both the risk and the potential for devastating consequences.
- Increased Exposure: Homes built in WUI areas are directly exposed to wildfire threats, leading to increased property damage and loss of life.
- Difficult Evacuations: Evacuating densely populated WUI areas during a wildfire can be extremely challenging, leading to delays and increased risk.
- Suppression Challenges: The proximity of homes to wildlands makes fire suppression efforts more difficult and dangerous for firefighters.
Fuel Load and Vegetation Management
The accumulation of dry brush, dead trees, and other flammable vegetation creates a significant fuel load, allowing wildfires to spread rapidly and intensely.
- Importance of Forest Management: Responsible forest management practices, including controlled burns and thinning of vegetation, are crucial for reducing fuel loads and mitigating wildfire risks.
- Community Involvement: Community involvement in fuel reduction efforts, such as brush clearing and defensible space creation around homes, is essential.
- Governmental Role: Government agencies play a key role in overseeing and supporting forest management and vegetation control programs.
Societal Shifts and Vulnerability to Wildfires
The impact of Los Angeles wildfires is not evenly distributed. Societal vulnerabilities significantly influence risk and recovery.
Socioeconomic Disparities and Wildfire Risk
Low-income communities often lack resources and access to wildfire mitigation strategies, making them disproportionately vulnerable.
- Limited Access to Resources: Many low-income communities lack the financial resources to implement wildfire preparedness measures, such as creating defensible space around their homes.
- Evacuation Challenges: Limited access to transportation and other resources can hinder evacuation efforts in low-income communities.
- Recovery Difficulties: Low-income communities often face greater challenges in recovering from the devastation of a wildfire due to limited access to insurance and other support systems.
The Role of Public Awareness and Preparedness
Effective communication and education are crucial for mitigating wildfire risks. Increased public awareness and preparedness can significantly reduce the impact of wildfires.
- Community Preparedness Plans: Developing and implementing community preparedness plans, including evacuation routes and communication strategies, is crucial.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Government agencies and community organizations play a vital role in educating the public about wildfire risks and preparedness measures.
- Early Warning Systems: Investing in and improving early warning systems for wildfires is crucial for providing timely alerts to residents.
The Rise of Disaster Betting and its Ethical Implications
The rise of disaster betting, including wagering on the extent of wildfire damage, raises serious ethical concerns.
The Mechanics of Disaster Betting
Disaster betting markets function similarly to other speculative markets, using data and predictive models to assess the likelihood of various outcomes. However, profiting from human suffering raises profound ethical questions.
- Data-Driven Predictions: These markets rely on data from various sources, including weather patterns, historical wildfire data, and even social media sentiment, to predict the severity of events.
- Ethical Concerns: The fundamental ethical concern is the commodification of human suffering and the potential for exploitation.
- Examples: While specific examples are often kept private due to the sensitive nature, the existence of such markets is increasingly documented.
The Legal and Regulatory Landscape
The legal status of disaster betting varies across jurisdictions, and the challenges of regulating these markets are significant.
- Lack of Clear Regulations: Many jurisdictions lack specific laws addressing disaster betting, creating a regulatory vacuum.
- International Challenges: The cross-border nature of online betting makes regulation even more complex.
- Ongoing Debates: The ethical and legal implications of disaster betting are subject to ongoing debate and discussion.
The Psychological Impact of Disaster Betting
Disaster betting can have serious psychological consequences for both bettors and those affected by the disaster.
- Addiction and Exploitation: The potential for gambling addiction and the exploitation of vulnerable individuals are serious concerns.
- Psychological Trauma: For those affected by the disaster, the knowledge that others are profiting from their suffering can add to their trauma.
- Responsible Gambling Initiatives: Promoting responsible gambling initiatives and providing resources for problem gamblers is crucial.
Conclusion
The devastating Los Angeles wildfires highlight a complex interplay between environmental challenges, societal vulnerabilities, and the ethically problematic rise of disaster betting. Addressing the root causes—climate change, inadequate preparedness, and the ethical concerns surrounding disaster betting—is paramount. We must invest in climate change mitigation, improve community preparedness, and foster responsible regulations to prevent the normalization of profiting from human suffering. Understanding the multifaceted nature of the Los Angeles Wildfires is a critical first step towards building a more resilient and ethical future. Let's work together to mitigate future wildfire risks and create safer, more equitable communities.

Featured Posts
-
 Animateur Phare De M6 Son Avis Exclusif Sur L Arrivee De Hanouna
May 11, 2025
Animateur Phare De M6 Son Avis Exclusif Sur L Arrivee De Hanouna
May 11, 2025 -
 Resi Awards 2025 A Celebration Of Excellence
May 11, 2025
Resi Awards 2025 A Celebration Of Excellence
May 11, 2025 -
 April 17 20 Rays Vs Yankees Whos On The Injured List
May 11, 2025
April 17 20 Rays Vs Yankees Whos On The Injured List
May 11, 2025 -
 The Cost Of Perus Mining Ban A 200 Million Gold Production Loss
May 11, 2025
The Cost Of Perus Mining Ban A 200 Million Gold Production Loss
May 11, 2025 -
 Witness The Excitement Houstons Astros Foundation College Classic
May 11, 2025
Witness The Excitement Houstons Astros Foundation College Classic
May 11, 2025
