The Nothing Phone (2): Modular Design And Its Implications
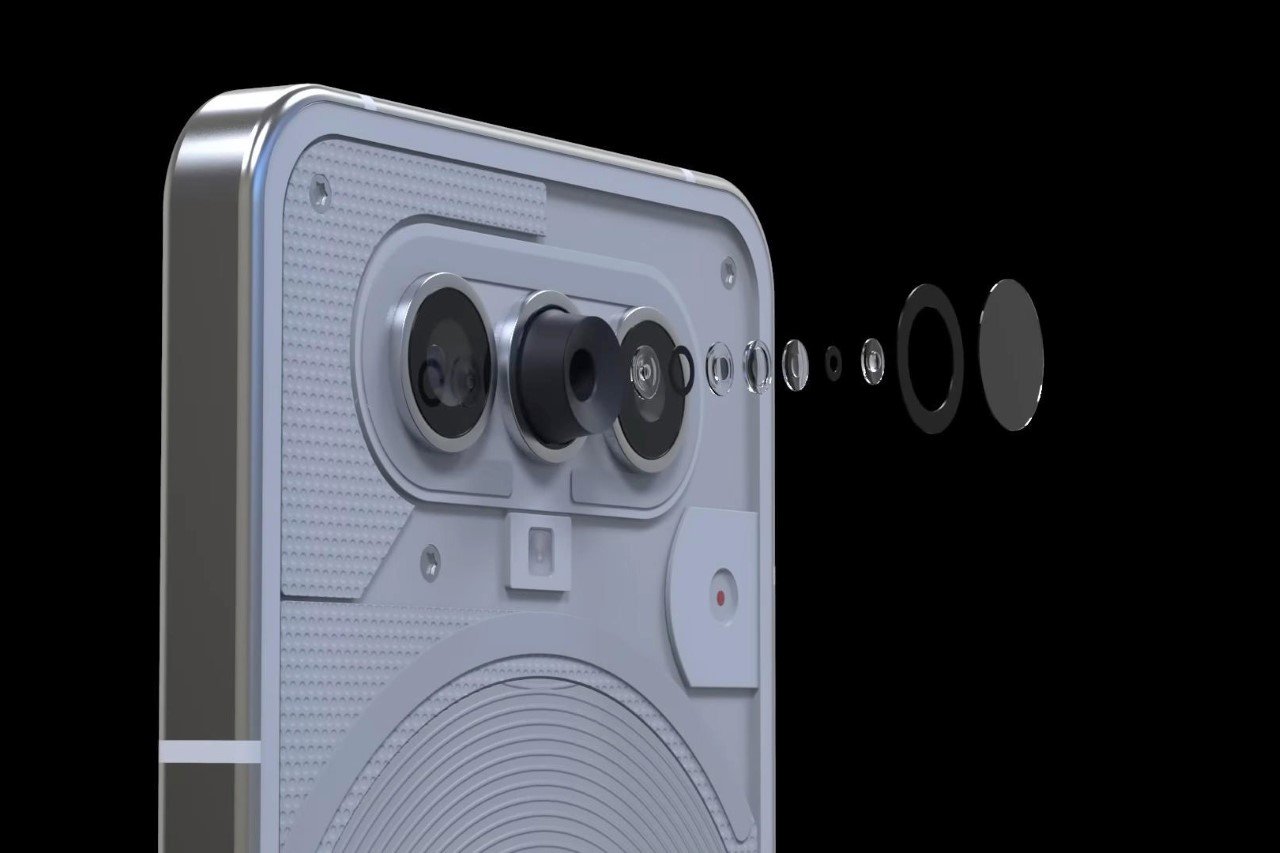

Table of Contents
<p>The Nothing Phone (2) has generated significant buzz, not just for its sleek aesthetics and innovative Glyph Interface, but also for its potential implications stemming from its partially modular design. This article delves into the Nothing Phone (2)'s modular approach, examining its benefits, limitations, and the broader impact on the smartphone industry and consumer experience. Keywords: Nothing Phone (2), modular design, smartphone design, repairability, sustainability, Glyph interface, customizable phone, future of smartphones</p>
<h2>What is Modular Design in the Context of the Nothing Phone (2)?</h2>
<p>Modular design in smartphones refers to the ability to easily replace or upgrade individual components. Unlike fully modular phones where almost every part is user-replaceable, the Nothing Phone (2) takes a more nuanced approach. While not completely modular in the sense of offering fully user-replaceable internal components like a motherboard, it prioritizes repairability. This means certain parts, potentially including the battery and back panel, are designed for easier access and replacement by both professionals and (with some skill) users. This contrasts sharply with many modern smartphones where even basic repairs necessitate specialized tools and expertise.</p>
<ul> <li><b>Ease of repair and replacement of specific components:</b> The Nothing Phone (2)'s design aims to simplify repairs, reducing the need for complete device replacement and promoting a longer product lifespan.</li> <li><b>Potential for user upgrades and customization:</b> While not as extensive as fully modular phones, the design potentially allows for some degree of user customization through replaceable parts. Future iterations might expand on this aspect.</li> <li><b>Environmental benefits related to reduced e-waste:</b> Easier repairability directly contributes to reduced electronic waste, a significant environmental concern associated with the short lifespans of many modern smartphones.</li> <li><b>Limitations of the Nothing Phone (2)'s modularity compared to fully modular phones:</b> The Nothing Phone (2) doesn't offer the complete component replacement seen in truly modular designs. Replacing internal components will likely still require professional assistance.</li> </ul>
<h2>The Environmental Impact of Modular Smartphone Design</h2>
<p>The link between modularity and reduced e-waste is undeniable. A modular smartphone, like a partially modular phone such as the Nothing Phone (2), significantly reduces the environmental impact of its lifecycle. By extending the lifespan of the device through repairability, the demand for new phones is lessened, directly impacting manufacturing processes and resource depletion. This contrasts with traditional "throwaway" phone models where even small issues often lead to complete device replacement.</p>
<ul> <li><b>Extended lifespan of the device due to repairability:</b> A phone that can be easily repaired is likely to last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements.</li> <li><b>Reduced demand for new phones, lowering manufacturing impact:</b> Lower demand translates to reduced material usage, energy consumption, and overall carbon footprint during manufacturing.</li> <li><b>Opportunities for using recycled materials in replacement parts:</b> Modular design encourages the use of recycled components in repair parts, further minimizing environmental impact.</li> <li><b>Challenges in achieving truly sustainable modularity (e.g., sourcing materials):</b> Ensuring the ethical and sustainable sourcing of materials for replacement parts is crucial for truly minimizing the overall environmental impact.</li> </ul>
<h2>The User Experience and Customization Options</h2>
<p>Modularity enhances the user experience by offering customization beyond software. While the Nothing Phone (2)'s level of customization is limited compared to fully modular designs, the potential for personalization remains. The ability to replace certain components allows users to tailor the phone to their specific preferences, extending its usefulness and relevance over time. This fosters greater user satisfaction and could build stronger brand loyalty.</p>
<ul> <li><b>Personalization options through modular components:</b> Users can potentially choose different back panels, battery types, or other components to personalize their device aesthetically and functionally.</li> <li><b>Ability to tailor the phone to specific user needs and preferences:</b> Replacing a battery that's starting to degrade allows users to maintain optimal performance without replacing the entire device.</li> <li><b>Potential for community-driven customization and repair solutions:</b> The easier access to internal components could foster online communities focused on sharing repair tips and customizing the Nothing Phone (2).</li> <li><b>Challenges in balancing user-friendliness with technical complexity:</b> Making a modular design easy for the average user to maintain and customize requires careful consideration of its technical aspects.</li> </ul>
<h2>The Future of Smartphones: A Modular Path?</h2>
<p>The wider adoption of modular design in the smartphone industry holds significant potential. Increased competition among manufacturers could drive innovation and lead to more sustainable practices. However, challenges remain. Manufacturing costs and complexity associated with modular designs can present obstacles. Standardization across brands would significantly enhance the viability of a truly modular ecosystem.</p>
<ul> <li><b>Potential for increased competition and innovation:</b> Modular designs might encourage smaller companies to enter the market, offering unique and innovative components.</li> <li><b>Economic implications for manufacturers and consumers:</b> While initially more expensive, modular designs could prove more cost-effective in the long run due to extended device lifespans and easier repairs.</li> <li><b>The role of technology advancements in enabling better modularity:</b> Advancements in materials science, miniaturization, and connector technology are essential for improving modular designs.</li> <li><b>The need for standardization to facilitate modularity across brands:</b> A common standard for modular components would allow for greater interoperability and expand the potential benefits of this approach.</li> </ul>
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
<p>The Nothing Phone (2), while not fully modular, represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and customizable smartphone future. Its design offers a glimpse into the potential benefits of modularity, from reduced e-waste to enhanced user experiences. However, challenges in manufacturing and standardization remain. The Nothing Phone (2)'s partially modular approach encourages a conversation about the future of smartphone design and its potential environmental impact.</p>
<p><b>Call to Action:</b> Learn more about the innovative design features of the Nothing Phone (2) and explore the implications of modular design for the future of smartphones. Are you ready to embrace the modular future? Research the Nothing Phone (2)'s modular aspects and contribute to the conversation about sustainable smartphone design. Consider the environmental and user experience benefits of modular smartphones and how this approach can shape the future of mobile technology.</p>

Featured Posts
-
 Blue Ivy Carters Super Bowl Style A Fan Favorite
Apr 30, 2025
Blue Ivy Carters Super Bowl Style A Fan Favorite
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Du An 500k V Mach 3 Ghi Dau An Cua Cong Nhan Dien Luc Mien Nam
Apr 30, 2025
Du An 500k V Mach 3 Ghi Dau An Cua Cong Nhan Dien Luc Mien Nam
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Tpbl
Apr 30, 2025
Tpbl
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Canadas Next Prime Minister Top Economic Challenges
Apr 30, 2025
Canadas Next Prime Minister Top Economic Challenges
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show Postponed Impact Of Ohio River Flooding
Apr 30, 2025
Thunder Over Louisville Fireworks Show Postponed Impact Of Ohio River Flooding
Apr 30, 2025
